![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
338 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Professional Qualifications for Firefighters |
NFPA 1001 Chapter 6, Section 6.4.2 |
|
|
Operations and Training for Technical Search and Rescue |
NFPA 1670 |
|
|
Professional Qualifications for Technical Rescuers |
NFPA 1006 |
|
|
Areas where assistance can be useful are; |
1. Sizing up the initial incident upon arrival. |
|
|
Water is governed by _______ _______ that impact its movement. |
Physical Laws |
|
|
Directions of waterways |
1. Upstream |
|
|
The right side of the river as one is looking downstream. |
River right |
|
|
The left side of the river as one is looking downstream. |
River left |
|
|
Water moves in a ________ ________. |
Laminar flow. |
|
|
Water near the shore moves _________. |
Slower. |
|
|
Water near the shore moves in a ________ flow. |
helical |
|
|
Water near the shore is pulled to the _______ of the waterway and _____ _____, returning to the shore in a _______ motion. |
Middle, dives down, corkscrew motion. |
|
|
Water near the center moves ________. |
faster. |
|
|
When water encounters a curve, it tends to _______ _______ material, which undermines the banks. |
Carry away |
|
|
The fastest moving water is found in the ______ of the stream and moves to the ______ of the curve. |
Middle, outside |
|
|
The slowest moving water is found at the _____ of a turn. This creates an _____ effect called a ______ _______. |
Inside, eddy, shore eddy. |
|
|
Calm areas separated from the main current flowing down stream. |
Eddies |
|
|
An obstacle upstream from it breaks the current and gentle reversing current is developed. |
Eddies |
|
|
This is where debris and victims can be found. |
Eddies |
|
|
Safe refuge for rescuers. |
Eddies |
|
|
This has the greatest influence on the look of a waterway. |
Water level. |
|
|
These cause a swelling on the surface, which is an indication of an obstacle below. |
Obstructions |
|
|
Protruding obstacles cause the water to part in a ___ pointing _______. |
V, upstream. |
|
|
Indicates an obstruction to avoid. |
Obstructions |
|
|
When water flows over a steep vertical drop, the force of the water creates a _______ just downstream of the drop. |
Depression *vertical drops |
|
|
The depression can get so deep that water normally flowing downstream is forced to _______ ________ ________ to fill the hole. |
Move back upstream *vertical drops |
|
|
Gravity has overcome the force of the current. |
Vertical drops |
|
|
Vertical drops set up a continuous recycling of the water we call... |
A hydraulic, or hole. |
|
|
The line where the recycling water is separated from the main downstream current is called a _______ _______. |
Boil line. |
|
|
Water from vertical drop is quite ________ and buoyant objects may not float well. |
turbulent |
|
|
Safety considerations for Low-head dams: (1) Do not place rescuers ________ from these dams unless they are well trained. (2) Avoid area where __________ are located, usually near bridge abutments, trees, fencing, and the like. (3) Avoid _______ _______ areas. (4) Be aware that _______ _______ that can occur in mountainous, desert or commercial areas due to intense monsoon storms or areas prone to hurracaines. |
1. upstream 2. strainers 3. shallow rock 4. flash flooding |
|
|
Man-made vertical or near vertical drop structures that stretch across a waterway. |
Low head dams |
|
|
This causes anyone to be forced to the bottom of the waterway until they reach the ______ ______, where they are brought to the surface and pulled back upstream where the process happens again. |
Boil line |
|
|
Escape from a low head dam is not possible unless a rescue is accomplished from the _______. |
Shore |
|
|
Basic equipment that rescuers should have are the following; |
1. Personal flotation devices. 2. Foam collar. 3. Whistle. 4. Rescue Knife. 5. Rescue helmets. 6. Safety shoes. 7. Throw bags. |
|
|
Type III / V US Coast Guard approved. Designed to keep a person upright and tilted slightly back in the water. |
Personal flotation devices |
|
|
Designed to keep a person's head out of the water. |
Foam Collar |
|
|
Used for communications and as a warning device. |
Whistle |
|
|
Aid in disentangling a rescuer. |
Rescue knife |
|
|
Rescue Helmets are _______, and provide less ______ than structural firefighting helmets. They also provide ______ _______ protection. |
Lighter, drag, full head. |
|
|
