![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
59 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Patient complaining of Acute pelvic pain, Vaginal bleeding, + HCG, Adnexal mass? Two possibilities?
|
1. Ectopic Pregnancy
2. Intraperitoneal fluid |
|
|
What are the four different ways that a placenta is graded? Describe all?
|
1. Grade 0= Smooth chorionic plate, Normal texture.
2. Grade 1= Subtle indentations, homogeneous, shows some calcifications. 3. Grade 2= Mild to medium sized indentations in the chorionic, comma like densities, basal echoes. 4. Grade 3= Indentations in the chorionic plate that extend to the basal layer, may contain both highly echogenic and anechoic areas, irregular densities, lacunae. |
|
|
In a pregnancy what structure is seen first?
|
The yolk sac
|
|
|
At which week do you first see a fetal heart beat? How big should the gestatianal sac be?
|
1. 6th week
2. 4mm |
|
|
When there is a retention of a dead fetus, when the fetus dies but is retained within the uterus, what has occurred?
|
Missed abortion - usually before the 13th week
|
|
|
At what range of weeks does the fusion of the amnion and chorion occur?
|
12 to 16 weeks
|
|
|
What are the four placental positions related to placenta previa?
|
1. Low lying
2. Marginal 3. Partial 4. Complete or total |
|
|
True or False? CRL is not considered an accurate measurement?
|
FALSE
|
|
|
Which line is closest to the sac?
|
Decidua Capsularis
|
|
|
What is the most common cause of vaginal bleeding, unplanned abortion(miscarriage) of the fetus and gestational sac before 23 weeks gestation?
|
Spontaneous Abortion
|
|
|
What are the two layers of the double sac sign?
|
Decidua capsularis and Decidua parietalis(Vera)
|
|
|
What is the difference between a fetal heart rate and a maternal heart rate?
|
Fetal heart rate is twice as fast
|
|
|
What is the amniotic fluid produced by?
|
Fetal kidneys
|
|
|
In the fetal heart, what alows blood to flow from right to left atrium? What happens to this after some time?
|
Foramen Ovale, eventually it will close
|
|
|
Cross-sectional anatomy of the fetal head should be defined at the varying levels, starting at the level of what? And name the structures going inferiorly?
|
Lateral Ventricles. Thalamus, lateral ventricles, third ventricle, CSP, sylvian fissures, cerebral hemispheres, the vermis of the cerebellum, and the cisterna magna.
|
|
|
What are two common sites for an ectopic pregnancy?
|
Fallopian Tubes and abdomen
|
|
|
20 year old female, severe pelvic pain, no LMP's, right side pain, what is not one of them?
|
A. Ectopic pregnancy
B. Spontaneous Abortion C. Hytitadid Form Mole D. Fibroids |
|
|
What hormone causes ovulation?
|
LH
|
|
|
What are the three layers of the Meninges? Which one is more vascularized?
|
Dura Mater, Arachnoid Layer, Pia Mater. Pia Mater is the most vascular.
|
|
|
Which hormone is secreted by a growing follicle that helps the endometrial layer to regenerate?
|
Estrogen
|
|
|
The zygote or cell mass repeatedly divides and eventually forms a cluster of? Resembles a berry?
|
Morela
|
|
|
What connects the third and fourth ventricle?
|
Aquadect of sylvius
|
|
|
Where does the fetus implant?
|
Chorium frondosum
|
|
|
The cephalic index should be between what two measurements?
|
0.72 to 0.86
|
|
|
What is the most acurate measurement for dating GA?
|
CRL
|
|
|
Lateral ventricles are divided into five regions, what are they?
|
1. Frontal horns
2. Lateral bodies 3. Occippital horns 4. Temporal 5. Atria |
|
|
Fetal heart activity should be detected by what week?
|
6 week
|
|
|
Hydatidiform mole causes everything except this?
|
A. Bleeding
B. Vomiting C. Enlarged Uterine size for dates D. HCG titer is very high E. May develop a neoplasm F. Benign tumor |
|
|
What is the common site for spinal defects?
|
Lumbar
|
|
|
A mass may be seen at the cord insertion site which is phisiological omphaloceles and herniates at what weeks?
|
8 to 12 weeks
|
|
|
T or F Methotrexate can treat an ectopic pregnancy?
