![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
70 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What two portions is the respiratory system divided into?
|
Conducting Portion
Respiratory Portion |
|
|
Where is the Conducting Portion?
|
From nasal cavity through the terminal bronchioles.
|
|
|
Where is the Respiratory Portion?
|
From respiratory bronchioles through alveoli.
|
|
|
What are the main functions of the Conducting Portion?
|
To clean, moisten and warm the air before it gets to the Respiratory Portion.
|
|
|
Much of the conducting portion is lined with _____ epithelium which is really a _____ epithelium with ____ cells.
|
Respiratory Epithelium
Pseudostratified Ciliated Columnar Goblet cells |
|
|
What are the five types of cells in the respiratory epithelium?
|
1. Pseudostratified Ciliated Columnar cells
2. Goblet cells 3. Basal cells 4. Small granule (K) cells 5. Brush cells |
|
|
What are Basal cells and where would you find these?
|
These are found in the Respiratory Epithelium. They are small and round and differentiate into the other cell types.
|
|
|
Small Granule (K) Cells
Where? Function? |
Neuroendocrine cells of the Respiratory Epithelium
May effect goblet cell mucous secretion and ciliary activity. |
|
|
These cells of the Respiratory Epithelium have microvilli and are thought to be a type of chemoreceptor.
|
Brush cells
|
|
|
Underlying the respiratory epithelium and the basement membrane is a layer of CT called the ____.
|
Lamina Propria
|
|
|
What two portions is the respiratory system divided into?
|
Conducting Portion
Respiratory Portion |
|
|
Where is the Conducting Portion?
|
From nasal cavity through the terminal bronchioles.
|
|
|
Where is the Respiratory Portion?
|
From respiratory bronchioles through alveoli.
|
|
|
What are the main functions of the Conducting Portion?
|
To clean, moisten and warm the air before it gets to the Respiratory Portion.
|
|
|
Much of the conducting portion is lined with _____ epithelium which is really a _____ epithelium with ____ cells.
|
Respiratory Epithelium
Pseudostratified Ciliated Columnar Goblet cells |
|
|
What are the five types of cells in the respiratory epithelium?
|
1. Pseudostratified Ciliated Columnar cells
2. Goblet cells 3. Basal cells 4. Small granule (K) cells 5. Brush cells |
|
|
What are Basal cells and where would you find these?
|
These are found in the Respiratory Epithelium. They are small and round and differentiate into the other cell types.
|
|
|
Small Granule (K) Cells
Where? Function? |
Neuroendocrine cells of the Respiratory Epithelium
May effect goblet cell mucous secretion and ciliary activity. |
|
|
These cells of the Respiratory Epithelium have microvilli and are thought to be a type of chemoreceptor.
|
Brush cells
|
|
|
Underlying the respiratory epithelium and the basement membrane is a layer of CT called the ____.
|
Lamina Propria
|
|
|
What is the name for the anterior part of the nasal cavity?
|
Vestibule
|
|
|
In the nasal cavity, coarse hairs called ___ filter the larger particles.
|
Vibrissae
|
|
|
The epithelium of the nasal cavity begins as ____ in the anterior vestibule and then changes to a ____ further on.
|
Stratified Squamous keratinized
Stratified Squamous Non-keratinized |
|
|
The lateral of the nasal cavity have three bony projections called the ___, ____, and ___, to increase surface area.
|
Superior Conchae
Middle Conchae Inferior Conchae |
|
|
The inferior and middle conchae are covered with a ____ epithelium. The superior conchae is covered with a _____ epithelium.
|
Respiratory epithelium
Olfactory epithelium |
|
|
Where would you find swell bodies?
|
The lamina propria of the respiratory epithelium lining the inferior and middle conchae.
|
|
|
Where are the receptors for smell located?
|
Located in the olfactory epithelium that lines the superior conchae.
|
|
|
What are the three cell types of the olfactory epithelium?
|
1. Sustentacular cells
2. Basal cells 3. Olfactory cells (bipolar sensory neurons) |
|
|
Olfactory cells are what type of neurons?