_______ ________ work better in water rescue operations then firefighter work boots. They are _________, and less prone to __________________________________. |
Running shoes, lighter, slip on wet surfaces. |
|
|
A very versatile tool in rescue. Foam floatation rings are sewn into the bottom. |
Throw bags |
|
|
A rope of _______ ________ or _________ is stuffed into the bag, which allows it to float on the surface. |
Blended nylon or polypropylen. |
|
|
The throw bag is tossed to a victim from the shore using a __________ _________ with the rope paying it out as it goes. |
Pendulum swing |
|
|
Typically the best throwing distance for a throw bag is usually about _____ to _____ ft. |
40 to 60 ft. |
|
|
Once the victim has the bag, the rescuer can pull them to shore using ____ _____ _____ _____ ______. |
the rope from the bag. |
|
|
With submerged victim rescues, the initial action of an IC is to _______ ___ ______ _______. Additional resources can be _________. |
Dispatch a dive team. Helicopters. |
|
|
What should be done if a victim cannot be immediately spotted in deep water? |
1. Request dive teams and get an estimated time of arrival (ETA). 2. Establish a point last seen (PLS). |
|
|
Use the PLS as a basis for starting a ________ ________. |
Perimeter search. |
|
|
If victim went down in calm water their location can be based on _____________________________. |
Witnesses on the shore. |
|
|
Use the _____ ______ _______ as the PLS. |
Last visual contact |
|
|
At the PLS 1. Perform a ______ _______ ________ ________. 2. Get your bearings based on _________ _________. 3. Try to __________ the position. |
1. Quick visual surface search. 2. Geographical markings. 3. Triangulate. |
|
|
Potential problems with submerged vehicles. 1. Need for _______ gear at the incident. 2. Powerful _________. 3. Poor visibility in _______ ________. |
1. SCUBA. 2. Undercurrents. 3. Murky water. |
|
|
Many passenger vehicles will _______ for a short period of time. |
Float |
|
|
Buses will tend to ______ almost immediately and _______ as they descend. |
Sink, turtle |
|
|
The amount of air that is in the vehicle is directly related to the amount of ________________________________. |
damage the vehicle has sustained. |
|
|
Low speed crashes percent a _______ _______ of rescue. |
Greater chance |
|
|
In a _____________, it will take longer for the vehicle to sink. |
low-speed crash |
|
|
In a low-speed crash, Vehicle will tend to _______ _________ allowing the rear window to be above water longer. |
Tilt forward |
|
|
Rear windows are __________________ so access to the victim is _______ . |
Easier to break, quicker. |
|
|
Side windows are _______ and may be lowered by the occupant. They are also _______ _______, so access for an unconscious victim is easier. |
Accessible, easily broken. |
|
|
Avoid _______ for removal of victims due to difficulty of opening them. |
windshields |
|
|
What are the clues for locating a submerged vehicle? |
1. Escaping air bubbles. 2. Oil or gas slick. 3. Articles floating near the surface. 4. Headlights shining from below. |
|
|
This may be necessary before the vehicle rescue can proceed. |
Stabilizing the vehicle |
|
|
In calm water, _______ _______ can be used to anchor the vehicle to a bridge, tree, or other strong anchor. |
Guide ropes |
|
|
What can be used for additional stabilization on a vehicle rescue? |
A winch or tow truck. |
|
|
Moving the vehicle to a better position can be accomplished with: |
1. Tow truck. 2. A frame with a winch. 3. Crane. 4. Rope-hauling systems (under limited conditions) |
|
|
The vehicle _______ can be a hindrance to the rescue. |
Position |
|
|
If vehicle is submerged, access through the doors maybe difficult due to the _______ _______ between the inside and outside of the vehicle. |
Pressure differential |
|
|
Vehicle doors may be damaged due to _______ _______. |
Prior impact |
|
|
Absolutes for water rescue. |
1. Always wear a PFD. 2. Never wear turnout gear. 3. Never put your feet down if swept away. 4. Never count on the victim to help. 5. Never tie a rope around a rescuer. |
|
|
Firefighters arriving at a structural collapse will need to complete the following tasks simultaneously; 1. Search for _______ _______. 2. Prevent secondary collapse through _______. 3. Rescue _______ _______. 4. Knock down fire from _______ _______. 5. Identify and react to _______ _______ _______. 6. Treat _______. |
1. Missing victims. 2. shoring. 3. trapped victims. 4. gas leaks. 5. Hazardous materials releases. 6. casualties. |
