![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
52 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
The 5 basic groups of microorganisms |
Bacteria Fungi ( including yeasts and molds) ProtozoansAlgaeViruses Algae Viruses |
|
|
Dengue Fever |
A mosquito borne and potentially dangerous infection if you are infected more than once |
|
|
Sudden acquired respiratory syndrome SARS |
Caused by a Coronavirus belonging to a family of common cold causing viruses. Only presents a danger to those with weakened immune system. |
|
|
Escherichia coli O157:H7 |
A strain of E coli that is very common in processed meats and fish. Presents a great risk to children who in just the organism. |
|
|
Normal flora |
microbes which normally live in or on your bodies but that can cause disease if given the opportunity E-coli , Staphylococcus aureus, & Candida albicans (yeast)are well known inhabitants of the human body |
|
|
Opportunistic pathogens |
Microbes that can cause disease if given the opportunity, which are most microbes |
|
|
1995 |
Rabies made a surprise comeback in the San Antonio area To local children died needlessly of a rare amoeba infection from swimming in stagnant water in the summer Also that summer news reports appeared of a relatively new tick-borne disease called HGE human granulocytic ehrlichiosis |
|
|
2002 |
West Nile virus became a nuisance in the United States |
|
|
In the past 10 years... |
Antibiotic-resistant tuberculosis, MRSA methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and VRE Vancomycin resistant enterococcus became household names |
|
|
Human papilloma virus |
Was all over the news in 2007 when Governor Rick Perry made Texas the 1st state to mandate the vaccine for this virus as a preventative of cervical cancer |
|
|
Swine flu (H1N1) |
2009 Texas was brought to nation's attention because swine flu quickly spread to more than 70 countries Center for Disease Control reported between April and October 22 million Americans had contracted the virus 98000 required hospitalization and about 3,900 people died |
|
|
Mumps |
Re-emerged worldwide in 2009 largely due to unvaccinated individuals and those with expired vaccines |
|
|
2014 |
Saw a huge outbreak of impetigoIn Africa , an outbreak of Ebola virus came to the Forefront again but by using good quarantine procedures the outbreak soon subsides In Africa , an outbreak of Ebola virus came to the Forefront again but by using good quarantine procedures the outbreak soon subsides In Africa , an outbreak of Ebola virus came to the Forefront again but by using good quarantine procedures the outbreak soon subsides |
|
|
Carolus Linnaeus |
Develop a taxonomic system for naming plants and animals which is also used for microbes. Uses the genus and species in the name. Genus is always capitalized but the species is never capitalized. Both the genus and the species names are always italicized or underlined even when genus is abbreviated. |
|
|
Eukaryotes vs. Prokaryotes |

|
|
|
Fungi |
Eukaryotic NOT photosynthetic Unique cell walls much like insects -Important in the degradation of dead plants and animals - divided into yeast and molds based on morphology |
|
|
Molds vs. Yeasts |

|
|
|
Protozoa |
Single-celled eukaryotes Most like us No cell walls Must live in water or animal hosts Asexual reproduction mostly but sexual reproduction possible Classified by motility into 4 groups: - pseudopodia (amoeba) - ciliata. Only eukaryotes have cilia. - flagellates, flagella or longer and fewer than cilia, whiplike in eucaryotes - Apicomplexans inability to move |
|
|
Algae |
Eukaryotic Unicellular or multicellular All are photosynthetic Characterized by color, products stored, and cell wall composition Provide most of Earth's oxygen |
|
|
Prokaryotes |

Unicellular No nuclei No membrane-bound organelles Live singlely or in clusters |
|
|
Viruses |
Acellular Obligate intracellular parasites Submicroscopic |
|

Robert Hooke 1665 |
Devised a very crude microscope which he used to observe cork cells as he called them. He proposed that these cells were the building blocks of all living things. His microscope was probably too crude to allow him to see bacteria or other single-celled organisms. |
|
|
Built a more complex microscope using magnifying lenses. He was able to see small organisms in rainwater and in scrapings from his teeth. He was amazed to see animalcules as he called them priding himself that he kept his teeth clean by his standards. He saw various shapes of bacteria which today we would consider normal flora of the mouth |

