![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
39 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
ascending limb
|
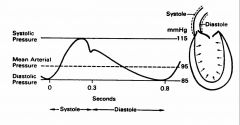
Aortic Pressure Wave
aortic wall distension occurs during the rapid ejection phase of the cardiac cycle represented on the graph as the ________. |
|
|
Maximum aortic ______= maximum extent of aortic wall distension.
|
pressure
|
|
|
________ marks the end of ventricular systole (aortic valve closure).
|
Dicrotic notch
|
|
|
________ refers to when the blood is forced through peripheral vessels as aortic walls recoil.
|
Diastolic runoff
|
|
|
Pressure progressively declines to the arterial ______ value, just prior to the next ejection.
|
diastolic
|
|
|
Arterial pressure is normally substantially ______ than ventricular pressure during ventricular diastole.
|
greater
|
|
|
Pulse pressure =
|
systolic pressure - diastolic pressure
|
|
|
Mean arterial pressure (Pa or MAP)=~
|
estimated as diastolic pressure plus 1/3 of the pulse pressure.
|
|
|
Compliance is a measure of the _______ of the vessel wall
|
"expandability”
|
|
|
slope
dV/dt |
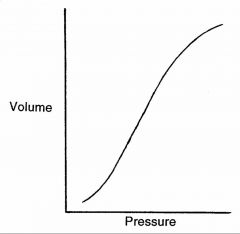
Arterial compliance (Ca) is the ____ of the pressure-volume curve at any point.
in other words Ca= |
|
|
Ca is not constant, but changes at very ___ or ___ pressure levels.
|
low
high |
|
|
Ca decreases progressively with ____ , especially at the higher pressures
|
age
|
|
|
Compliance is the reciprocal of _______. C.
|
wall stiffness
|
|
|
To compare vessels of different sizes or types, _________ is often used, rather than compliance
|
DISTENSIBILITY
|
|
|
distensibility =
|
% change in volume/ change in pressure
|
|
|
decreases
|
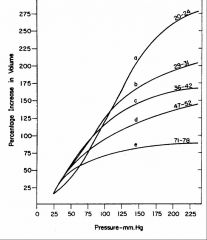
Increasing age progressively ________ the slopes of arterial pressure-volume curves
|
|
|
MAP depends directly upon the mean ____ of blood in the arterial system (Va), which determines how greatly the arterial walls are distended.
|
volume
|
|
|
Ca does NOT determine the final magnitude of changes in either ___ or ___ following changes in CO or TPR. (This may sound strange at first, but has been verified. And note that the statement applies to mean arterial volume and pressure, not the diastolic or systolic values.)
|
Va
MAP |
|
|
MAP =
|
CO•TPR
|
|
|
Mean arterial pressure (MAP) is directly proportional to mean arterial blood _____.
|
volume
|
|
|
Ca does NOT determine the final magnitude of changes in either ___ or ___ following changes in CO or TPR. (This may sound strange at first, but has been verified. And note that the statement applies to mean arterial volume and pressure, not the diastolic or systolic values.)
|
Va
MAP |
|
|
rate of change
|
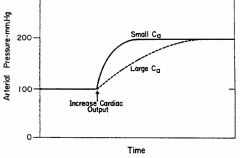
Ca influences only the _______ of Va and MAP following changes in CO (see figure below) or TPR.
|
|
|
the rate of change of MAP is _______ related to the magnitude of Ca.
|
inversely
|
|
|
Assuming arterial compliance (Ca) is constant, pulse pressure is _______ proportional to SV.
|
directly
|
|
|
Pulse pressure (systolic P-diastolic P) is _________to stroke volume
|
perportional
|
|
|
A consequence of hemorrhage is a decrease in SV. What is the expected effect of hemorrhage per se on pulse pressure (assuming no change in Ca or TPR
|
Decreases SV= decreased pulse P
|
|
|
Ca is the ___ of the pressure-volume curve
|
slope
|
|
|
Assuming SV is constant, pulse pressure is ______ related to Ca
|
inversely
|
|
|
One of the consequences of arteriosclerosis is a decrease in Ca. Assuming that no other factor changes, what would be the expected effect of arteriosclerosis on pulse pressure?
|
-increase
|
|
|
If all other factors remain constant, changes in TPR will cause systolic and diastolic pressures and MAP to change in the same direction, BUT _______ will not be changed (Fig. 6-14, left). I.e., TPR doesn’t directly determine ________
|
pulse pressure
pulse pressure. |
|
|
However, increases in TPR may result in a decrease in ____.
|
Ca
|
|
|
However, increases in TPR may result in a decrease in Ca. How will the latter affect pulse pressure
|
Inversely perportional, increase pulse pressure
|
|
|
c. In addition, an increase in TPR may result in a decrease in SV. How will the latter affect pulse pressure?
|
Perportional, decrease pulse presure
|
|
|
Therefore, changes in TPR may affect pulse pressure _______ because of changes in Ca or SV.
|
indirectly
|
|
|
Normally, pulse contours are progressively ______ as pressure changes are transmitted to peripheral arteries
|
distorted
|
|
|
When Ca is decreased (e.g. by arteriosclerosis), there is _____ peripheral distortion of the pulse contour
|
less
|
|
|
Pressure waves move _____ than the blood actually flows a given distance from the heart
|
faster
|
|
|
Pressure wave velocity is ______ related to Ca
|
inversely
|
|
|
How will progressive arteriosclerosis be expected to affect the velocity of pressure wave transmission?
|
Lower compliance—faster velocity
|

