![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
86 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Circular flow of income and spending |
Illustration of the linkages between different sectors of the economy. It shows the flow of money in an economy as it passes from producers to consumers. |
|
|
3 examples of an economic unit |
Households, firms, government |
|
|
3 ways of measuring total economic activity |
Spending Output Income |
|
|
Define macroeconomics |
Interrelationships between economic variables at an economy wide scale |
|
|
3 examples of withdrawals from the circular flow |
Savings Taxes Spent on imports |
|
|
3 examples of injections into the circular flow |
Investment Government spending Money brought in from exports |
|
|
3 effects of injections exceeding withdrawals |
More jobs Increased national income More money in the economy |
|
|
3 impacts of withdrawals exceeding injections |
Output falls Employment falls National Income falls |
|
|
Income definition |
Amount of earnings in a period |
|
|
Wealth definition |
A stock of assets |
|
|
What is the wealth effect |
An increase in spending that accompanies an increase in wealth |
|
|
Define Aggregate demand and name all the components of AD |
Total demand for goods and services produced in the economy over a period of time C + I + G + (X - M) |
|
|
Define gross investment |
Total investment in capital goods |
|
|
Define net investment |
Total investment - depreciation |
|
|
Name 3 things that can affect the size of the shift in AD |
Time Lags The Accelerator The Multiplier |
|
|
Define the multiplier effect and give the equation for it |
The ratio of a change in equilibrium real income to the autonomous change that brought it about 1/1-MPC |
|
|
Explain the link between MPC and the multiplier |
The greater the MPC, the bigger the multiplier will be |
|
|
Give 4 problems with the multiplier |
It is hard to calculate Takes time to come into effect Some money may leak out The trade cycle will impact on the size of the impact the multiplier has |
|
|
Define aggregate supply |
The total level of goods and services produced in an economy over a period of time |
|
|
Give 4 factors that can affect SRAS |
Price of Raw materials Exchange rate Level of taxation Anything that changes costs (regulation, wages, subsidies, taxes etc) |
|
|
Give 4 factors that can increase LRAS |
Improvements in education Improvements in technology Increase in productivity Change in population Reliance on unrenewable resources |
|
|
What is a bottleneck |
When 1 factor of production is not available, so supply is constrained and costs will rise as the economy grows |
|
|
What are the 4 key indicators of economic performance |
Economic growth Inflation Unemployment Balance of Payments |
|
|
Give 3 economic objectives that aren't the main 4 |
Fiscal balance Low inequality Environmental protection |
|
|
Give an advantage and disadvantage of increasing government spending on education to influence the key economic objectives |
Advantage - component of AD so AD will rise, and will increase supply of skilled labour Disadvantage - long run factor, creates a short run opportunity cost |
|
|
Give an advantage and disadvantage of decreasing government spending on the main economic objectives |
Advantages - Improve the fiscal balance and lead to a Lower budget deficit (particularly good for UK) Disadvantages - component of AD, so AD will fall and could lead to a long run worsening of the budget deficit as unemployment rises and tax revenue falls |
|
|
Give an advantage and disadvantage of increasing taxation on the key government objectives |
Advantages - lead to a rise in tax revenue and an improvement in the budget Disadvantages - will lead to a fall in spending as people have less disposable income |
|
|
Give an advantage and disadvantage of decreasing taxation on the key economic objectives |
Advantage - more disposable income so an increase in consumption, which is a component of AD. Lead to economic growth Disadvantages - lead to inflation and a worsening of the budget deficit |
|
|
Give an advantage and disadvantage of lowering the interest rates on the key economic objectives |
Advantages - flow of hot money and more borrowing, so consumption and thus AD will rise Disadvantages - lead to a fall in investment in UK banks, and could cause inflation to rise. Unrealistic for the UK with interest rates already at 0.5%, lowering them further could cause a liquidity trap. |
|
|
Give an advantage and disadvantage of increasing interest rates on the key economic objectives |
Advantages - make it more expensive to borrow, so consumption will fall as more people save. Lead to AD falling therefore inflation improving Disadvantages - fall in consumption and AD will cause a dramatic fall in economic growth |
|
|
Give 4 policies other than fiscal and monetary that the government can use to influence the kep economic objectives |
