![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
116 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Dye
|
Organic
Water soluble Creates a bond with fibres Most permanent form of textile dyeing |
|
|
Pigment
|
Insoluble therefore requires a binding agent.
|
|
|
What is the difference between DYE and PIGMENT?
|
Dye becomes one with the fibres(chemical bond), where as pigment just sits on top of the fibres.
|
|
|
Dye Lot
|
A batch of textile that was dyed in the same bath.
A lot of fabric dyed in the same solution ;) (each DYE LOT may produce slightly different colour results) |
|
|
Lab Dip
|
Just the dip!
A sample done by the dyeing lab. Meant to test out the dye. |
|
|
Colourfastness
|
How FAST the colour fades.
COLOURFASTNESS is GOOD - the textile holds it's colour well: it doesn't fade or bleed. COLOURFASTNESS is BAD - colour is not sticking around and is fading and bleeding all over the place! |
|
|
Metamerism
|

Two colours look the same under one type of light but not another.
Quite a mesmerizing effect ;) "meta" meaning "after" "merism" meaning "contrasting" |
|
|
Elastomer
|
Natural or Synthetic
At room temperature stretches twice it's length and bounces back to original length. Gggrreaaaat elasticity! |
|
|
Elastoester
|
Manufactured fibre
50% aliphatic polyether and 35% polyester(at least and measure by weight) |
|
|
What is the difference between ELASTOMER and ELASTOESTER?
|
Elastomer can be natural OR synthetic.
Elastoester is only synthetic (manufactured). To remember: Elastomer - shorter word = simpler = one Elastoester - longer word = complex = combination of 50% polyether and 35% polyester (at least) |
|
|
Elesterll-P
|
Bi-component of polyester
Stretch and recovery can vary. To remember: elesterLL-p = LL(double "L") = bi = Bi-component + bi = varies it's preference [ ;) ] = stretch can vary |
|
|
Lastol [Subclass]
|
Subclass of an elastic olefin
|
|
|
Spun Dyed
|
Dyed during the spinning process
Used on synthetic, filament, staple or yarn |
|
|
Stock Dyed
|
Fibres dyed in a "dye stock" BEFORE they are spun.
To remember: soup stock = the fibres are dyed in a dye soup OR think of stock as a quantity. |
|
|
Yarn Dyed
|
Dyed Yarn!
Yarn dyed after the yarn has been spun. |
|
|
Piece Dyed
|
A "piece" of cloth dyed after it has been woven or knitted into said "piece" of cloth
|
|
|
Union Dyed
|
Dyeing fabric made of a "union" of multiple types of fibres
|
|
|
Garment Dyed
|
This rarely looks good....
Dyeing the garment AFTER it has been constructed. |
|
|
Cross Dyed
|
A method of coloring fabric using the blend of fibres of which some have already been dyed.
|
|
|
Fluorescent Dye Class
|
Dye class that creates white fibres
Found in some laundry detergents - maintains the fluorescent white of the fibres |
|
|
Vat
|
Dyeing method of dyeing fabric in a vat(bath)
Best used on cotton and some polyester fibres. |
|
|
Spectrophotometer
|
Measures the amount of light reflected and absorbed by an object.
To remember : Spectro = Spectrum Photo = to make a record of Meter = to measure Measures the spectrum of light that an object reflects or absorbs. |
|
|
Acid Dye
|
Primarily used with natural protein fibres and nylon
|
|
|
Azoic Dye
|
Dye that is not actually directly applied as dye; it creates the dye within the fibre as a chemical reaction.
VERY colourfast! To remember: A-zoic = gets and "A" for colourfastness =because the colour is created WITHIN the fibre |
|
|
Cationic Dye
|
Used with acrylic fibres
Basic Dye Used to dye paper |
|
|
Developed, Direct Dye
|
Dye directly applied to fabric
Vibrant colours but washes out Simple to use = at home use |
|
|
Disperse Dye, Fluorescent
|
Water insoluble
Used to permanently dye polyester and acetate |
|
|
Mordant
|
Pre-treatment of metal salt
Used to improve colour absorption in natural fibres by bonding the dye with fibres |
|
|
Reactive Dye
|
Used [primarily] with natural fibres and rayon
Create a chemical bond(reaction) with cellulose fibre Good colourfastness! |
|
|
Sulfur Dyes
|
Used primarily with cotton
Made insoluble within the fibre by oxidation |
|
|
Grin Thru
|
Elastomeric fibres that break and "grin through" the fabric surface
|
|
|
Rubber [Neoprene]
|
Rubber comes from a tree = NATURAL fibre
|
|
|
Spandex [Lycra]
|
Manufactured Fibre - Man made
Consists of at least 85% segmented polyurethane |
|
|
Metallic Fibres
|
Manufactured (manmade) fibres
Made of metal or a core coated in metal(obviously!) Thin sheet of ALUMINIUM laminated on both sides with acetate or polyester |
|
|
Aramid [Kevlar/Nomex]
|
Manufacter fibre (manmade)
|
|
|
Glass
|
Manufactured Fibre
i.e.: Fibre Glass used for heat insulation |
|
|
Fluoropolymer (PTFE)
|
Manufactured
Strong resistance to solvents, acids and bases. To remember: FLUORO - Fluorescent = glow sticks = raves. People drop acid at raves and dance to heavy base. They are not bothered by acid or base = FLUOropolymer is also not bothered(strong resistance to bases, acids and solvents) ALSO : Contains at least 95% long chain polymer synthesized from aliphatic fluorocarbon polymers |
|
|
Stainless Steel
|
Metal that doesn't rust
|
|
|
Colourway
|

