![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
164 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
compression of nerves, arteries, and veins that come from the area between the clavicle and first rib. subclavian vein and artery |
what is TOS? |
|
|
disturbance of the brachial plexus due to a structural anomaly |
what is true TOS? |
|
|
a longer cervical TP or a cervical rib |
what is the reason for true TOS? |
|
|
incidence 0.74%
female:male ratio is 7:3 complete vs incomplete |
what is the % of cervical rib incidence of TOS? |
|
|
incidence: 0.76%
equal occurrence in men and women |
what is the % of anomalous 1st ribs of TOS pts? |
|
|
structural abnormalities |
what is the primary case for TOS? |
|
|
1.scalene triangle 2.costoclavicular space 3.pec minor 4.elevated 1st rib |
what are the entrapment areas for TOS? |
|
|
20-50 yo |
what is the TOS age range ? |
|
|
< 5% teenagers 10% over 50 rarely > 65 70% female 70% cervical ribs occur in females |
what % of the population has TOS? |
|
|
swelling of muscle belly - pain, parathesias,numbness, weakness
scarring/fibrosis of muscle belly - occipital headaches, muscle spasms
ex: neck trauma |
what occurs with neurogenic TOS? |
|
|
pain, parathesias, numbness , weakness, necrosis, escemia, edema, swelling throughout the affected extremity |
what are the symptoms of neurogenic TOS? |
|
|
radial and musculocutaneous nerve distributions |
what nerves are affected with the "Upper Plexus"? |
|
|
median and ulnar nerve distributions |
what nerves are affected with the "Lower Plexus"? |
|
|
distal of brachial plexus |
what is a peripheral nerve distribution ? |
|
|
occipital headaches- postural related
perceived muscle weakness - actual weakness and atrophy are rare
vasomotor symptoms- vasospasm, edema, hypersensitivity, chronic regional pain syndrome (CRPS) |
what are the symptoms of neurogenic TOS? |
|
|
careful pt history and thorough appropriate physical examination |
how is TOS diagnosed? |
|
|
no single test has sufficient specificity to prove or exclude the diagnosis |
what specific test can help dx TOS? |
|
|
neurogenic- heaviness, progressive weakness, numbness, tingling in fingers, progressing up arm |
what is nTOS? |
|
|
venous- cyanotic arm with distended forearm muscles |
what is vTOS? |
|
|
arterial- ischemic, cramping pain, temperature change, flaky dry skin, hair growth |
what is aTOS? |
|
|
scalenes aniticus and medius muscles, pec minor and costocoracoid lig., costoclavicular membrane and subclavius muscle, first rib, cervical rib anomalies, long TP, clavicle abnormalities |
what are some TOS causes? |
|
|
edema, venous distension, paget schroetter syndrome, clotting, DVT, cyanosis |
what happens with compression to a (vascular) subclavian vein? |
|
|
loss of pulse, claudication, thrombosis, aneurysm |
what happens with compression to a (vascular) subclavian artery? |
|
|
raynauds phenomenon- feeling of cold and numbness to extremities |
what happens with compression to a nerve to the sympathetic nervous system? |
|
|
pain, parathesias, motor weakness |
what happens with compression to a nerve to the peripheral nervous system? |
|
|
carpal tunnel, ulnar nerve compression, rotator cuff tendonitis, cervical spine strain/sprain, fibromyositis, cervical disk disease, cervical atrhritis, brachial plexus injury |
what are the differential diagnosis of nTOS? |
|
|
pulse exam- listen for bruits(abnormal artery sounds)
edema/cyanosis/colatteral veins
tenderness over scalene muscles or pec minor (trigger points)
reduced sensation to very light touch in fingers
provacative maneuvers
|
what would be examined in a TOS physical exam? |
|
|
Scalenes
1.pt seated ,arms at sides, the radial pulse is palpated and the examiner listens for bruits above the clavicle 2.elevate arm and turn the chin both away from the involved side. 3.a positive test results in diminished radial pulse, bruit, numbness , tingling. subclavian artery is being subcluded |
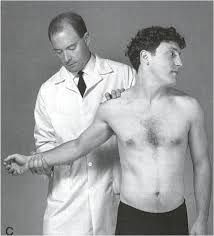
what is the Adson test? |
|
|
up to 50% of healthy volunteers have a positive test-unreliable for diagnosis of TOS |
what % of people have a positive Adson test? |
|
|
pec minor
examines neural tissue compromise through the pec minor axillary interval |

what is the Wrights Test? |
|
|
Vascular compromise- axillary interval
1.elevated arm stress test 2.most accurate clinical test 3.hold surrender position for 3 min. while opening/ closing hands
creating oxygen build up of pain/fatigue |
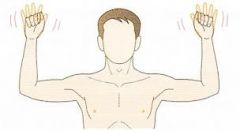
what is the ROOS test? |
|
|
decreased radial pulse
military brace
dropping the clavicle onto the first rib |
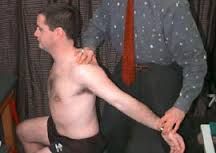
what is the costoclavicular maneuver? |
|
|
putting strain on UE nerve distribution .
