![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
31 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the 2 main structures of the nervous system?
|
1. Central nervous system (CNS)
2. Peripheral nervous system (PNS) |
|
|
What structures make up the central nervous system?
|
1. Brain
2. Spinal cord |
|
|
What makes up the peripheral nervous system?
|
-Cranial and spinal nerves
|
|
|
What are the areas of the brain?
|
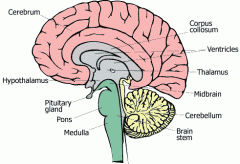
1. Cerebrum
2. Cerebellum 3. Midbrain 4. Brain stem |
|
|
What are the meninges?
|
-The 3 membranes that line the skull and vertebral canal and enclose the brain and spinal cord.
|
|
|
What are the 3 layers of the meninges?
|
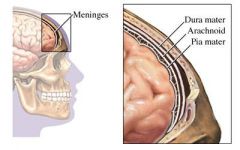
1. Dura mater (outer layer)
2. Arachnoid (middle layer) 3. Pia mater (closest to brain) PAD |
|
|
What are the 2 divisions of the peripheral nervous system?
|
1. Sensory
2. Motor |
|
|
What are the 2 divisions of the motor system?
|
1. Somatic (voluntary)
2. Autonomic (involuntary) |
|
|
What functions are the somatic system responsible for?
|
-Motor skills
-Skeletal muscle regulation -ie walking and lifting |
|
|
What functions are the autonomic system responsible for?
|
-Regulates involuntary functions
-ie heartbeat, breathing |
|
|
What are the two divisions of the autonomic system?
|
1. Sympathetic (activating, fight or flight)
2. Parasympathetic (calming, relaxation) |
|
|
How does a stroke occur?
|
-From impaired blood flow due to vessel occlusion (ischemic) or hemorrhaging (hemorrhagic)
|
|
|
How common are stroke?
|
-Third most common cause of death.
|
|
|
What are the risk factors for stroke?
|
-Smoking
-Hypertension -Diabetes -Gender -Race |
|
|
What is Parkinson's Disease?
|
-Disruption of motor control due to loss of cells that produce the chemical dopamine.
|
|
|
What causes Parkinson's Disease?
|
-Loss of dopamine producing cells in the brain.
|
|
|
What are the symptoms of Parkinson's Disease?
|
-Involuntary shaking
-Rigidness -Slow movements |
|
|
What are treatments for Parkinson's?
|
-Dopamine replacement or dopamine reuptake inhibitors
-Surgery to create lesions -Deep brain stimulation |
|
|
What are the symptoms of dementia?
|
-Loss of memory
-Loss of understanding -Poor judgement -Altered mood and personality -Mental confusion -Difficulty recognizing friends and relatives |
|
|
What are treatments for dementia?
|
-Medications
|
|
|
What is multiple sclerosis?
|
-Degenerative and progressive disease in which autoimmune system attacks itself.
|
|
|
What parts of the body does multiple sclerosis affect?
|
-Central nervous system; white matter of brain and spinal cord.
-Causes demyelination of nerves -Causes hardening of tissues |
|
|
What are symptoms of multiple sclerosis?
|
-Periods of remission
-Muscular weakness -Numbness in face and extremities -Loss of short term memory |
|
|
What are the treatments for multiple sclerosis?
|
-Steroids to slow or arrest disease process
-Treatment to manage symptoms -No cure |
|
|
What is epilepsy?
|
-Seizures caused by uncontrolled electrical discharge in part of the brain.
|
|
|
What are the causes of epilepsy?
|
-Genetic
-Trauma to brain -Post-infection scarring |
|
|
What is most common treatment of epilepsy?
|
-Medication
|
|
|
What is meningitis?
|
-Infection of the membranes covering the brain and spinal cord (meninges).
|
|
|
What are the causes of meningitis?
|
-Bacteria
-Virus -Infection |
|
|
What are the symptoms of meningitis?
|
-Fever
-Neck stiffness -Confusion -blue spots (tiny bleed spots) |
|
|
What is facial palsy?
|
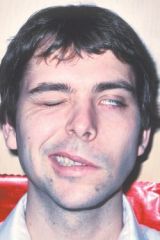
-The paralysis of any structures innervated by the facial nerve
|