Ways in which colour can be used to create options for the same fabric.
Usually the colours of colour ways look well together or follow a theme. |
|
|
Strike Off
|
Test Length of Fabric
A length of fabric printed to test: pattern registration pattern repeat matching of shades in the design |
|
|
Photosensitive Dyes (LUMI)
|

Dyes sensitive to light(photo)
Dyes activated with sunlight or very bright light. The pattern areas are covered, then the fabric is exposed to light. Where the light hits, dye changes colour; covered areas remain a contrasting(previous) colour. (pic sample) |
|
|
Holographic
|

Appears to be 3D
You see it on cash all the time! Composed of layers of images(which gives it the 3D effect) |
|
|
Screen Printing aka Silk Screening
|

A screen marked with pattern.
The negative areas of the image are solid where as the positive ares are porous. A dye/pigment paste is pressed through the porous areas of the screen and is transferred onto the fabric in a pattern. |
|
|
Direct Printing
|
Colour is DIRECTLY applied to the fabric.
Example: painting with a brush directly onto a textile; stamping |
|
|
Discharge Printing
|

Process in which the dye is removed(discharged) from fabric, in a patten.
|
|
|
Resist Printing
|
a resist(solution, paste, gell etc.) is applied to the fabric in a pattern.
The fabric is then dyed where the dye does not affect the areas protected by the resistance of the resist! [much cleaner than discharge because the fibres have never been dyed] |
|
|
Heat Transfer Printing
|
Transferring a print onto a textile with help of heat.
The heat heats up the paint and helps it adhere to the textile like glue. [sits on top of the surface of the textile. Is prone to peeling/chipping off with wear] |
|
|
Foil Printing
|

Printing a pattern using foil and an adhesive.
Foil only sticks to the glue(administered in a pattern) |
|
|
Jet Printing
|
Colour application through a tiny jet in a pattern.
Like a colour jet printer. |
|
|
Engineered Print
|

The print is predetermined to appear in specific areas of the garment.
ie. Alexander McQueen (may his soul rest in peace) |
|
|
Duplex Print
|

Process in which BOTH(DU-plex) sides of the fabric are printed.
|
|
|
Burn Out Printing
|

Textile composed of two different fibres:
Mesh base (manufactured fibre) Fibres woven through the mesh made of organic fibres A chemical is applied in a pattern which eats away(BURNS) the natural fibres, leaving a lovely pattern. |
|
|
Flocking Printing
|
An adhesive is applied to a textile in a pattern
Then tiny fibres are poured on top of it - the fibres stick(FLOCK) only to the glue(in a pattern) The pile sits on top and cannot be seen on the other side of the fabric UNLIKE burn out fabrics. |
|
|
Bleeding
|
The dye bleeds(leaves) from the fabric.
Happens to dyes that are not chemically bonded to the fabric like DEVELOPED DYES (because they sit on top of the fibre) |
|
|
Crocking
|
![Colour that transfers with abrasion
[I can't think of anything to create this memorable :( ]](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/81/08/67/4810867_m.png)
Colour that transfers with abrasion
[I can't think of anything to create this memorable :( ] |
|
|
Migration
|
Dye migrates(shifts) from it's designated area to the surrounding areas of the textile.
Kind of like a bad mascara migrates down your eye after a long day. |
|
|
Fume Fading
|
Colour fades/changes when exposed to fumes (gases, pollutants)
|
|
|
Tendering
|
The fabric "tenders" or weakens when exposed to degradants
Degradants = acids, bleach.... anything that can eat away at fabric. |
|
|
Frosting
|