positive response indicates compression of cervical roots or brachial plexus
negative response is usually adequate to rule out nTOS |
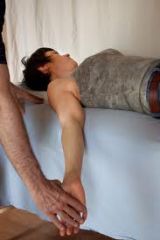
what is the Upper Limb Tension Test (ULTT)? |
|
|
nerve glides
used to help reduce nerve impingement symptoms down the extremity |
what is nerve flossing? |
|
|
inert and dynamic structures |
what structures does stability require? |
|
|
introduced a model of spinal stabilization with three interdependent subsystems |
who is Panjabi? |
|
|
lig, capsule, structures that cannot contract |
what is a passive subsystem? |
|
|
multifidii, TrA. , muscle |
what is an active subsystem? |
|
|
nerves that innervate |
what is a neural control subsystem? |
|
|
spine stays in position where there is no stress or strain on passive subsystem |
what is the neutral zone? |
|
|
activation of the subsystems |
what is the elastic zone? |
|
|
osteoligamentous and neuromuscular components of the spine fail to prevent slippage |
what is postural instability? |
|
|
pain increases , ligaments expand to support |
what is a ligament stretch? |
|
|
will create hyper mobility , we need stability |
what will and adjustment do to lower back pain? |
|
|
occurs during function, not at rest. theres a malignancy if theres pain at rest. |
when would a pt feel low back pain? |
|
|
the TrA and the multifidii |
what muscles are the first to activate with rapid UE movement? |
|
|
with isometric contractions |
how is the TrA activated? |
|
|
a moth eaten effect happens to this muscle with atrophy. does not spontaneously return |
what happens to the multifidii during a L/S injury? |
|
|
shuts off during injury |
What happens to the multifidii after injury? |
|
|
slow oxidative, endurance |
what are type 1 muscle fibers? |
|
|
fast glycolitic, power |
what are type 2 muscle fibers? |
|
|
turn into FT instead of ST |
what happens to the stabilization muscles after an injury? |
|
|
creates intramuscular stability that compresses the diaphragm , creating intrabdominal pressure |
what happens when you hold your breathe (Valsalva Manuever)? |
|
|
shoulder flex |
trunk ext
|
|
|
shoulder ext |
trunk flex |
|
|
hip flex |
trunk flex |
|
|
hip ext |
trunk ext |
|
|
lipping |
what is a direct correlation of instability in the spine? |
|
|
dysfunctions off the spine and its, not diseases |
what are DDD and DJD considered? |
|
|
self manipulater- crack head fidgety-constantly changing position postural nystagmus-juddering back and forth use of UE to return from forward bent position steppage found in standing- refers to SP segmental muscle guarding/ chemical holding pattern in standing which disappears in prone grades 5 and 6 of mobility |
what are the signs of instability? |
|
|
unstable |
when the SP disappears in prone? |
|
|
stable |
when the SP remains in prone? |
|
|
condition of the spine or degeneration |
what is spondylosis? |
|
|
fx of the pars articularis |
what is spondololysis? |
|
|
slippage of the body, ant. slippage , and going to see steppage
ex: gymnasts-backbending |
what is spondylolithesis? |
|
|
fx of the pars articularis that looks like a collar |
what is the scottie dog fx sign? |
|
|
posterior displacement of one of the vertebral bodies |
what is a retrolisthesis? |
|
|
creep, nociceptors, fidgity |
what are the effects of mechanical stress on the spine? |
|
|
exaggerated curves lead to stretch on passive structures-creep and fluid redistribution-making tissue vulnerable to injury |
what are the effects of impaired postural support from trunk muscles? |
|
|
loss of length tension curve |
what happens with stretch weakness? |
|
|
loss of elasticity |
what happens with tight weakness? |
|
|
nods and or nutates |
what does the multifidii do to the sacrum? |
|
|
greater demand on passive structures creating fatigue |
what is the effect of impaired muscle endurance? |
|
|
postural fault, postural dysfunction |
what are the pain syndromes related to impaired posture? |
|
|