|
Bipolar sensory neurons
|
|
|
Olfactory Cells (bipolar sensory neurons)
The cilia at the apex of these cells act as receptors for ____. The axons of these cells form ____ that carries olfactory information into the CNS. |
Chemical Stimuli
Cranial Nerve 1 (Olfactory Nerve) |
|
|
Where would you find Bowman's Glands and what type of secretion do these have?
|
Under the olfactory epithelium
Mostly serous |
|
|
Paranasal Sinuses are lined with a thin _____. Their secretions are moved into the nasal cavity by ____.
|
Respiratory Epithelium
Cilia |
|
|
The nasopharynx is lined with ____ epithelium.
|
Respiratory Epithelium
|
|
|
Oropharynx:
Because it is also part of the digestive system, it is subject to ____. It is lined with ____ epithelium. |
abrasion
stratified squamous nonkeratinized |
|
|
The larynx is responsible for ____. The epithelium is mainly a ____.
|
voice production
respiratory epithelium |
|
|
The lamina propria of the respiratory epithelium of the larynx contains _____ glands and ____.
|
muco-serous glands
cartilages |
|
|
What type of cartilage makes up the laryngeal cartilages?
|
Hyaline (the large cartilage)
Elastic (the smaller cartilages) |
|
|
During swallowing, the larynx is pulled ____. The epiglottis is pushed ____.
|
The larynx is pulled up beneath the back of the tongue.
The epiglottis is pushed backward by the tongue and serves as a cap over the laryngeal inlet. |
|
|
What kind of epithelium covers the epilottis?
|
Upper part is stratified squamous nonkeratinized epithelium.
Lower surface is respiratory epithelium. |
|
|
The lamina propria of the epiglottis contains ____ glands and ___ cartilage.
|
Muco-serous glands
Elastic |
|
|
Below the epiglottis are two sets of folds of mucous membranes. The upper set is the ____. The lower set is the ____.
|
False Vocal Cords
True Vocal Cords |
|
|
What epithelium lines the:
False Vocal Cords True Vocal Cords |
Respiratory Epithelium
Stratified Squamous Nonkeratinized Epithelium |
|
|
The lamina propria of the False Vocal Cords contains ____. THe lamina propria of the True Vocal Cords contains ____.
|
Muco-serous glands
Vocal ligaments and vocalis muscle. |
|
|
What is the function of the vocalis muscle?
|
It produces different voice frequencies by varying the tension of the true vocal cords.
|
|
|
The vocal cords are devoid of _____ which delays the spread of cancer.
|
Lymphatics
|
|
|
What hapens to the vocal cords during coughing?
|
The TRUE vocal cords are first adducted (close together) to raise the intrathoracic pressure. Then they are suddendly abducted resulting in the sudden release of the compressed air.
|
|
|
What can cause voice impairment in laryngitis?
|
Edema of the mucous membrane (mucosa) covering the vocal cords.
|
|
|
The lining of the trachea is ____ epithelium.
|
Respiratory Epithelium
|
|
|
The lamina propria of the trachea contains ____ glands and ____ cartilages.
|
Muco-serous glands
C-shaped hyaline cartilage rings |
|
|
What muscle lies between the ends of the C-shaped cartilages of the trachea? What is its function here?
|
Trachealis Muscle
It allows the tracheal lumen to constrict during coughing to help make the air exit more forcefully. |
|
|
What type of ligament connects the ends of the C-shaped cartilages of the trachea? What is its function?
|
Fibroelastic Ligament
prevents over distension of the trachea |
|
|
The Primary Bronchi are similar in structure to the trachea except that ___?
|
The cartilage rings are complete now, rather than C-shaped.
|
|
|
What type of epithelium lines the bronchi?
|
Respiratory epithelium
|
|
|
The lamina propria of the bronchi contains ___ glands, ____ fibers, and _____ muscle that spirals around the bronchi.
|
Muco-serous glands
Elastic Fibers Smooth Muscle |
|
|
Bronchioles have a diameter of less than ___ mm.
|
5 mm
|
|
|
What type of epithelium covers bronchioles?
|
Simple ciliated columnar or cuboidal
|
|
|
The lamina propria of the bronchioles and terminal bronchioles has what features? What does it lack?
|
Has elastic fibers and smooth muscle.
