![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
61 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
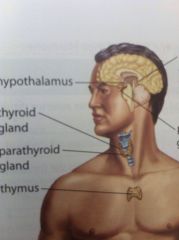
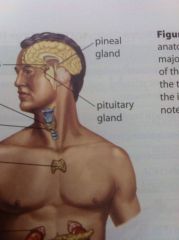
Locate the Pineal gland.
|
Small gland on top of the cerebellum.
|
|
Locate the hypothalamus
|
Directly across from the pineal gland beside the frontal love
|
|
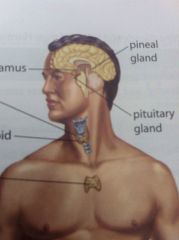
Locate the pituitary gland.
|
The dangly thing below the hypothalamus
|
|

Locate the thyroid and parathyroid glands
|
The thyroid is in the neck and the parathyroids are 4 spit peas on the edges of the thyroid
|
|
Locate the thymus
|
Under the collar bone
|
|
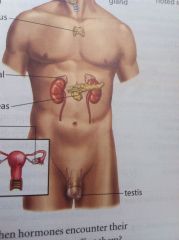
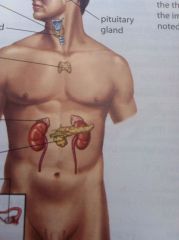
Locate the adrenal gland and pancreas
|
Adrenal gland is on top of kidneys while the pancreas is in the middle a
|
|
|
What hormones does the anterior pituitary secrete?
|
hGH, TSH, ACTH, PRL, LH, FSH
|
|
|
What does the posterior pituitary secrete ?
|
ADH, Oxytocin
|
|
|
What does the Thyroid Secrete?
|
Thyroxin, calcitonin
|
|
|
What does the parathyroid secrete?
|
PTH
|
|
|
What does the adrenal cortex secrete?
|
Aldosterone, androgens, cortisol
|
|
|
What does the adrenal medulla secrete?
|
Epinephrine
|
|
|
What does the pancreas secrete?
|
Insulin, glucagon
|
|
|
What do the ovaries secrete?
|
Estrogen, progesterone
|
|
|
What do the testes secrete?
|
Testosterone
|
|
|
Function of hGH?
|
Growth of all tissues
|
|
|
Function of TSH?
|
Stimulates the thyroid to produce thyroxin and calcitonin
|
|
|
Function of ACTH?
|
Stimulates the adrenal cortex to produce cortisol, androgens and aldosterone
|
|
|
Function of FSH?
|
Stimulates production of ova and sperm
|
|
|
Function of LH?
|
Stimulates sex hormone production.(testosterone, estrogen)
|
|
|
Function of PRL?
|
Stimulates milk production from mammary glands.
|
|
|
Function of ADH?
|
Water retention by kidneys
|
|
|
Function of oxytocin?
|
Uterine muscle contractions and release of milk
|
|
|
Function of thyroxin?
|
Metabolism
|
|
|
Function of calcitonin?
|
Takes calcium from the blood to the bones
|
|
|
Function of calcitonin?
|
Takes calcium from the blood to bones
|
|
|
Function of PTH?
|
Takes calcium from bones to blood
|
|
|
Function of cortisol?
|
Raises blood glucose levels and breaks down proteins.
|
|
|
Function of aldosterone?
|
Reabsorption of Na and H2O by kidneys
|
|
|
What is a tropic hormone
|
Target another gland to secrete something. Ie/ ACTH targets the adrenal cortex which then secretes cortisol aldosterone and androgens
|
|
|
What is a tropic hormone
|
Target another gland to secrete something. Ie/ ACTH targets the adrenal cortex which then secretes cortisol aldosterone and androgens
|
|
|
What is a non tropic hormone?
|
Secrets directly. Ie/ oxytocin.
|
|
|
What is the adrenal cortex responsible for?
|
Long term stress response.
|
|
|
What is the adrenal cortex responsible for?
|
Long term stress response.
|
|
|
What is the adrenal medulla responsible for?
|
Short term stress response.
|
|
|
What are beta cells?
|
Cells that secrete insulin.
|
|
|
What are alpha cells?
|
Cells that secrete glucagon
|
|
|
Describe the negative feedback for insulin/glucagon
|
When low blood glucose occurs, your pancreas secretes glucagon which breaks down fat-> glucose and glycogen->glucose. When high blood glucose occurs your pancreas secretes insulin which the liver stores glucose as glycogen , muscles store glycogen and fat uses glucose to form fat.
|
|
|
What is known as the master endocrine gland?
|
The pituitary
|
|
|
What is a lipid soluble hormone?
|
steroid hormone (testosterone)
|
|
|
What is a water soluble hormone?
|
Amino acid based( insulin, thyroxin )
|
|
|
What is known as the master endocrine gland?
|
The pituitary
|
|
|
What is a lipid soluble hormone?
|
steroid hormone (testosterone)
|
|
|
What is a water soluble hormone?
|
Amino acid based( insulin, thyroxin )
|
|
|
Describe the feedback loop for ADH
|
Osmoreceptors in the hypothalamus stimulate the posterior pituitary to release ADH which targets the kidneys and arteries to vasoconstriction and take water from the kidneys back to the blood.
|
|
|
What is diabetes insipidus caused by?
|
Lack of ADH production
|
|
|
What does the pineal gland secrete?
|
Melatonin which regulates the bodies sleep wake cycle
|
|
|
What is known as the master endocrine gland?
|
The pituitary
|
|
|
What is a lipid soluble hormone?
|
steroid hormone (testosterone)
|
|
|
What is a water soluble hormone?
|
Amino acid based( insulin, thyroxin )
|
|
|
Describe the feedback loop for ADH
|
Osmoreceptors in the hypothalamus stimulate the posterior pituitary to release ADH which targets the kidneys and arteries to vasoconstriction and take water from the kidneys back to the blood.
|
|
|
What is diabetes insipidus caused by?
|
Lack of ADH production
|
|
|
What does the pineal gland secrete?
|
Melatonin which regulates the bodies sleep wake cycle
|
|
|
What is the feedback loop for thyroxin?
|
When metabolism is low the hypothalamus sends releasing factor to the pituitary gland which secrets TSH to stimulate the thyroid gland. The thyroid gland then produces thyroxin which increases metabolism which shuts down the negative feedback loop.
|
|
|
Describe the feedback loop for PTH and Calcitonin.
|
When blood calcium is low the parathyroid glands secrets PTH to take calcium from bones to the blood raising blood calcium levels. When blood calcium levels get too high the thyroid gland is stimulated to secrete calcitonin to take calcium from the blood to the bones.
|
|
|
Describe the feedback loop for cortisol.
|
The hypothalamus sends releasing factor the the anterior pituitary which secrets ACTH to the adrenal cortex which secrets cortisol increasing blood sugar levels and then shuts off the - feedback loop
|
|
|
What works together to keep sodium in the body?
|
ADH and aldosterone.
|
|
|
What part of the pancreas secrets glucose regulating hormones?
|
Islets of langerhans
|
|
|
What is glucose stored as?
|
Glycogen
|
|
|
What converts glycogen back into glucose?
|
Glucagon
|
|
|
How is it possible for individuals with type 1 diabetes to receive insulin?
|
Recombinant DNA technology
|