Job creation schemes Supply side policies Regulation and Deregulation Altering the exchange rates |
|
|
Give 5 reasons for government spending |
Social reasons (decrease inequality) Reduce unemployment Provision of public goods Overseas spending Merit goods |
|
|
What is the government target for fiscal policy |
Creating a budget surplus by 2019 |
|
|
What is the laffer curve |
As tax increases tax revenue increases to a point. After that point, revenue will fall as unemployment rises |
|
|
Give 4 examples of supply side policies and an advantage / disadvantage for each |
Spending on education (more skilled labour, long run impact ) Deregulation (efficiency and innovation up, health and safety down and worker exploitation up) Reducing tax burden (more money available to invest or increase supply, budget deficit rises) Privatisation (profit motive means efficiency and quality rise, prices also rise due to profit motive) |
|
|
Give 4 advantages and disadvantages of supply side policies |
Advantages - inflation down, unemployment down, economic growth up, long run improvement in fiscal balance Disadvantages - short run opportunity cost, time lag, bottlenecks, no change in AD |
|
|
What are nominal and real interest rates |
Nominal - interest rates not taking into account inflation Real - interest rates minus inflation |
|
|
Give one group who would want to see interest rates rise and one who would want to see interest rates fall |
Rise - global investors Fall - mortgage holders |
|
|
How would a rise in interest rates affect inflation |
Lead to a rise in the market rate Lead to domestic and external demand falling Lead to total demand (AD) falling Domestic inflationary pressure down Inflation down |
|
|
Describe the quantitative easing transmission mechanism |
BoE purchases bonds They are sold so there is more money in the economy economy Banks are now more likely to lend Positive wealth effect is created, so MPC rises |
|
|
Give an advantage and disadvantage of quantitative easing on the key economic objectives |
Advantage - leads to consumption and therefore AD rising, so economic growth will increase Disadvantages - mass inflation |
|
|
Define economic growth |
Increase in the productive capacity of the economy over time |
|
|
Give 4 measures of economic growth |
GDP GNP GNI Real GDP |
|
|
Describe the Great Depression |
Fact: USA unemployment hit 24.9% in 1933 Cause: stock market crash led to immediate drop in confidence and therefore demand Impacts: world GDP fell Policies used: USA (New deal fiscal policy) UK (Emergency budget cut public sector wages) |
|
|
Describe the Global Financial Crisis |
Cause: US economic slump and fall in mortgage prices in US led to increased risk in the financial system
Impacts: collapse in confidence and banks stopped lending. 2007 nothern rock collapsed, nationalisation of RBS and Lloyds Policies used: cut spending and increased taxes (fiscal austerity). Historically low interest rates |
|
|
What is export and consumption led growth |
Export - an increase in GDP caused by a rise in exports Consumption - higher consumer spending leading to increased economic growth |
|
|
Give 3 advantages disadvantages and 4 constraints on economic growth |
Advantages - disposable income up, unemployment down, tax revenue up Disadvantages - inflation up, balance of payments worsens, environmental impact Constraints - factors of production |
|
|
What is a positive and negative output gap |
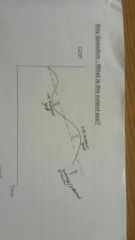
Positive - When GDP is above the productive potential (boom) Negative - when GDP is below the productive potential |
|
|
Give 3 implications of a positive output gap and 2 implications of a negative output gap |
Positive - inflation up, unemployment down, BoP worse Negative - GDP down, unemployment up |
|
|
Give 4 ways that a negative output gap can be closed |
Increase government spending Decrease taxation Decrease interest rates Increase money supply (QE) |
|
|
Give 1 problem of measuring the output gap |
Hard to measure economic growth |
|
|
Define productivity |
Measure of the efficient use of factors of production |
|
|
What is the productivity gap |
Low productivity when compared to other countries |
|
|
Give 2 things that cause a productivity gap |
Difference in skilled labour Less technology |
|
|
How could a country improve its productivity |
Supply side policies |
|
|
How do economic growth and development differ |
Growth measures changes in GDP or GNP and can be depicted on a PPF. Development also measures social factors. Uses PPP rather than nominal exchange rates. It takes into account relative cost of living and inflation rates in different countries |
|
|
Give 6 problems with using GDP as an indicator of standard of living |
Ignores effects of growth (pollution) Hidden income isn't taken into account (cash in hand) Informal economy is ignored (housework etc) Cost of living is ignored Inequality is ignored Quality is ignored |
|
|
Describe inequality as a measure of economic development |