|
|
If collapse is part of a terrorist attack, then _______ _______ must be considered. |
Secondary devices |
|
|
Collapses due to large scale events may overtax resources and require fire companies to be on their own for possibly _______ until state or federal urban search and rescue units arrive. |
72 hours |
|
|
A systematic approach to structural collapse operation. 1. It is based on a _______ of the most experienced fire departments and rescue organizations. 2. It is now the _______ _______ for structural collapse around the world. 3. The procedure or approach is called the _____________________________. 4. It can be applied to _______ _______ situation so that they can be effectively managed. |
1. Consensus. 2. Recognized procedures. 3. The five stages of collapse operations. 4. Any size collapse. |
|
|
The five stages of collapse operations. |
Stage 1: Response, size up, and reconnaissance. Stage 2: Surface search and rescue. Stage 3: Void space search operations. Stage 4: Selected debris removal. Stage 5: General debris removal. |
|
|
FEMA search assessment marking. 1. Single / upon entry into structure indicates _______. TF ID, date an entry time noted. 2. Crossing X upon exit, Date and time noted in _______ _______. Additional information placed in _______ _______ of X. 3. Right - _________, bottom - _______ ____ _______. 4. What do you do when new search completed? |
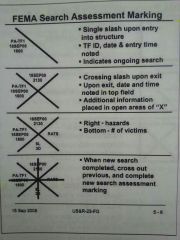
1. Ongoing search. 2. Top field. Open areas. 3. Hazards, # of victims. 4. Cross out previous, and complete new search assessment marking. |
|
|
In Stage 1, when responding you should consider _______ _______ : |
Possible causes:
1. Fires 2. Natural gas explosions. 3. Vehicle striking structures. 4. Construction accidents. 5. Mudslides. 6. Floods. 7. Avalanches. 8. Earthquakes. 9. Bombings. 10. Terrorist attacks. 11. Possible secondary explosions. |
|
|
When conducting a Size-up, consider the _________ of the affected area. |
extent |
|
|
When conducting a Size-up, consider if it is a ___________ building or an entire ___________ or ________. |
single building, neighborhood or city. |
|
|
Conduct an ______ ______ size-up of the involved building(s) and the ________ ________. |
eight-sided, surrounding area. |
|
|
When conducting a Size-up, check the ______________________________________________. |
top, bottom-basement, and four sides of the building. |
|
|
When conducting a Size-up, check the ______ ______ around the building for falling hazards from adjacent structures and other aerial hazards. |
air space |
|
|
When conducting a Size-up, conduct a ________ ________ of the ground around the structure, looking for hazards like ruptured gas mains, broken water mains, railroad tracks, and other potential ground-level problems. |
rotary sweep |
|
|
What are the factors that can indicate how many victims might be trapped and where they might be? |
1. Time of day 2. Day of week 3. Holiday 4. Occupancy type 5. Overall situation in immediate area of collapse. 6. Condition of the area surrounding the actual collapse. 7. Construction and material involved 8. Pattern of collapse |
|
|
Improper placement of apparatus at an emergency incident can _______________________. |
complicate the situation. |
|
|
The proper placement of apparatus should support the _____________________________. |
IC strategic decisions. |
|
|
Assign at least _____________________ at or near the front of the affected building. |
one aerial ladder |
|
|
Have aerial ladder raised so observers can view the collapse scene and act as a __________. |
lookout |
|
|
Engine Company personnel can be used for: |
1. Cutting teams 2. Medical teams 3. Rescue teams |
|
|
Rescue Companies and Technical Rescue Teams are placed ____________________ but not ___________. This commonly is ____________________________. |
close to the collapse, but not in it. In front of the building. |
|
|
Paramedic or advanced life support units or ambulances are placed in a _________ group and ________ from the collapse zone. |
medical, away |
|
|
Chief Officers establish a command post that has a ______ _______ view of the incident. Make sure it is _________ the collapse zone. |
two-sided, outside |
|
|
Specialized companies and units placements is based on ______________________________________. |
incident specific objectives. |
|
|
Heavy equipment placing is based on _________________________________.