Happens when dye rubs off of the fabric because it has not penetrated into the fibres deep enough(just hangs out on top)
Happens to jeans a lot and they start looking "frosted" |
|
|
Out of Register
|

When print layers are not aligned properly
To remember: remember this shopping cart heading for the "register" to check out OR Register as in a musical tone = out of register = out of key |
|
|
Off Grain
|
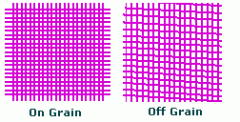
Warp and Filling yarns (weft) are not meeting at 90 degree angles
Happens a lot to muslin ( by the salvage). |
|
|
Off Shade
|
Fabric that is meant to be the same colour does not match shades.
Would happen with VAT and STOCK DYES because fabric is dyes in batches. You have probably seen with with some dollar store objects! |
|
|
Ombre
|

No need to explain!
|
|
|
BREAK TIME!!!
|
Option 1: Cat Vines
www.youtube.com/watch?v=4tzhyfWHdLo Option 2: Shake it with Beyonce! www.youtube.com/watch?v=pZ12_E5R3qc Option 3: Go eat something! www.yourfridge.kitchen |
|
|
Ikat
|

Certain yarns are treated with resist before woven into a fabric. Then the fabric is dyed - revealing a pattern through uncoloured yarns.
|
|
|
Finish
|
A finish applied to a fabric to complete it.
finish examples: fire retardant, waterproofing, anti-static, mercerizing |
|
|
Scouring
|
Finished step in which soil, excess chemicals or fibre coatings are removed.
Fabric that had a resist solution on it may be scoured to remove the resist chemicals after the printing process. |
|
|
Calendaring
|
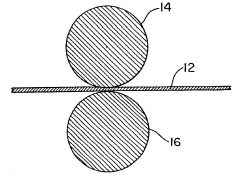
Finishing technique - fabric is passed between to cylinders to achieve an effect
The cylinders have grooves on them that press an "effect" onto the fabric. (not a pattern, but a finishing effect for the fabric) ie. Used on Moire to produce it's "watery" effect |
|
|
Cire
|

Finishing - high lustre
A thermoplastic fabric is calendared through one hot/one cold rolls. The hot roll melts one side of the fabric just enough to give it high lustre. |
|
|
Converter
|
A plant/factory that receives unfinished textiles and finishes(converts) them to be ready for use.
|
|
|
Bleaching
|
Process that uses bleach to lift colour or remove stains
Bleaching may cause TENDERING of fibres. |
|
|
Glazing
|
An agent is applied to the surface of the fabric, which then is heat pressed - resulting in a lustrous finish.
|
|
|
Moire
|

Fabric finish create through calendaring.
Pressing two unbalanced, shiny, plain weave fabrics together through CALENDARING. |
|
|
Singeing (to singe)
|
Applying high heat to manufactured fibre ends (like polyester) which melts the fibres.
Can be used to melt "fuzz" - creating a smoother surface |
|
|
Ammoniating
|
Finish that increases absorbency of cellulosic fibres
|
|
|
Tenter Frame
|
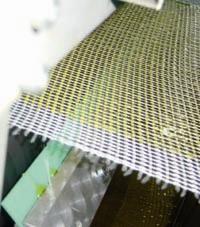
A "frame" that carries a textile through a heat finish.
It's purposed is to prevent the textile from shrinking during a finishing process. ie: A wool fabric would need support from a TENTER FRAME while going through a finishing process, otherwise it would just shrink and lose it's shape |
|
|
Schreiner
|
Schreinerizing fabric - etching fine lines on a fabrics surface
Creates subtle luster, may increase surface cover. To remember: Schre = shredder= shreds paper into strips(fine lines) |
|
|
Bio-Polishing
|
Bio - Natural
Polish - Finish An enzyme treatment for natural(cellulosic) fibres Used to produce a softer hand and to reduce pilling |
|
|
Mercerization
|
A finish
Sodium hydroxide used on cotton/hemp to increase absorbency, lustre and strength. |
|
|
Optical Brighteners
|
Chemical compound used to produce a white appearance; found in detergents to make whiter whites!
Same compound as used in Fluorescent Dyes! |
|
|
Embossing
|