|
|
|
Describe the happiness index as a measure of economic development |

|
|
|
What is the easterlin paradox |

|
|
|
Give 3 other methods of measuring happiness |
Human Development Index (takes into account many factors, complex) Access to technology (measure of disposable income, difficult to quantift) Infrastructure indicators (measure of country's productivity, hard to measure) |
|
|
Define inflation |
The general and sustained rise in prices |
|
|
How do the ONS find out the typical spending pattern of British households for CPI and RPI |
Living costs and food survey (RPI) Household final monetary consumption expenditure survey (CPI) They ask 1000 households to record their spending over a 2 week period Calculate and average basket kd spending |
|
|
What is the international measure of inflation |
Harmonised Index of Consumer Prices |
|
|
What does CPI include that RPI doesn't and visa versa |
RPI includes housing costs (e.g taxes rent mortgage etc), CPI doesn't CPI includes uni fees, air fares, payments on retirement homes, RPI doesn't |
|
|
What method do each form of inflation use to calculate aggregate prices |
RPI - arithmetic mean CPI - geometric mean |
|
|
Give 3 problems with using CPI as a measure of inflation |
Doesn't take into account a change in quality Doesn't include housing costs Rate doesn't apply to everyone as some are more affected by costs than others |
|
|
What are the 2 different views of what causes inflation |
Monetarist view - excessive growth in the money supply and output Keynesian - rise in the costs on the supply side or an increase in demand. Caused by demand pull inflation (demand rises faster than what can be supplies at existing prices) or cost push (increased costs to producers lead to higher prices for consumers) |
|
|
Give 4 costs of inflation |
Erosion of values (bad for pensioners, savers etc) Unemployment Shoe leather costs Uncertainty |
|
|
Define stagflation, deflation, and disinflation |
Stagflation - inflation accompanied with unemployment and falling economic growth Deflation - general and sustained fall in prices Disinflation - decline in the rate of inflation |
|
|
What could create deflation |

|
|
|
Give 4 problems with deflation |
Less confidence Less investment Negative wealth effect More money owed on mortgages |
|
|
Describe 2 methods of measuring unemployment. Who aren't included in either? |
Claimant Count (to see able to work but can't so are claiming benefits) Labour Force Survey (quarterly survey of 60k households. Covers those who have looked for work in the last 4 weeks and can start in the next 2. Claimant count doesn't include a number of groups who are classed as unemployed under the ILO definition (e.g 16 and 17 yr olds, partners with high income) Pensioners, hidden unemployed and voluntary unemployed are not included |
|
|
Give 1 problem with full employment |
Lack of flexibility in the market |
|
|
Give and define 5 types of unemployment |
Real wage (high wages cause excess supply of labour) Seasonal (some jobs only needed at certain times of the year) Structural (change in UK economic structure leads to redundancy) Cyclical (downturn leads to reduced AD and less demand for workers) Frictional (time taken moving between jobs) |
|
|
How are unemployment and inflation related |

Inverse relationship shown by the Phillips curve |
|
|
Describe the current account |

|
|
|
Give 3 SR and 3 LR factors that cause a current account deficit in the UK |
SR -stronger pound, euro zone crisis, high inflation LR - productivity gap, higher investment abroad, lack of raw materials |
|
|
Give and explain 3 factor that nfluence the exchange rate |
Changes in the current balance Change in interest rates Speculation |
|
|
Effect of high and low exchange rate |
High - current account deficit (SPICED) Low - current account surplus (WPIDEC) |
|
|
Give 3 potential problems with trade |
Language barriers Overspecialisation Differences in legal requirements |
|
|
Give 3 advantages and disadvantages of free trade |
Advantages - efficiency, choice, competition Disadvantages - environmental impact, structural unemployment, dependence on foreign markets |
|
|
Give 4 solutions to current account deficit |
Protectionist policies Supply side Exchange rate adjustment Monetary policy Single currency |
|
|
Define inequality |
Unequal distribution of income |
|
|
Give 4 causes of inequality |
Unemployment High interest rates Regressive tax Reduction in benefits |
|
|
Give 3 solutions to inequality |
Progressive tax Education Training |

