![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
52 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
2 Functions of the lymphatic system |
1. Immunlogical defense 2. Conduit for rturn of interstitial fluid to the blood stream |
|
|
8 Components of the lymphatic system |
1. Thymus 2. Tonsils 3. Spleen 4. Lymph nodes 5. Hemal nodes 6. DIffuse lymphatic tissue and lymphatic nodules found in mucous membranes 7. circulating lymphocytes and plasma cells 8. lymphatic capillaries and vessels |
|
|
What are primary organs? Name 3. |
Organs where lymphocytes originate (antigen independent)
1. Thymus 2. Bone marrow 3. Peyer's patches |
|
|
What are seconday organs? Name 3 |
Organs to which lymphocytes migrate and proliferate (antigen dependent)
1. Spleen 2. Lymph nodes + nodules 3. Tonsils |
|
|
When is the thymus largest? |
In young animals. It regresses in size with age and is basically non-existent in adults
At its largest it almost fills the ventral part of the mediastinum |
|
|
What does the thymus do? |
Produces T lymphocytes |
|
|
When is the thymus most active? |
During embryonic and prepubertal period |
|
|
What is on the outside of the thymus? |
A connective tissue capsule which penetrates and divides the organ into lobules |
|
|
Where is the thymus located? |
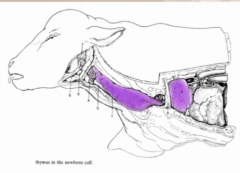
Extends down the neck, enters thoracic inlet and occupies big part of the mediastinum |
|
|
What do bone marrow and payer's patches do in the lymphatic system? |
Source of B lymphocytes - once produced they enter the blood stream and go to secondary lymphoid organs |
|
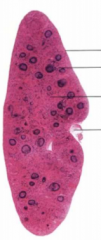
Name these parts of the spleen |
Top to bottom:
Capsule with serous tunic
Lymph follicule (white spleen pulp)
Sinus (red spleen pulp)
Hilus |
|
|
Where is the spleen located? |
Left side of the body in the abdominal space |
|
|
What is white pulp? |
Lymph follicles (nodules) developing in the spleen
|
|
|
What is red pulp? |
Sinus of the spleen, where RBCs are located |
|
|
What does the spleen do? |
Filters blood
Looks for breakdown products of arythrocytes
Can identify antigens in the system as part of the lymphocyte system |
|
|
How is the lymphatic system different from the blood circulatory system? |
Not a complete circle like the blood system.
There are termination points (villi with hollow tubes) where interstitial fluid enters due to high osmotic pressures |
|
|
Once fluid enters the lymp tubes where does it go? |
To lymph nodes |
|
|
Where do lymph nodes usually develop? |
Where multiple capillaries come together |
|
|
What is the path lymph takes to, through and from a lymph node? |
Enters lymph node through afferent vessels in the periphery
Goes through nodules (concentrations of lymphocytes) that sit close to the cortex
Move deeper into the medulla into loose lymphoreticular tissue
This is where efferent vessels originate and takes lymph out of the lymph node via the hilum |
|
|
How are porcine lymph nodes different from other species? |
Circulation is reversed
Afferent vessels enter through the hylum
Nodules are more focused in the center around the entrance points of the afferent lymph vessels
Efferent vessels penetrate the capsule to leave the lymph node |
|
|
Compare porcine lymph nodes to other species lymph nodes (pictures) |
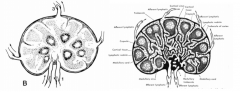
|
|
|
What is a tonsil? |
Aggregation of uncapsulated lymph nodes
|
|
|
Where are tonsils located? |
Located in the mucosa (moist area)