deviation from normal alignment but no structural limitation.pain usually due to mechanical stress. correct posture, correct pain. |
what is postural fault? |
|
|
adaptive shortening and weakness .leads to further dysfunction
ex:impingement |
what is postural dysfunction? |
|
|
idiopathic, irreversible fixed lateral curve . rib promenance on convexity posteriorly no matter the position , theres always a fixed curve |
what is structural scoliosis? |
|
|
AKA: postural
changed with position, or align pelvis. L/L discrepancy |
what is nonstructural/functional scoliosis? |
|
|
stretch: concavity
strengthen: convexity |
what do we want to do to the convexity and concavity with scoliosis? |
|
|
1.proprioception and control: put them in the position we want and don't want. awareness of symptoms and verbal cueing
2.impaired jt ,muscle, and connective tissue mobility-use mobs and stretching
3.impaired muscle performance strengthening |
what are the general management guidelines to postural alignment? |
|
|
most common c/o with impaired posture. about 20% of all recurrent HA are cervicogenic |
what is the most common cause of tension and cervical headaches? |
|
|
1.between vertebra of C1 & C2 2. under and around Inferior capitis obliques 3.under semispinalis 4.under upper trap |
what are the 4 entrapment sites of the cervical spine? |
|
|
unilateral HA neck pain-to head fluctuates from mild to severe increased with sustained postures, neck positions postural dysfunctions |
what are the signs and symptoms of cervicogenic headaches? |
|
|
joint mobs- subcranial, thoracic strengthen deep flexors increase lumbar posture increase shoulder girdle strength/posture increase neuro tissue |
what are the general management guidelines for cervicogenic headaches? |
|
|
cervical flexion-rotation test. loss of ROM to either side by 10 degrees is correlated to CHAs |
what test can identify CHAs? |
|
|
hydraulic, weight bearing, shock absorber
body and intervertebral disk |
what is the functional component of ant. portion of the spine? |
|
|
provides movement .TP and SP as attachments for muscles for control and stability
articular processes and facet jts |
what is the functional component of post. portion of the spine? |
|
|
same as the lumbar spine |
what is the lower thoracic mobility compared too? |
|
|
SB and rotation and occur to opposite sides |
what happens to the lumbar /thoracic facets in neutral? |
|
|
facets slide down (closing) |
L/T backward bending? |
|
|
facets slide up (opening) |
L/T forward bending? |
|
|
contralateral facet slides up (opens)
ipsilateral facet slides down (closing) |
L/T sidebending? |
|
|
contralateral facet becomes a fulcrum, ipsilateral facet opens |
L/T rotation? |
|
|
same as the cervical spine |
what is upper thoracic mobility compared too? |
|
|
rotation and side bending occur to the same side |
what happens to the C/T facet of C2 and below? |
|
|
facets slide anteriorly and superiorly (up and forward) |
C/T forward bending? |
|
|
facets slide posteriorly and inferiorly (down and back), ligamentum lava folds inward-could cause compression to cord |
C/T backward bending? |
|
|
contralateral facet slides superiorly and anteriorly (up glide), ipsilateral facet slides posteriorly and inferiorly( down glide) |
C/T sidebending |
|
|
same as for side bending |
C/T rotation? |
|
|
the same as occiput |
what direction does the atlas always move? |
|
|
acts as a washer between the skull and C2 |
what does atlas act as between the skull and C2? |
|
|
knodding, 20 degrees of flexion and extension |
what is AO primary motion? |
|
|
occipital condyles are stuck to atlas |
what is a sticky atlas? |
|
|
aa jt |
what jt provides the largest component of cervical axial rotation? |
|
|
10 degrees of flexion/extention, 5 degrees sidebend and 45-50 degrees of rotation |
what are the degrees of movement at the AA jt ? |
|
|
alar ligaments |
what ligament restrains rotation at the AA jt? |
|
|
initially -sharp, local LBP -may experience a ripping or tearing sound.