Does NOT have glands or cartilage. |
|
|
Bronchioles
PSNS stimulation causes? SNS causes? |
PSNS- (Vagus Nerve) decreases the diameter of bronchioles
SNS- (Epi) increases the diameter |
|
|
These denote the end of the conducting portion of the respiratory system.
|
Terminal bronchioles
|
|
|
What epithelium covers the terminal bronchioles?
|
Simple ciliated columnar to cuboidal
|
|
|
Where would you find Clara cells?
|
In the epithelium of the terminal bronchioles and the respiratory bronchioles.
|
|
|
What is the function of Clara cells?
|
They have secretory granules of surfactant to lower surface tension. Also may detox pollutants and serve as cell progenitors.
|
|
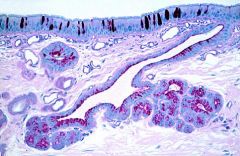
What type of epithelium is this?
|
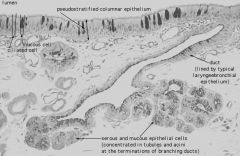
Pseudostratified columnar
Respiratory Epithelium |
|
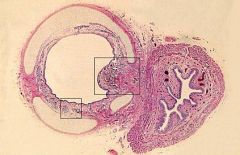
What is the structure on the left?
What is the cartilage shown? |
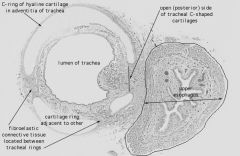
Trachea
Hyaline Cartilage |
|
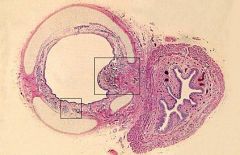
What is the structure on the left?
What is the cartilage shown? |
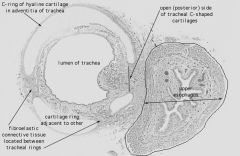
Trachea
Hyaline Cartilage |
|
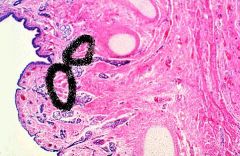
This is the trachea.
What is circled? |
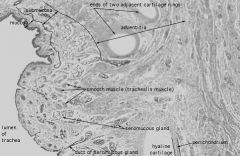
Trachealis Muscle
|
|
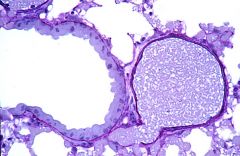
What type of cells are lining the bronchiole seen here?
|
Clara cells
|
|
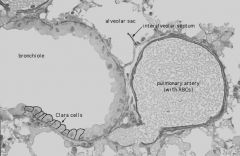
What is the structure in the middle? What surrounds it?
|
Bronchiole
Alveoli |
|
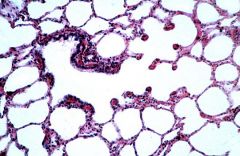
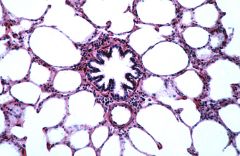
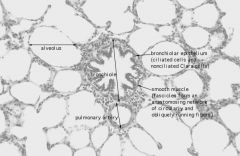
Identify the:
Bronchiole Terminal Bronchiole Alveoli Alveolar Ducts |
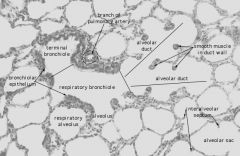
Respiratory Bronchiole
Terminal Bronchiole Alveoli Alveolar Ducts |
|
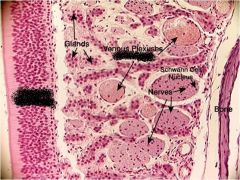
What is the epithelium on the left?
How can you tell? |
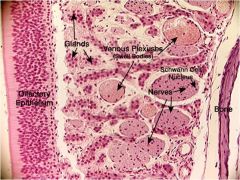
Olfactory epithelium
There are swell bodies present |

