![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
65 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the parts of an EKG?
|
P, QRS, T waves
|
|
|
How do you calculate the heart rate on an EKG?
|
count the number of boxes between R-waves then divide into 300 (300/ # of big boxes)
|
|
|
What rhythms do you defibrillate for? and at what joule?
|
ventricular tachycardia, ventricular fibrillation
360 joules |
|
|
what rhythms do you cardiovert for? and at what joule?
|
Atrial flutter, Atrial fibrillation
50-100 joules |
|
|
What rhythms do you pace?
|
Bradycardia, Asystole
|
|
|
what does the wedge pressure look at?
|
the systemic vascular system
|
|
|
what is the normal value for PCWP?
|
4-12 mmHg or 8-24 cmH2O
|
|
|
what is indicated if the PAP and the PCWP are both elevated?
|
The problem is Cardiogenic
|
|
|
What is indicated if the PAP is up but nothing else?
|
the problem is Non-cardiogenic
|
|
|
How do you treat dampening?
|
A=Aspirate
F=Flush with heparin R=Rotate |
|
|
The BTFDC is inflated when? and with how much air?
|
inflated when inserted into right atrium and measuring PCWP. You use 1.5 cc of air
|
|
|
CVP represents what?
|
The right side of the heart
|
|
|
What are some other names for CVP?
|
Right atrial pressure
Right side preload Right atrial filling pressure Right vent. end diast. pressure |
|
|
How is MAP and MPAP calculated
|
[(2 x Diastolic) + Systolic ]/ 3
|
|
|
What 3 ways can Cardiac Output be measured? How do you calculate CO?
|
Thermal Dilution
Dye Dilution Fick Equation CO= SV x HR |
|
|
What is the Fick Equation?
|
VdotO2 / (CaO2-CvO2) x 10
|
|
|
When do you want a wedge pressure? is it performed on inspiration or expiration?
|
When looking at the lungs and Left heart
performed at end exhalation |
|
|
what is the conduction pathway of the Heart?
|
SA node--AV node--Bundle of His--R and L bundle branches--Purkinji fibers
|
|
|
What is a bronchogram used to diagnose?
|
Bronchiectasis
|
|
|
What is Cardiac Tamponade?
|
When compression of the heart takes place due to blood or fluid accumulation in the pericardial sac
|
|
|
Where is the Bicuspid Valve?
|
between the Left atria and the ventricle
|
|
|
Where is the Tricuspid Valve?
|
between the R atria and ventricle
|
|
|
What is stenosis of the valves (bicuspid stenosis)?
|
it's a narrowing of the valvular opening.
|
|
|
What does A-fib feel like in the radial pulses?
|
it will feel erratic
|
|
|
what are some of the complications of a Pulmonary Catheter?
|
QT arrhythmia
Hemorrhage Clot formation infection |
|
|
How is the P-A CXR shot?
|
from Back to front
|
|
|
How is the A-P shot? and what is more readily seen?
|
It is from the front to back and allows better visualization of the heart.
|
|
|
What CXR shoots from the side and allows visualization of the lung behind the heart as well as the bases
|
Lateral
|
|
|
What is the position used for V/Q scans? and how are they positioned?
|
Obligice- Pt is turned to 45 degrees to either side.
|
|
|
what position has the patient leaning back at a 45 deg. angle an allows viewing of the upper lobes?
|
Apical Lordotic
|
|
|
What position is used to diagnose a pleural effusion or pneumothorax?
|
Lateral deculutis
|
|
|
Elevation of ones side of the diaphragm can indicate what?
|
Gas in the stomach or atelectasis
|
|
|
The diaphragm appears where on a CXR?
|
at the level of the 10th rib on inspiration
|
|
|
Which Lung is larger?
|
The right
|
|
|
What percentage of air does each lung hold?
|
right =55%
Left = 45% |
|
|
what are the indications, routes, and dosage of Epinephrine
|
Indications= Asystole,Sinus arrest,Vfib
Routes= IV, ETT, Intra cardiac Dosage= 1ml/kg every 5 min then flush with 10cc of NS |
|
|
what are the indications, routes, and dosage of Lidocaine
|
indications= PVC's,Vtach,Vfib.
Routes= IV bolus, IV drip, ETT Dosage= 1mg/kg IV bolus |
|
|
what are the indications, routes, and dosage of Atropine
|
indications= Sinus Brady, Asystole, AV node Brady
Routes= IV bolus, ETT Dosage= Dead is 1mg/ 2 min, Alive is 0.5mg/ 2 min |
|
|
What does Epinephrine do?
|
Increases HR
Increases force of contraction Increases coronary perfusion Vasonstriction |
|
|
What does Lidocaine do?
|
decreases ventricular activity
|
|
|
What does Atropine do?
|
increases HR
Increases force of contraction |
|
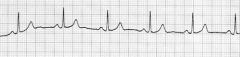
|
Normal Sinus Rhythym
|
|
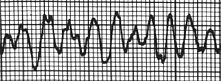
|
Ventricular Tachycardia
|
|
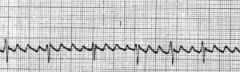
|
Atrial Flutter
|
|
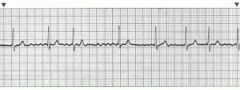
|
Atrial Fibrillation
|
|
|
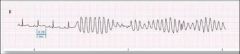
Toursades
|
|
|
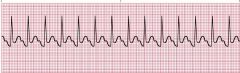
Sinus Tachycardia
|
|
|
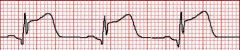
Injury (ST elevation)
|
|
|
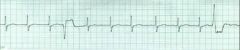
Multifocal PVC's
|
|
|
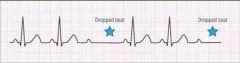
2 degree Heart block type 2
|
|
|
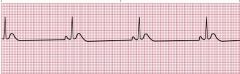
Sinus Bradycardia
|
|
|
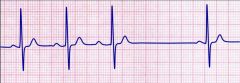
2 degree heart block type 1 (wenkebach)
|
|
|
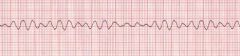
Ventricular Fibrillation
|
|
|
A-aDO2
or A-a gradient |
PAO2-PaO2
Normal= 10-15 mmHg on RA 25-65 mmHg on 100% Shunting>300>V/Q mismatch |
|
|
CaO2
O2 carried to the Tissues |
(Hb x 1.34 x SaO2) + (PaO2 x .003)
Normal= 16-20%vol |
|
|
CvO2
oxygenated blood returning to heart |
(Hb x 1.34 x SvO2) + (PvO2 x .003)
Normal= 12-15%vol |
|
|
C(a-v)O2
how much O2 was taken by Tissues |
CaO2-CvO2
Normal is <5%vol |
|
|
QT equation
Measures CO |
VO2 / (C(a-v)O2) (10)
Normal is 4-8 LPM |
|
|
VD/VT
Portion of blood not taking part in O2 exchange |
(PaCO2 - PeCO2) / PaCO2 x 100
Normal is 20-40% in spontaneous breathing pt 40-60% in ventilated pt's |
|
|
O2ER
Oxygen used by tissues |
CaO2-CvO2 / CaO2
Normal is 20-28% |
|
|
VD
Deadspace |
1cc/lb of ideal body weight
|
|
|
Vt
Tidal Volume |
VdotE/RR
Normal is 5-7LPM |
|
|
VdotD
Deadspace minute ventilation |
RR(lbs)
|
|
|
VdotA
Alveolar minute ventilation |
VdotA / VdotD
|
|
|
VdotE
Minute Ventilation |
Vt x RR
Or VdotA + VdotD Normal is 5-10LPM |