pain increased with sitting/ forward bending
SLR: 30-60 degrees
once settled (+/- 2weeks) radiating symptoms develop
loss of skin sensation and motor function, diminished DTRs, neurotension signs |
what are the signs and symptoms of a HNP? |
|
|
LB first aid and education |
what is a HNP tx immediately(acute)? |
|
|
positional distraction |
what is a HNP tx in the settled stage? |
|
|
manipulation to hypomobile segments (avoiding rotation), stabilization, general conditioning. with gradual return to function |
what is the HNP tx in the chronic stage? |
|
|
movement of the spine |
what are facet its responsible for? |
|
|
1.synovitis/hemarthrosis 2.stiffness 3.painful entrapment 4.mechanical blocking 5.arthrosis |
what are the 5 typical facet jt dysfunctions? |
|
|
facet strain,guarded movements, voluntary and involuntary muscle guarding,treat with rest, cautious movements for 10 days |
what process occurs during synovitis/hemarthrosis? |
|
|
resolved synovitis,hemarthrosis-presents with stiffness (asymptomatic) - increase risk of re injury , treat with manipulation |
what occurs with stiffness during FJD? |
|
|
inferior articulating facet unable to glide down on superior articulating facet. pain with return to neutral-pain free into forward bending, treat with isometric contraction of multifidii-3 protective mechanisms of the facet, manipulation, gapping |
what occurs with painful entrapment during FJD? |
|
|
loose body in jt or impact,relatively pain free, motion blocked in one direction, treat with rotational manipulation over bolster (L spine), strong traction with SB away, rotate towards ( C-spine) |
what occurs with mechanical blocking during FJD? |
|
|
trauma, overuse, posture, dull ache, or local pain. treat with postural corrections and manipulation to segments above and below |
what occurs with arthrosis during FJD? |
|
|
constriction or narrowing of a passageway |
what is stenosis? |
|
|
gives bilateral symptoms, lordosis can relieve pressure |
what is central stenosis? |
|
|
gives unilateral symptoms, foramen innervated |
what is lateral stenosis? |
|
|
bike test |
what test is used to distinguish between vascular and neurogenic signs? |
|
|
intermittent claudication |
what is a vascular sign of stenosis? |
|
|
used when extension activities are contraindicate |
what are Williams flexion exercises? |
|
|
to move the pain to a central location. person |
who is Robert McKenzie? |
|
|
back bending only relieves pressure, does not put the NP back in the disk. grades 1&2 mechanoreceptors help this pain. |
what does back bending do, with an ext. bias? |
|
|
steppage, guarding, fidgiting ,etc |
what are signs of instability? |
|
|
grades 5&6 of mobility |
what grades of mobility are used with signs of instability? |
|
|
pain with non organic origin. we cannot tx, its psychological |
what are Waddell signs? |
|
|
skin discomfort on light palpation |
what is WS for superficial tenderness? |
|
|
tenderness crossing multiple anatomic boundaries |
what is the WS for nonatomic tenderness? |
|
|
eliciting pain when pressing down on the top of the pts head |
what is the WS for axial loading? |
|
|
rotating the shoulders and pelvis together should not be painful as it does not stretch the structures of the back |
what is the WS of pain on simulated rotation? |
|
|
if pt complains of pain on straight leg raise , but not if the examiner extends the knee with the pt seated |
what is WS for distracted leg raise? |
|
|