See them in oro and nasopharynx, in GI tract and reproductive tract
At the origin of lymph drainage pathways |
|
|
How many lymph nodes does lymph encounter before reentering systemic circulation? |
At least two
= multiple points where lymph encounters lymph nodes or nodules to present antigens to the immune system |
|
|
Two types of tonsils: |
Tonsillar fossa - fold that stands up above the surrounding tissue - seen in dogs
Tonsillar sinus - invagination with thick lymphoid tissue in the wall - seen in cows |
|
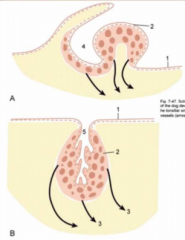
Name the parts of the tonsils |
1 = epithelium 2 = palatine tonsil 3 = efferent vessels (arrows) 4 = tonsillar fossa 5 = tonsillar sinus |
|
|
A few notes about tonsils in other species:
Dog: Cat: Pig: Cattle: Goat: Horse: |
Dog: tonsillar fossa - see lots on dorsal surface of oropharynx
Cat: very similar to dog
Pig: tonsils more diffuse, thickening on roof of oropharynx, some on roof of nasopharynx
Cow: Invaginated tonsils, thick walls - Diffuse ventrally, larger tonsils in nasopharynx on walls of nasal septum
Goat: thickenings present in oropharynx, some on nasal septum in nasopharynx but not invaginated
Horse: diffuse in oro and nasopharynx - similar to pig |
|
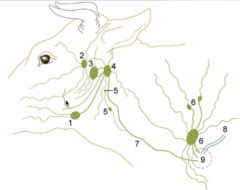
Name the 3 lymphocenters of the head |
#1 - Mandibular lymphocenter - mandibular lymph node
#2 - Parotid lymphocenter - parotid lymph node
#3/4 - Retropharyngeal lymphocenter - Medial (#3) retropharyngeal lymph node is dorsal to roof of pharynx (quite deep) - Lateral (#4) is close to wing of atlas (also quite deep but can sometimes be palpated) |
|
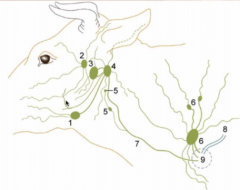
Name the lymphocenters of the neck |
5 = deep cervical lymph nodes (cranial, middle and caudal) 6 = superficial cervical lymph nodes 7 = tracheal duct 8 = thoracic duct 9 = area where lymphatic vessels enter veins |
|
|
Which veins does lymph usually enter in the neck? |
Jugular vein or cranial vena cava |
|
|
What are the differences between lymph nodes in the cow and the horse? |
Cows usually have large singular or paired lymph nodes Horses have clusters of small lymph nodes (still in same regions)
- not as easily palpated in the horse |
|
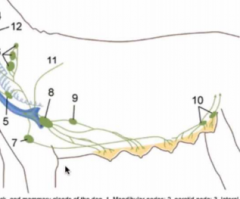
Name #7, 8, 9 and 10 |
7 = sternal lymph node 8 = axillary lymph node (drains the forelimb and deep structures of shoulder) 9 = accessory axillary lymph node (not consistent, may not be present) 10 = superficial inguinal lymph nodes |
|
|
How many tracheal ducts are there? |
2, one on each side of the trachea |
|
|
5 lymphocenters of the Thoracic space |
1. Dorsal thoracic lymphocenter - includes the intercostal set (upper parts of first few intercostal spaces)
2. Thoracic aortic set - located along aorta
3. Ventral thoracic lymphocenter - 2 portions: cranial sternal near manubrium, and possibly caudal sternal (mostly prominent in ruminents and usually not seen in other animals)
4. Mediastinal lymphocenter - cranial, middle (by base of the heart) and caudal
5. Bronchiole lymphocenter - associated with tracheal bifurcation |
|
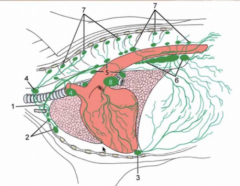
Name them all! |
1 = thoracic duct 2 = cranial sternal lymph nodes (part of ventral thoracic lymphocenter) 3 = caudal sternal lymph nodes (ventral thoracic lymphocenter) 4 = cranial mediastinal lymph nodes 5 = middle mediastinal lymph nodes 6 = caudal mediastinal lymph nodes 7 = intercostal and thoracic aortic lymph nodes 8 = tracheobronchial lymph nodes |
|
|
Left thoracic duct |
