![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
21 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
what are the main features of an atheroma formation? |
fatty deposit forms within the all of an artery . fatty streak that are accumulations of LDLs and dead muscle cells . streaks enlarge to form an atheromatous plaque . they bulge into the lumen and narrow wit so that the blood flow through it is reduced, and pressure increases.. atheroma can lead onto two life threatening conditions ,thrombosis and aneurysm
|
|
|
what are the main features of a thrombosis formation? |
. begins with the formation of an atheroma . formation of a blood clot . atheroma plaque can burst under pressure causing splits in the endothelium lining . this can cause complete blockage of the artery or it can break off and dislodge a blood vessel |
|
|
what are the main features of an aneurysm? |
. ballon like swelling of the artery . starts with the formation of atheromas . plaque weaken and damage endothelium lining of the artery wall, and increase blood pressure . this pressure pushes out the inner layers to form a ballon like swelling on the outside of the artery . this may burt causing a haemorrhage |
|
|
what is a myocardial infarction? |
. is more commonly known as a heart attack . occurs by the blockage of the coronary artery that supplies blood to the heart . this stops the hear from being able to function and therefore after a while the body dies |
|
|
what are the four main risk factors associated with CHD? |
. high blood pressure . high blood cholesterol and bad diet . smoking . genetics |
|
|
explain the risk of smoking on CHD |
. smoking causes lots of carbon monoxide in the blood . this lessens the oxygen in the blood . which means less oxygen to tissues . leading to a myocardial infarction . smoking also reduces the amount of anti oxidants in the blood . this weakens artery walls and they begin to break . this may cause a myocardial infarction . DEATH . ALSO, nicotine stimulates adrenaline in the blood, seeding up heart rate hence raising blood pressure . nicotine also makes red blood cells 'sticky' |
|
|
explain the risk of high blood pressure on CDH |
. no exercising overweight ect.. or perhaps diabetes ect.. . high blood pressure . atheroma formation . blood clots . myocardial infarction . DEATH |
|
|
explain the risk of high blood cholesterol and poor diet on CHD |
diet high in saturated fat leads to high blood cholestrol . diet high in salt also leads to high blood pressure . these both lead to atheroma formation . leading to blood clots . myocardial infarction . DEATH |
|
|
describe he features and functions of the left and right ventricles |
. left hand side ventricle has a much thicker, more muscular wall than the right hand side ventricle . this is because it has the whole body to pump blood around to . where as the right hand side only needs to pump to the lungs which are relatively close by . they have thicker walls than the atria |
|
|
describe the features and functions of the atrioventricular valves |
. link the atria to the ventricles . stop back flow of the blood when ventricles contract . the valves connected to the left handed are bicuspid (two flaps) . the valves connected to the right hand side of the heart are tricuspid (three flaps) |
|
|
describe the features and the function of the Semi lunar valves |
. link the ventricles to the pulmonary artery and aorta . stop back flow of blood back into the heart after the ventricles contract |
|
|
describe the features and functions of the chords in the heart |
. attach the atrioventricular valves to the ventricles to stop them being forced up into the atria when the ventricles contract |
|
|
explain the roles of the heart valves and how they work |
. the heart valves only open one way . whether they are open or closed depends on their relative pressure of the heart chambers . high pressure behind a valve its forced open . high pressure in front, stays firmly shut |
|
|
what is the aorta connected to, does it carry oxygenated blood and where does it send its blood? |
. connected to the left ventricle . does carry oxygenated blood . all parts of the body apart from the lungs |
|
|
what is the vena cava connected to, does it carry oxygenated blood and where does it send its blood?
|
. connected to the right atrium . carries de oxygenated blood from around the body other than the lungs |
|
|
what is the pulmonary artery connected to, does it carry oxygenated blood and where does it send its blood?
|
. connected to the right ventricle . carries deoxygenated blood to the lungs . unusually for a artery carries deoxygenated blood |
|
|
what is the pulmonary vein connected to, does it carry oxygenated blood and where does it send its blood?
|
. connected to the right atrium . brings oxygenated blood back from the lungs to send it around the body through the right ventricle . unusually for vein, it carries oxygenated blood |
|
|
revise where everything is in the structure of the heart cause AQA are bitches and they will ask you (flip side of this card shows the structure of the heart! now go revise it!) |
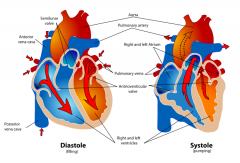
|
|
|
what artery supplies the heart its self with oxygen? |
. coronary arteries . branch off the aorta as it leaves the heart chambers . blockage of this will cause a myocardial infarction and most probably DEATH |
|
|
what controls the heart beat? |
. heart is myogenic, which means it can beat by its self without telling it what to do aslong as it has a healthy blood supply . the process of speeding or slowing this heart rate is controlled by the SAN node, AVN node and the bundle of his |
|
|
explain how the cardiac cycle is controlled |
. wave of electrical energy spreads out from the SAN across both atria causing them to contract . |