|
incident specific objectives.
|
|
|
Provide ________ _________ for Heavy Equipment from staging. |
Access routes |
|
|
Factors for establishing staging areas include; |
1. Ground vibration 2. Debris-filled streets 3. Distance that equipment must be carried. |
|
|
Stage 1 includes; |
1. Possible Causes 2. Size-up 3. Factors that indicate # of victims and their location. 4. Apparatus placement. |
|
|
The searching for and rescuing of victims trapped at or near the surface beneath structural and non-structural elements. |
Stage 2: Surface Search and Rescue |
|
|
Victims found __________________ should be removed first. |
on top of the debris |
|
|
Initial operations should be directed at victims who ___________________________________. |
can be seen or heard. |
|
|
Victims whose location is known, even if they cannot be seen or heard, should be ___________. |
secondary. |
|
|
Rescuing secondary victims may require various ________________________________________. |
hand tools and hydraulic jacks. |
|
|
Basic and advanced ______________________ may be needed to prevent secondary collapse. |
shoring systems |
|
|
Firefighting personnel may be required to assist in supplying ____________ equipment and cutting wood to provide _______________________. |
shoring, shoring material. |
|
|
Passersby and relatives should be prevented from ____________________________________. |
accessing the debris piles. *Securing the Incident |
|
|
Removal of debris must be __________ and ____________. |
careful and deliberate. *Securing the Incident |
|
|
_____________________ is generally not used in Stages 1, 2,and 3. If it is used, _____________________________ must be used. |
Heavy Equipment, special care and discipline |
|
|
If working on top of the collapse, firefighters need to be cautious of _________________________. |
where and how they move. *Firefighter Assignments |
|
|
Firefighters may be used to establish ____________________ to remove debris. |
bucket brigades *Firefighter Assignments |
|
|
When is it time to transition to stage 3 operations? Who determines this? |
When the last readily accessible victims are removed and signs of additional victims diminish. IC determines this after discussing the situation with subordinates. *Transition to Recovery |
|
|
There is a nationally approved marking system that identifies _________________________________. It helps to prevent _______________________________.