Finish - Creates a 3D effect.
A CALENDARING effect. One of the rolls has a 3D, heated pattern which then is pressed into a synthetic fabric, permanently "melting" a 3D design. |
|
|
Desizing
|
Removing the physical or biological aids that helped the fabric retain it's shape during weaving.
|
|
|
Slashing
|
Preparing warp yarns with starch, resin or gelatinous substances to increase body and abrasion resistance.
This step will strengthen the yarn enough to survive a high speed weaving process - won't break, tangle, or tear. |
|
|
Sueding/Peach Skin
|
Rotating sandpaper "fuzzes" the textile surface to create a suede finish.
|
|
|
Napping
|
A wired brush is run over a textile surface to create a nap
Produces softer hand and better insulation. |
|
|
Shearing
|
Cutting away protruding fibres or yarns off the textile surface to ensure a levelled finish.
|
|
|
Brushing
|
Brush that removes unwanted fibre ends from the fabric's surface.
"BRUSHES" away the impurities |
|
|
Flocking
|

Short fibres are bonded to the surface of a fabric with an adhesive.
^here are some nails that have been flocked using the technique! |
|
|
Light Reflectant
|
A finish that reflects light in order to minimize colour fading from exposure to light.
|
|
|
Plisse
|

Effect that creates a permanently WRINKLED fabric.
Created with caustic soda paste - which unevenly shrinks and puckers the fabric. |
|
|
Seersucker
|

Made by slack-tension weaving process which puckers the fabric.
Has vertical crinkled stripes |
|
|
Stiffening Finishes
|
A finish that stiffens the fabric.
Creates resistance to bending or creasing ie. starching -the homemade method ;) |
|
|
Softeners
|
Softens the water - removes hardness ions from water
THUS Resulting in softer fabric |
|
|
Antimicrobial
|
Destroys or inhibits growth of disease causing microorganisms.
Probably good to use on hospital scrubs! |
|
|
Stonewash
|

Throwing a textile(commonly jeans) in a giant tumbler with stones.
Creates this effect ^ |
|
|
Acid Wash
|

Used on denim to create a visual effect
Achieved by wash with sodium hydrochloride bleach and pumice stones! |
|
|
Cellulase Wash
|
Enzymes are used to produce stone washing effect
Works by decomposing fibres |
|
|
Creping
|
Compacting process that softens fabric hand
|
|
|
Heat Reflectant
|
A finish that allows fibres to reflect heat.
Used in some awesome high tech over mitts btw! |
|
|
Antistatic
|
A compound added to the fabric's surface to reduce static.
Works by helping the fabric absorb moisture, conduct electricity and neutralize the buildup of static! |
|
|
Water Repellent
|
A finish that restricts water absorbency by fibres.
|
|
|
Water Proof
|
A fabric coating that eliminates gaps and prevents water from being absorber by the fabric(entirely)
|
|
|
Difference between water PROOF and water REPELLENT ?
|
Proof - roof - No water penetration AT ALL.
Repellent - repels water, but some may come through the surface of the fabric. |
|
|
Flame Retardant
|
Finish
Makes fabric resistant to combustion/catching on fire. ie: firefighting suits |
|
|
Moth Proofing
|
Finish used on moth delicatessen such as wool.
Repels the bugs, thus preventing them from feasting on your sweater. |
|
|
Parchmentizing
|
Acid finish
Used on cotton Produces fabric with a crisper/stiffer hand (kinda makes cotton feel like stiff linen) |
|
|
Relaxation Shrinkage
|
Fabric warping from excessive tension on it during the production process.
|
|
|
Compressive Shrinkage Control
|
Finish that removes stress from weaving and previous finishes applied to fabric.
|
|
|
Durable Press
|
Finish that improves the durability of the fabric.
Maintains wrinkle free appearance during use and care. |
|
|
Heat Set
|
When a fibre, yarn or fabric is "set" with heat.
The stability of the fabric or a texture/design feature is made permanent with heat. |
|
|
Wrinkle Free
|
Feature of fabric that minimizes wrinkling
Created trough a finishing process |
|
|
Soil Release
|
Coating used on fabrics to repel soil absorption into the fibres.
The finish makes it easier to remove soil during laundering. |
|
|
Stain Repellency
|
Finish that prevents unwanted substances from penetrating the fibres
Makes the stain sit on top of the fabric Fluorochemicals or silicone base finishes |
|
|
London Shrinkage
|
Process that relaxes wool fabrics
|
|
|
Encapsulation/Phase Change
|
Microcapsules that balance temperature
Applied to textiles to level(high/low) outer temperatures to make the wearer more comfortable. |
|
|
Halogenation
|
Wool finish.
Dissolves fibre scales in order to produce a washable fabric. |

