![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
31 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Action potential for a Purkinje fiber in the ventricles. Name the phases, explain actions and Ion flux.
|
Phase 0-Rapid depolarization-Rapid Na influx
Phase 1-Early repolarization-Cl influx Phase 2- Plateau- Ca influx Phase 3- Rapid depolarization-K efflux Phase 4-Resting Slow Na influx |
|
|
|
What is the Effective(absolute Refractory Period(ERP). What phases are included?
|
time when a second impulse cannot be initiated. Includes phase 0 through first half of phase three
|
|
|
|
single common most stimulation for arrhythmia
|
reentry
|
|
|
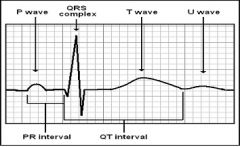
What's going on in heart during:
p wave PR interval QRS complex T wave QT interval |
p wave-atrial depolarization
PR interval-conduction time from atria to ventricles QRS complex-Ventricular depolarization T wave-ventricular repolarization QT interval-Ventricular depol. and repol. |
|
|
|
What are Two common mechanisms for arrhythmia formation
|
1. Abnormal impulse initiation: Most common form is altered automaticity: For example, increased sympathetic drive may cause sinus tachycardia whereas decreased SNS drive causes Bradycardia.
2. Abnormal impulse conduction: Most common form is Reentry. Result from scar tissue due to MI or other structural disease |
|
|
|
This arrhythmia originates in sinus node, atria or AV node. Give three examples.
|
Supraventricular.
Sinus Bradycardia/tachycardia PSVT(usually self fixing) AFlutter and AFib |
|
|
|
This class of arrhythmias originate below HIS bundle. Give three examples(which one includes Torsades)
|
Ventricular
VPC VT(includes Torsades de Pointes) VFib |
|
|
|
Name the conduction blocks
|
First, Second or third degree AV block
RIght or Left Bundle Branch block |
|
|
|
Morizicine is in what drug class?
|
Na Channel Blockers
|
|
|
|
Three Na Channel blockers that prolong repolarization. Class?
|
Class IA
Quinidine Procainamide Disopyramide |
May cause Torsades
|
|
|
Three Na Channel blockers that shorten repolarization
|
1B
Lidocaine Mexiletine Tocainide |
|
|
|
THese two Na channel Blockers have minimal effect on repolarization. Class?
|
1C
Flecainide Propafenone |
|
|
|
Class of Propranolol
|
Beta blocker
|
|
|
|
Four agents that block K efflux and prolong repolarization
|
Amiodarone
Sotalol Ibutilide Dofetilide |
|
|
|
Two CCBs
|
Verapimil
Diltiazem |
|
|
|
Two misc drugs that prolong AV conduction
|
Digoxin
Adenosine |
|
|
|
Drug of choice for PSVT
|
Adenosine IV push
|
|
|
|
Nonpharmacologic treatment for PSVT(done first)
|
Physical maneuvers to increase Vagal Tone
a. unilateral carotid artery sinus massage b. Valsalva maneuver(hold breath and bear down) |
|
|
|
Alternatives drugs besides DOC Adenosine for PSVT. For example, if pt has too much caffeine, cannot do adenosine.
|
BB, or CCB
|
|
|
|
Most common arrhythmia. What increases incidence?
|
AFib. Age and presence of HRT disease
|
|
|
|
Chaotic rhythm with multiple ectopic foci in atria firing randomly; multiple reentrant loops
|
AFib
|
|
|
|
No identifiable p wave. Which arrhythmia and what is atrial and ventricular rate?
|
Afib. Atrial rate 350-600. Ventricular rate 130-180. Irregularly irregular
|
|
|
|
Conditions associated with AF
|
Coronary heart disease
HTN Valvular heart disease HF |
|
|
|
Increases risk of stroke. Which arrhythmia?
|
AFib
|
|
|
|
Symptoms of Afib? Why?
|
Palpitations, dizziness, fatigue, chest pain, heart failure, sycope. Rapid ventricular rate decreases filling time
Loss of atrial contraction("kick") also decreases ventricular filling |
|
|
|
TREATMENT OF AF
If: Hemodynamic symptoms? What doesn't work? |
Electrical cardioversion. Digoxin, BB and 1 of 2 CCBs, Adenosine doesn't work due to short half-life
|
|
|
|
Treatment of AFib in hemodynamically stable patient:
|
Step 1: Slow ventricular rate w/ AV nodal blocking drugs
a. Digoxin b. Beta Blcoker c. Calcium channel antagonist Step 2. Attempt conversion to NSR a. Electrical cardioversion b. Pharmacological(IA,III) |
Note: if pt has been in AF>48 hours or of unk. duration, anticoagulation may be req/ to prevent stroke as a result of cardioversion procedure.
Step 3: If Cardioversion success keep at NSR a. Class III(amiodarone, sotalol) b. Group IA |
|
|
Rapid-Acting Insulin
a. name three b. Peak c. Duration |
a. Lispro/Aspart/Glulisine
b. 0.5-2hours c. lasts 5 hours |
|
|
|
Short-Acting Insulins
a. name them b. onset c. Peak d. Duration g. Injected how long before meals? |
a. Humulin R, Novolin R
b. onset: 0.5-1hr c. Peak: 2-3 hours d. Duration: 3-7 hours e. Injected 30-35 minutes before meals |
|
|
|
Intermediate-Acting insulin
a. Route of admin b. Names c. Onset d. Peak e. duration |
a. SubQ only
b. NPH, Humulin N, Novolin N(Isophane insulin suspension) -lente(insulin zinc susp-removed) c. Onset. 2-4 hours d. Peak: 6-12 hours e. Duration: 12-20 hours |
|
|
|
Long Acting insulin
a. names b. Duration c. Which one binds to albumin and has less peaks |
a. Glargine(Lantus) and Detemir(Levemir
b. 24 hours c. Detemir binds to albumin and less peaks, more truly basal |
|