|
False- there is no treatment for it.
|
|
|
Mean sac diameter, if more than 17mm and no fetal pole is seen what is the diagnosis?
|
Blited Ovum
|
|
|
34 year old female, pregnant, increased blood pressure, bleeding, and vomiting. This is a sign for?
|
Hydatitid Form Mole
|
|
|
To rule out an ectopic pregnancy, in an US diagnosis which two things should not be there?
|
Gestational sac and adnexal mass
|
|
|
How often should the fetal bladder empty?
|
30 to 45 minutes
|
|
|
The LS ratio determines what?
|
Lung Maturaty
|
|
|
What function does amniotic fluid have?
|
Permits cemetric growth of embyo, prevents adhesions from forming, cushions the embryo or shock absorber, helps prevent infections; allows for normal development of resperitarory, GI, and bone system; and a source of nutrients for the developing embryo.
|
|
|
What structures develop from the neurotube?
|
The brain and spinal cord
|
|
|
What 4 structures will develop from the hind brain or rombencephalon?
|
1. Medulla
2. Adult pons 3. Develops the fourth ventricle 4. Cerebellum |
|
|
The alimentary canal forms during the fourth week and divides into what three structures?
|
1. Fore gut
2. Mid gut 3. Hind gut |
|
|
What is an early sign of pregnancy?
|
Yolk sac- seen by the fourth week
|
|
|
In ultrasound what is the bladder considered?
|
Acoustic Window
|
|
|
What two things combine at the gestational sac, it appears hyperechoic and thick due to developing placental tissue?
|
1. Decidua Basalis
2. Chorion Fondosum |
|
|
What are the three layers of a pregnant womans gestational sac?
|
1. Decidua Basalis
2. Decidua Capsularis 3. Decidua Parietalis |
|
|
Amniotic Band Syndrome
|
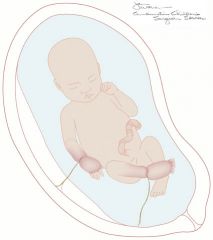
What syndrome has bands within the amniotic fluid adhere to the fetus and amputate portions of limbs?
|
|
|
Arnold-Chiari Malformation (Type II)
|
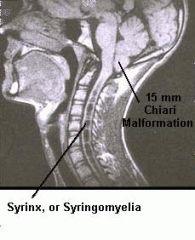
Low position of the cerebellum in the upper cervical spinal canal due to cord tethering. Associated with "lemon" skull shape, banana shaped cerebellum, and hydrocephalus?
|
|
|
Fluid Filled space at the back of the head that lies between the cerebellum and the skull?
|
Cisterna Magna
|
|
|
What sign has a change in the shape of the cerebellum (it becomes curved) that occurs in the presence of spina bifida?
|
Banana Sign
|
|
|
Which is not an indication of fetal hydrops?
|
1. Oligohydramnios
2. Polihydramnios 3. Fetal edema 4. Ascites 5. Pleural and pericardial effusion |
|
|
Normal ventricle measurements should not be greater than?
|
10mm
|
|
|
Fetal structures from the hind gut includes all except for?
|
1. Distal colon
2. Rectum 3. Portions of the bladder 4. Small intestines |
|
|
How many types of spontaneous abortions?
|
1. Threatend abortion
2. Incomplete abortion 3. Blited Ovum 4. Inevitable abortion 5. Septic abortion 6 All of the above |
|
|
When does an ectopic pregnancy rupture, what week?
|
8 to 10 weeks
|
|
|
How do you check for an abdominal pregnancy?
|
Superior to the uterus, and lies close to the wall.
|
|
|
What does PARA stand for?
|
1. P = Positive pregnancies
2. A = Aborted pregnancies 3. R = Premature pregnancies 4. A = Total number of full term pregnancies |
|
|
A small degree or dilatation of the central sinus echoes is permissable if a normal variant?
|
5 <-
|
|
|
Extra ovarian adnexal mass with thick echogenic border, this finding is suspecious for ectopic pregnancy, an example of?
|
Adnexal Ring
|
|
|
The BPD along with FOD is utilized to calculate what?
|
Cephalic Index
|
|
|
What is the most common fetal intracranial anomaly?
|
Anencephaly
|

