![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
31 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What artery can repture easily if weak while sneezing? |
Sphenopalatine artery |
|
|
-What nerves supply the nose? -What are they branches of? |
-The Ophthalamic nerve (V1) and maxillary nerve (V2) -Branches from the tregiminal nerve , cranial nerve V |
|
|
What are the names for nerves V, V1 and V2? |
-V = trigeminal nerve -V1 = Ophthalamic nerve -V2 = Maxillary nerve |
|
|
Where can the pharyngeal tonsils be found? What is another name for these tonsils? How many of them are there? |
-On the superior aspect of nasopharynx -The adenoids -1 |
|
|
What tonsils are located beside the opening to the Eustatian tube? |
The tubal tonsils |
|
|
What is the name of the tonsils located at the back of the mouth (oral cavity) ? |
The palatine tonsils |
|
|
What is Waldeyers Ring? |
A ring of tonsilar tissue in which all substances entering the body through the throat must first pass over |
|
|
What is the vallecula? |
It is a space between the back of the tongue and the epiglottis |
|
|
What is the name of the tissue which is punctured in a cricotomy coniotomy? What two structures does this tissue join? |
-Cricothyroid membrane/ligament , Conus elasticus -Joins the thyroid and cricoid cartilages together |
|
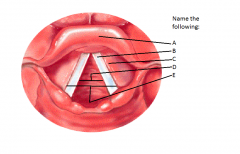
|
A - Epiglottis B - Vocal folds C - Vestibular folds D - Rima glottidis E - Rima Vestibuli |
|
|
What is the point which divides the supraglottic and infraglottic portions of the larynx? |
The vocal folds |
|
|
Under what circumstances would you perform a tracheostomy? |
For an infraglottic blockage |
|
|
A cricotomy can be done for what type of blockage? |
A supraglottic blockage |
|
|
The aditus is another name for what? |
The laryngeal inlet |
|
|
What are the three pairs of unparied cartilages in the larynx? |
-The thyroid cartilage -The cricoid cartilage -The epiglottis |
|
|
What paired cartilages sit on top of the cricoid? |
The arytenoid cartialges |
|
|
The two distinct processes on the arytenoids are called what? |
The vocal process and the muscular process |
|
|
What is the name of the ligament which connects the back of the epiglottis to the hyoid bone? |
The hyoepiglottic ligament |
|
|
What ligament connects the larynx to the trachea? |
The cricotracheal ligament |
|
|
The thyrohyoid membrane connects what two structures? |
The hyoid bone and the thyroid ligament |
|
|
What are the 3 parts to the intrinsic ligament of the larynx? |
-The quadrangular membrane -The lateral cricothyroid ligament -The median cricothyroid ligament |
|
|
The quadrangular membrane attaches to what? What does it form? |
-Attaches to the arytenoids and the thyroid cartilages -Its lower free margin forms the vestibular ligaments |
|
|
The vocal ligaments are formed by what? |
The upper free margin of the lateral cricothyroid ligament |
|
|
The space between the vocal folds and vestibular folds is called what? What other space arises within here? |
-The laryngeal ventricle -The Laryngeal saccule |
|
|
All infrahyoid muscles of the larynx are supplied by branches from roots C1-C3 except: A - Sternohyoid B - Omohyoid C - Thyrohyoid D - Sternothyroid |
C - Thyrohyoid |
|
|
Muscles that move the larynx superiorly are known as what? |
The suprahyoid muscles |
|
|
All intrinsic muscles of the larynx (except one) are innervated by what nerve? What is the exception? |
-The recurrent pharyngeal nerve -the cricothyroid muscles |
|
|
The cricothyroid muscles has 2 parts, what are they? What is the function of this muscle? What is its innervation? |
-A straight and oblique part -Pulls the thyroid cartilage down and forward and thereby increase tension on the vocal cords -The extrinsic pharyngeal nerve |
|
|
The posterior cricoarytenoids perform what function? |
External rotation of the arytenoids, hence opening the vocal folds |
|
|
What muscles act to close the vocal folds? Where do these muscle originate from? |
Lateral cricoarytenoids -The lateral surface of the cricoid |
|
|
What muscle fully close the rima glottidis? |
The interarytenoids |

