![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
75 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Metabolism |
The totality of an organisms chemical reactions |
|
|
Metabolic Pathways |
Begins with a specific molecule and ends with a product.
Each step is catalyzed by an enzyme |
|
|
Catabolic Pathways |
Release energy by breaking down complex molecules into simpler compounds. |
|
|
Cellular Respiration |
The breaking down of glucose in the presence of Oxygen.
This is an example of pathway of catabolism. |
|
|
Anabolic Pathways |
Consume energy to build complex molecules from simpler ones.
The synthesis of a protein from amino acids is an example of this. |
|
|
Bioenergetics |
Is the study of how organisms manage their energy resources. |
|
|
Energy is... |
The capacity to cause change. |
|
|
Kinetic Energy |
Energy associated with motion. |
|
|
Heat (Thermal Energy) |
Is kinetic energy associated with random movements of atoms or molecules. |
|
|
Potential Energy |
Is energy that matter possesses because of its location of structure. |
|
|
Chemical Energy |
Is potential energy available for release in a chemical reaction. |
|
|
Thermodynamics |
Is the study of energy transfer |
|
|
Is an organism an open or closed system? |
An organism is an open system. |
|
|
1st Law of Thermodynamics (The Principle of Conservation of Energy) |
Energy can be transferred of transformed, but it can not be created of destroyed. |
|
|
2nd Law of Thermodynamics |
Every energy transfer or transformation increases the entropy (disorder) of the universe. |
|
|
Free Energy |
More free energy = Less stable, more ability to do work.
Less free energy = More stable, less ability to do work. |
|
|
Exergonic Reaction |
Proceeds with a net release of free energy and is spontaneous.
Delta G < 0 |
|
|
Endergonic Reaction |
Absorbs free energy from its surrounding and is nonspontaneous
Delta G > 0 |
|
|
3 Types of Cell Work |
1) Mechanical 2) Transport 3) Chemical |
|
|
Energy Coupling |
Using an Exergonic process to drive an Endergonic process.
Overall this is an Exergonic process |
|
|
ATP (adenosine triphosphate) |
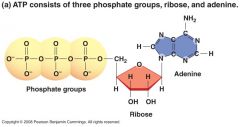
Cell's Energy shuttle
Is composed of ribose (a sugar), adenine (a nitrogenous base), and three phosphate groups.
|
|
|
Hydrolysis of ATP |
The release of energy comes from the chemical change to a lower state not from the broken phosphate bonds. |
|
|
The Regeneration of ATP |
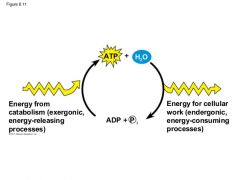
|
|
|
Catalyst |
A chemical agent that speeds up a reaction without being consumed by the reaction. |
|
|
Enzyme |
Is a catalytic protein. |
|
|
Active Energy |
The initial energy needed to start a chemical reaction is called this. |
|
|
How do enzymes lower the active energy (Ea) barrier? |
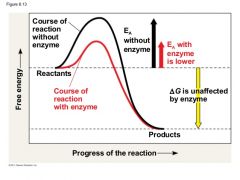
Enzymes lower the Ea
Enzymes do not affect the change in free energy. |
|
|
What is a substrate? |
The reactant that an enzyme binds on. |
|
|
What is the active site? |
the region on the enzyme where the substrate binds. |
|
|
Enzymes and substrate cycle.
What can affect this cycle? |
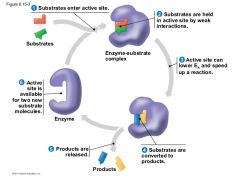
Changes in pH
changes in temp. |
|
|
What are cofactors? |
They are nonprotein enzyme helpers like vitamins and metals.
There can be organic cofactors called (coenzymess) or inorganic cofactors. |
|
|
What is the difference between competitive inhibitors and noncompetitive inhibitors?
(e.g.) Poisons, toxins, pesticides, and antibiotics. |
Competitive inhibitors bind to the active site. This competes with the substrate.
Noncompetitive inhibitors bind to another region on the enzyme causing it to change the shape of the active site. |
|
|
Describe the cycle of energy in our ecosystem. |
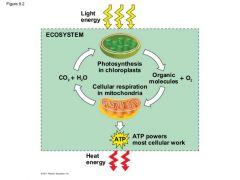
|
|
|
Is the breakdown (catabolism) of organic molecules exergonic or endergonic? |
Exergonic |
|
|
Define Fermentation: |
It is the partial degradation of sugars that occurs without O2 |
|
|
Define Aerobic Respiration |
Consumes organic molecules and O2, then yeilds ATP |
|
|
What does cellular respiration refer to: Aerobic or anaerobic respiration? |
Both.
But usually refers to aerobic. |
|
|
What are the three fuel sources for cellular respiration? |
Carbohydrates, fats, and proteins (amino acids). |
|
|
How do the catabolic pathways that decompose glucose and other organic fuels yield energy? |
The transfer of electrons during chemical reactions releases energy stored in organic molecules.