|
when a building has been searched. redundant searches of buildings. |
|
|
The nationally approved marking system includes a marking to indicate the ___________ of the structure and any _________________________________ based on the assessment of the team that searched it. |
stability, special dangers |
|
|
Marking should be __________________________ from a distance. |
readily identifiable |
|
|
Marks are usually made by using _______________________________ sprayed directly on the building at the __________________________. |
fluorescent orange, front or address side. |
|

FEMA Structure / Hazards Marking 1. 2x2 ft Square 2. / in Square 3. X in Square |
1. Structure relatively safe for US&R operations. 2. Structure significantly damaged. Shoring/removal of hazards may be required. 3. Structure not safe for normal US&R operations. Extensive safety measures must be taken before entry. |
|
|
This step is for searching potential survivable voids within the collapsed pile. |
Stage 3: Void space search operations. |
|
|
This is one of the most dangerous tasks in collapse rescue operations. |
Stage 3: Void space search operations. |
|
|
Stage 3: Void space search operations. These are skills that are beyond the typical firefighter and require ___________________________. |
Highly trained rescue personnel. |
|
|
First-due firefighters can assist in stage 3 operations by __________________________________. |
Providing materials for shoring and moving debris. |
|
|
Breaching of wall is ________________. |
Not recommended. |
|
|
Rather than breaching wall, it is safer to ______________ in floors and use the _______________ approach. |
Cut hole, vertical shaft approach. |
|
|
Shoring should be used to support weekened walls or floors, but not to _____________________________________. |
Restore structural elements to their original positions. |
|
|
_____________________ should be kept as short as possible to provide a more stable shoring. |
Timber shoring |
|
|
After all survivable void spaces have been searched, _________ __________ removal begins. This is Stage _______: _________________. |
Selective debris. Stage 4: Selected debris removal. |
|
|
In this phase heavy equipment is used as well as structural engineers in construction and demolition contractors. |
Stage 4: Selected debris removal. |
|
|
All accessible void spaces are checked for victims by rescuers. |
Working in voids |
|
|
As debris is encountered it must be __________ to allow forward movement. |
Removed. * Working in voids |
|
|
__________ is placed to maintain stability for ingress and egress of victims and rescuers. |
Shoring * Working in voids |
|
|
First-due firefighters are typically positioned at the _________ to help remove debris as it is passed out and to hand _______ _______ and equipment to rescuers working inside. |
Entrance, needed tools * Working in voids |
|
|
This is generally signals the and of search and rescue operations. |
Stage 5: General debris removal |
|
|
These operations should only be undertaken after all other potential life sustaining voids have been physically or technically explored for victims and there is a reasonable assurance that no survivors remain inside the collapse. |
Stage 5: General debris removal |
|
|
Rescuers and firefighters must remain alert for any potential ________________ or ________________ conditions. |
Signs of life or life-sustaining conditions. |
|
|
Rescuers and firefighters should also be alert for any _________________ or ___________________________________. |
Human remains, potential evidence of the cause of the collapse. |
|
|
This stage includes the use of heavy equipment to demolish or remove large parts of the structure. |
Stage 5: General debris removal |
|
|
This stage may require hundreds of personnel participating in the hand removal of tons of debris. |
Stage 5: General debris removal |
|
|
The search for _________________ continues to Stage 5. |
Deceased victims |
|
|
Size-up factors in High-Angle Rescue Operations: 1. What is the _______ ________ of the incident and the best _________ for rescue? 2. What is the victims __________? 3. Is victim able to ________ in his / her rescue? 4. What __________ is needed? |
1. Exact location, access 2. Predicament 3. Assist 4. Equipment |
|
|
What are the different types of rescue operations? |
1. Water rescue. 2. Structure collapse operations. 3. High angle rescue operations. 4. Trench and excavation collapse rescues. 5. Confined space rescue. 6. Elevator and escalator rescues. 7. Electrical emergencies. |
|
|
Do not cancel the _______________________________ until the victim is rescued. |
the response of rescue units or companies |
|
|
What are the 3 priorities of High-Angle Rescue operations? |
Priority 1: Ensuring firefighter safety. Priority 2: Secure victims in danger of falling from their current position, and securing vehicles in danger of rolling or falling. Priority 3: Treat the victim for immediate life-threatening conditions while waiting for the Rescue Company or Technical Rescue Team to arrive, or for first-responding units to establish and insert a litter team and prepare to raise the victim and rescuers. |