- enters into jugular vein or cranial vena cava - major lymph collecting channel - provides exit from cisterna chyli - comes between aorta and vertebrae at thoracolumbar junction, passing through aortic hiatus on diaphragm - found in left thoracic cavity on left face of aorta |
|
|
Is there a right thoracic duct? |
Yes, but not connected to cisterna chyli and isn't very large or as useful |
|
|
Abdominal Space Lymphocenters |
Celiac lymphocenter - lymph nodes going to organs provided by celiac artery
Cranial mesenteric lymphocenter - intestinal tract - duodenal, cecal and colic lymph nodes
Caudal mesenteric lymphocenter - lyph nodes of descending colon
|
|
|
Where do the abdominal space lymphocenters drain to? |
Cisterna chyli |
|
|
Lumbosacral Lymphocenters |
Renal lymphocenter - quite large
Lumbar lymphocenter - in lumbar vetebrae
Iliosacral lymphocenter - large, widely spread, covers roof of abdomen and pelvis. * near origin of external and internal iliac arteries *not as large in the dog, but prominent in other species |
|
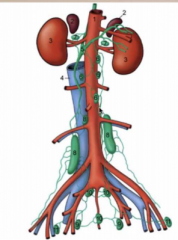
Name these! |
1 = aorta 2 = adrenals 3 = kidneys 4 = caudal vena cava 5 = cisterna chyli 6 = lumbar aortic lymph nodes 7 = renal lymph nodes 8 = medial iliac lymph nodes 9 = hypogastric lymph nodes 10 = sacral lymph nodes 11 = deep inguinal (iliofemoral) lymph nodes |
|
|
How does the cisterna chyli act like a pump for the lymphatic system? |
When diaphragm tightens and negative pressure in thoracic cavity increases, fluid is drawn forward through cisterna chyli |
|
|
Lymph nodes of the hindlimb (5) |
Iliosacral lymph nodes Subiliac lymphocenter - ahead of stifle popliteal lymph nodes - palpable above gastroc superficial inguinal lymph node sacral/ischial lymph node |
|
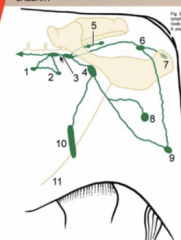
name these! |
1 = lateral iliac lymph node 2 = coxal lymph node 3 = medial iliac and sacral lymp nodes 4 = deep inguinal lymph node 5 = glueteal lymph node 6= ischial lymph node 7 = tuberal lymph node 8 = superficial inguinal (mammary) lymph node (quite deep) 9 = popliteal lymph node 10 = subiliac lymph node 11 = linea alba |
|
|
Which lymph nodes are usually palpable? |
Parotid lymph node Mandibular Superficial cervical subiliac popliteal |
|
|
Dogs do not have a _____________ lymph node |
Subiliac |
|
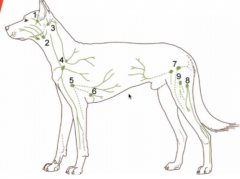
Name these! |
1 = parotid 2 = mandibular 3 = lateral retropharyngeal (inconsistent) 4 = superficial cervical 5 = axillary 6 = accessory axillary (inconsistent) 7 = superficial inguinal 8 = popliteal 9 = femoral (inconsistent) |
|
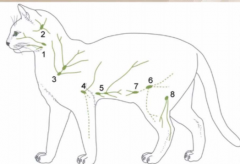
Name these! |
1 = mandibular 2 = lateral retropharyngeal 3 = dorsal superficial cervical 4 = axillary 5 = accessory axillary 6 = superficial inguinal 7 = caudal epigastric 8 = popliteal |
|
|
Where do B cells originate in birds? |
The cloacal bursa - largest in young birds around 6 weeks of age then becomes less prominent |
|
|
What is the cloaca? |
the only opening for the intestinal, reproductive, and urinary tracts |
|
|
Which birds have discrete lymph nodes? |
Typically none, but we see some discrete lymph nodes in ducks and geese - paired cervical thoracic nodes at thoracic inlet - pair of lumbar nodes near kidney |
|
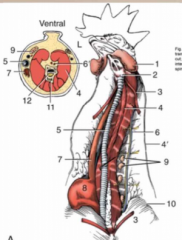
Name these! |
1 = Wattle 2 = Larynx 3 = Sternothyroideus 4 = cervical muscles 4' = cervical nerve 5 = trachea 6 = jugular vein and vagus 7 = esophagus 8 = crop 9 = thymus 10 = pectorals 11 = vertebrae 12 = spinal cord |

