![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
15 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Protection |
Meninges (3 Layers) -outer dura mater, middle arachnoid layer, inner pia matter Skull |
|
|
Meninges |
Covers to protect brain + spinal cord Outer Dura Mater (tough mother), middle arachnoid layer - cobweb tissue filled with fluid, inner pia mater (soft mother) - rich in blood vessels |
|
|
Blood Brain Barrier |
Filtration-regulation material entering CNS Materials enter CNS via diffusion or facilitated diffusion Seperation of blood and CNS |
|
|
Cerebral Cortex |
Non myelinated neurons Controls sensory, motor activity Thought, memory, emotion, logic, personality |
|
|
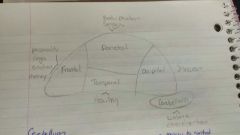
Cerebral Cortex Divided into 4 Lobes |
Occipital (eyes), Temporal (hearing), Frontal (voluntary movement, personality, intelligence, speech) Parietal (sensory info from skin receptors + info regarding body) |
|
|
Corpus Callosum |
connect left/right cerebral hemispheres Tell each half of brain what other half is doing |
|
|
Lobe Divisions |
|
|
|
Cerebellum (Hindbrain) |
Muscle coordination + balance |
|
|
Midbrain |
Receives specific sensory input; connects hind/fore brain Receives specific sensory input; connects hind/fore brain |
|
|
Thalamus (Forebrain) |
Relays info from senses to spinal cord + cortex. Processes crude sensations |
|
|
Hypothalamus (Forebrain) |
Regulates pituitary gland, heart rate, blood pressure + temp. 4 F's |
|
|
Pons (Hindbrain) |
Relays info between cerebellum + cerebral cortex |
|
|
Medulla Oblongata (Hindbrain) |
Controls subconscious activities ex. Heart rate, blood pressure, swallowing |
|
|
Ventricles |
Four hollow, fluid filled spaces 150mL cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) absorbs shock + nourish's CNS cells Composition strict via choroid plexus + BBB |
|
|
Cerebrospinal Fluid |
Transports hormones, white blood cells, + nutrientd across BBB for cells of brain + spinal cord. Shock absorber to cushion brain. |