This energy is used to synthesize ATP. |
|
|
What are chemical reactions that transfer electrons between reactants called? |
Redox reactions or oxidation-reduction reactions. |
|
|
What happens to a substance during oxidation? |
It loses electrons or H. This is known as oxidation.
OIL Oxidation is losing. |
|
|
What happens to a substance during reduction? |
The substance gains electrons or H.
Positive charge is reduced.
RIG Reduction is gaining. |
|
|
What is a reducing agent? |
The donor that gives and electron |
|
|
What is a oxidizing agent? |
The electron receptor. |
|
|
What is the difference between NAD+ and NADH? |
NAD+ is an electron receptor and an Oxidizing agent during cellular respiration.
NADH represents stored energy that is tapped to synthesize ATP |
|
|
Where does NADH take the electrons? |
To the electron transport chain! |
|
|
Is the electron transport chain a controlled or explosive reaction?
What pulls the electrons? |
Controlled.
O2 |
|
|
During cellular respiration, what route to the electrons take? |
Glucose > NADH > Electron transport chain > Oxygen. |
|
|
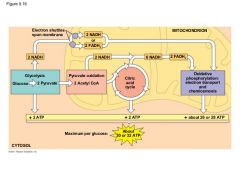
The 3 stages of cellular respiration: |
1) Glycolysis 2) Citric Acid Cycle (Kreb Cycle) 3) Oxidative Phosphorylation |
|
|
Define Glycolysis: |
Breaks down glucose (6C) into two molecules of pyruvate (3C) |
|
|
Define the Citric Acid Cycle: |
Completes the breakdown of glucose. |
|
|
Define Oxidative Phosphorylation: |
Accounts for most of the ATP synthesis.
Generates 90% of the ATP through redox reactions. |
|
|
For each molecule of glucose degrades to CO2 and water by respiration the cell makes up to ____ molecules of ATP |
32 molecules of ATP. |
|
|
Glycolysis "Sugar splitting"
What does it do? Where does it take place? What are it's phases? Can it happen with or without Oxygen? |
Breaks glucose into two molecules of pyruvate. Occurs in the Cytoplasm. Energy investment phase, and energy pay off phase. It can occur with or without O2. |
|
|
Energy investment phase |
The cell spends 2 ATP to break up glucose |
|
|
Energy pay-off phase |
ATP is produced by substrate-level phosphorylation. |
|
|
After Glycolysis what is the net product? |
2 ATP 2 NADH 2 Pyruvate + Water and heat |
|
|
What does Pyruvate need to enter the Mitochondrian? And what happens to the Pyruvate there? |
It requires O2.
Oxidation will occur. |
|
|
The Oxidation of Pyruvate to Acetyl CoA |
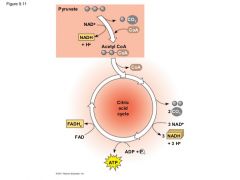
Net 2 NADH |
|
|
Where does the Citric Acid Cycle take place? |
The matrix of the Mitochondria. |
|
|
The Citric Acid Cycle produces what net total? |
2 ATP 6 NADH 2 FADH2
Per Molecule of glucose. |
|
|
Going into the Citric Acid Cycle, What two molecules get combined? |
Acetyl CoA & oxaloacetate
Together they for Citrate. |
|
|
Citric Acid Cycle Diagram: |
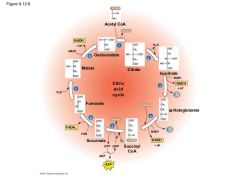
Step 3: NADH Step 4: NADH Step 5: ATP Step 6: FADH2 Step 8: NADH |
|
|
What carries electrons to the Electron Transport Chain to produce the majority of ATP later on? |
NADH & FADH2 |
|
|
Where is the ETC located? |
The inner membrane. The Cristae |
|
|
1 NADH yields ____ ATPs
1 FADH2 yields ____ ATPs |
NADH = 3 ATPs
FADH2 = 2 ATPs |
|
|
Electrons pass through proteins including ___? |
Cytochromes. |
|
|
Does the ETC actually produce any ATP? |
No only ATP Synthesis does. |
|
|
What do proteins in the ETC do? |
They pump H+ from the matrix into the intermembrane space. |
|
|
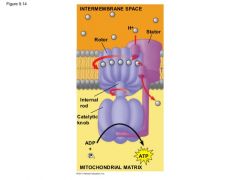
Where does the H+ go once it is in the intermembrane space? |
It floats over to the ATP Synthase. |
|
|
What does the ATP Synthase do with all the H+? |
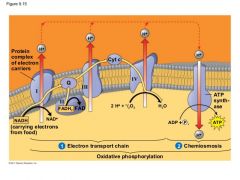
|
|
|
ATP Synthase |
|
|
|
Cellular Respiration |
|
|
|
How many ATPS does Areaobic Respiration create vs. Fermentation? |
32 ATPS to 2 ATPS |
|
|
Photosynthesis |
Photosynthesis |