stocking sensory loss, or sensory loss in an entire extremity or side of the body |
what is the WS for regional sensory change? |
|
|
weakness that is jerky , with intermittent resistance ( such as cog wheeling, or catching) |
what is the WS for regional weakness? |
|
|
exaggerated painful response to a stimulus , that is not reproduced when the same stimulus is given later |
what is the WS of overaction? |
|
|
same side as the concavity |
what side of the body would you place a pt who has scoliosis in sideline to manipulate? |
|
|
awareness of the pts movement and how it increase symptoms. help the pt understand the link. neuromuscular re-education |
what is kinesthetic awareness? |
|
|
should be relative to the pts comfort |
what is considered a neutral spine? |
|
|
starting with stabilization exercises to fundamental body mechanics |
what is kinesthetic training integration? |
|
|
scalene muscle stretch, posterior occiput glide. end with traction |
what techniques can increase axial extension? |
|
|
short sub occipital muscle stretch / subcranial release |
what techniques can increase upper cervical flexion? |
|
|
mobilization-glenohumeral jt, scapula, AC/SC jt |
what techniques increase scapular and humeral muscle flexibility ? |
|
|
k to c, ppt, prayer stretch, manual techniques |
what techniques can increase lumbar flexion? |
|
|
90 degrees is bad |
what degree of motion should a total hip pt never be stretched? |
|
|
press up, standing BB |
what techniques can increase lumbar ext? |
|
|
prayer stretch, side lying over ball/ bolster, manual techniques |
what techniques can increase lateral flexibility of the spine? |
|
|
superficial muscles around injury, not localized |
what is global stabilization? |
|
|
wt shifts, quadriped, standing, squatting |
what are transitional stabilization exercises? |
|
|
designed specifically for the pts condition |
what should HEPs be designed for? |
|
|
repetitive- lifting , reaching, pushing/pulling, rot./turning, transitional movements. transfer of training |
what are intermediate and advanced exercise techniques for functional training ? |
|
|
splenius cervicis semispinalis sternocleidomastoid rectus capitis post. major rectus capitis post minor sup. obliqus capitis inf obliques capitis splenius capitis |
what mm do cranial/ cervical ext? |
|
|
sternocleidomastoid scalenes longus colli |
what mm do cranial/cervical flexion? |
|
|
splenius cervicis sternocleidomastoid scalenes spinalis longissimus illiocastalis external obliques internal obliques quadratus lumborum rectus capitis post. major sup. obliques capitis splenius capitis |
what mm do ipsilateral side bending? |
|
|
sternocleidomastoid scalenes multifidii external obliques |
what mm do contralateral rotation? |
|
|
spinalis longissimus illiocastalis quadratus lumborum |
what mm do back bending? |
|
|
splenius cervicis internal obliques rectus capitis post. major inf. obliques capitis splenius capitis |
what mm do ipsilateral rotation? |
|
|
rectus abdominis external oblique internal oblique |
what mm do trunk flexion? |
|
|
multifidii Tra |
what mm are primary spine stabilizers? |
|
|
longus colli |
what mm is the primary cervical stabilizer? |
|
|
external intercostals |
what mm aids in inspiration? |
|
|
internal intercostals |
what mm aids in expiration? |
|
|
prone ,supine, quadriped,bridge, tallknealing, standing |
what is the lumbar stabilization sequence? |
|
|
meniscoids, lig. flavum, multifidii |
what are the protective mechanisms of the facets? |