Van Leeuwenhoek 1700s |
|
|
Spontaneous generation (Abiogenesis) |
The belief that life can arise from nonliving matter. A theory that has been disproven. |
|
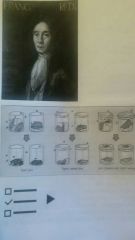
Francisco Redi |
Was one of the first early scientists to oppose spontaneous generation. His early experiments he put meat in several different jars and demonstrated that after a period of time fly larvae were present in the decaying meat, however when he filled the jars no larvae grew. After some criticism he modified the experiment by placing gauze over the tops of his jars to allow oxygen. The Flies were kept out of course and no larvie appeared. |
|
|
John T. Needham |
Boiled beef gravy and hay infusions then capped the cultures and observe the tubes were full of microbes a few days later. It was later determined that he probably did not boil long enough to kill all microbes (sterilize) the broths. |
|
|
Lazzaro Spallanzani |
Countered Needham's experiment by boiling cultures for 1 hour then sealing them in glass vials. Spontaneous generation did not occur. The criticism over Spalding's on his work was that he heated cultures too long and killed the "life force" |
|
|
PASTEUR experiment to disprove ABIOGENESIS |
As late as 1858 scientists were still debating spontaneous generation. Finally passed or devised an experiment to disprove it. He placed nutrient broth into number of flask he then boiled The Flash to kill all microbes. He heated the long necks of the flask and bent them into an S shape. Microbes were unable to fall from the air into the flask and even though the flask or open to the air nothing ruin the broth. |
|
|
THE SCIENTIFIC METHOD |

|
|
|
Aseptic techniques |
Pasteur's work lead to the development of aseptic techniques which are methods of handling steel material in a way to maintain sterility: free of all life |
|
|
Golden Age of Microbiology |
1857 - 1914
Number of important advances in microbiology were spearheaded by Pasteur, Joseph Lister and Robert Koch |
|
|
PASTEUR |
In the mid 1800s Pastor worked in the wine and beer industry. Predominantly used were used in a process that we now know as fermentation. In which sugar is converted into alcohol.
Willie's beverages were shipped over long distances they spoiled by the time they reach the destination. This was caused by growth and Metabolism of contaminating bacteria that had converted the alcohol to acetic acid (vinegar). He developed a technique pasteurization which is now more commonly associated with the milk industry. Is Method involved heating alcoholic beverages long enough to kill the microbes without destroying the flavor of the beverage.
|
|
|
Germ theory of disease |
The linkage of human and animal diseases with microbes. With infectious diseases there is a causative agent |
|
|
Joseph Lister |
the first physician to use carbolic acid (phenol) to disinfect medical instruments in wounds. Because of this there was a drastic decrease of infections following surgery in childbirth Credited for using the first disinfectant and antiseptic in surgery |
|
|
Semmelweis |
Do the first trials with hand washing and chlorinated lime water |
|
|
Disinfectant |
Chemical used to kill microbes on an object
Does NOT steralize. It sanitizes |
|
|
Antiseptics |
Are used to kill microbes on skin & mucous membranes
Does not sterilize. It sanitizes. |
|

ROBERT KOCH |
Went about the process of proving The Germ theory of disease find studying the etiology or cause of disease Based off his studies and racks he developed several postulates that are still used today and identifying causative agents of infectious disease. He isolated bacillus anthracis from cattle that had died of anthrax he then injected a pure culture of the bacterium into healthy cattle which is undeveloped Anthrax and died. |
|
|
Koch's postulates |
1. Pathogen must be present in every case of the disease 2. Pathogen must be isolated from a disease host 3. Pathogen is grown in pure culture and identified by extensive means. 4. Pure culture must calls The Identical disease when introduced into a healthy host 5. Pathogen must be reactivated in pure culture, identified and shown to be identical to the original isolate. |
|
|
Attenuated microbes |
Those that are mutated in some way so that they cannot produce a full-blown infection |
|
|
Magic Bullet |
A cure for every known infectious disease |
|
|
Vaccines |
Substances, usually parts of microbes, or microorganisms that are attenuated or killed. Vaccines are injected into the human body which in turn develops an immune response to Target microorganism. Upon subsequent exposure the individual is protected against the disease-causing microbe |
|
|
One of the first vaccines was the one against... |
Smallpox |
|
|
1776 Edward Jenner |
Noted that a milkmaid who had been exposed to cowpox was immune to smallpox. He demonstrated that material from a cowpox pustule could be diluted and given to a healthy individual who subsequently developed local inflammation but did not develop the disease |
|
|
Types of vaccines now available |
Killed attenuated subunit toxoid |
|
|
Chemotherapy |
The use of synthetic or naturally occurring drugs in therapy against disease |
|
|
Synthetic drugs |
Those chemotherapeutic agents that are produced in the laboratory |
|
|
Paul Ehrlich |
Developed one of the first synthetic drugs in the battle against syphilis. He developed salvarsan to treat syphilis |
|
|
Salvarsan |
An arsenic derivative used to treat syphilis. Before its development the only drug against syphilis available with quinine which was also used to fight against malaria |
|
|
Antibiotics |
Chemotherapeutic agents that are produced Naturally by microorganisms |
|
|
Alexander Fleming |
Discovered antibiotics by accident. He was throwing out some Petri plates containing bacteria because they had become contaminated with mold. He noticed a clear Zone around the mold where the bacteria could not grow. That mold is now known as penicillin chrysogenum |
|
|
Recombinant DNA technology is divided into... |
Microbial genetics & Molecular biology |