|
|
High-Angle Rescue Priority 2 |
Priority 2: Secure victims in danger of falling from their current position, and securing vehicles in danger of rolling or falling. |
|
|
High-Angle Rescue Priority 3 |
Treat the victim for immediate life-threatening conditions while waiting for the Rescue Company or Technical Rescue Team to arrive, or for first-responding units to establish and insert a litter team and prepare to raise the victim and rescuers. |
|
|
High-Angle Rescue Priority 1 |
Ensuring firefighter safety |
|
|
In a High-Angle Rescue, if it has been determined that a rope system will be used, establish ______________________________. |
bomb proof anchors. |
|
|
In a High-Angle Rescue, if vehicles are used as an anchor, ________ the wheels and _______________________ from the ignition. |
chalk, remove the keys |
|
|
Any point where the rope passes a stationary object, it must be __________ with edge protection to prevent damage to the rope. |
padded |
|
|
_______ should be worn by all ffs engaged in the operation. |
PPE |
|
|
At night, ___________ are recommended, and all members should carry at least _______ preferably _______ , backup source of light. |
headlamps, one, two |
|
|
Only _______________ harnesses or other approved rescue harnesses should be permitted for rescue operations. |
NFPA-compliant |
|
|
_________ and _________ should also be provided for the victim and can be taken to the victim by the first rescuer or the ______ team. |
A helmet and goggles, litter team. |
|
|
Whenever possible, ____________ should be used to lower the first rescuer over the side, and always when raising victims and rescuers. |
two ropes |
|
|
The second rope is the ________ ________. In some cases, the rescuer to rappel on the main line with a safety line attached to his _________ _________ and ________ ________ for fall protection. |
safety line, seat harness, chest harness |
|
|
Which cable winches should not be used to raise victims? |
Non-Rescue rated |
|
|
Even rescue-rated winches should be used ______________. |
judiciously |
|
|
Caution is advised whenever the cable winch operator does not have a direct _________________ visual contact with the rescuers. |
line-of-sight |
|
|
In the event of communication delay, it is possible for the ____________________________ to pull rescuers through brush and rocks before the operator realizes it. |
powerful cable winch |
|
|
Injured victims should be securely packaged in a ________________ before any raising or lowering operations. |
rescue litter |
|
|
If the victim is a __________ __________ or a _____________, the fire department should operate with a unified command structure with law enforcement to handle the incident. |
potential jumper, hostage |
|
|
Law enforcement will be tasked with _________ __________ and _________ __________. |
crisis negotiations, scene security |
|
|
FD is tasked with ___________ ____________ and other involved personnel and to provide aid in the case of ________ or if __________________ as a result of the action being taken. |
assisting negotiators, injuries, a fire occurs |
|
|
En-route to potential jumper rescue, gather critical information from the dispatcher regarding the ________ of the incident and if the subject is __________. |
nature, armed. |
|
|
If available and appropriate for the situation, request a ___________________ to respond to provide fall protection. |
rescue fall cushion |
|
|
In a potential jumper rescue, ensure that ________ _____________ and _________ __________ have been notified. |
law enforcement, crisis negotiators |
|
|
Coordinate with _____________ ____________ _____________ or _____________ ____________ _____________ via radio for any other needs. |
responding rescue company, technical rescue team |
|
|
In potential jumper rescue size-up, upon arrival asses and report the following; |
1. Exact location of the incident, and the best access and staging of FD units and ambulances to maintain a secure perimeter around the operational area. 2. The nature of the subjects predicament. |
|
|
In a potential jumper rescue, until arrival of the Rescue Company or Technical Rescue Team, ffs can coordinate with ________ ___________ to develop the basic strategy. |
law enforcement |
|
|
In a potential jumper rescue, other law enforcement officers on the scene may be compelled to take action if _____________________________. FFs should be aware of all these issues so they can stay out of the ______________________________. |
the subject becomes a threat, potential line of fire. |
|
|
In a potential jumper rescue, if FD arrives first and there are no crisis negotiators, it may be necessary for ________________ ffs to be designated to ________________________________. The goal is to attempt to ___________ the situation and avoid making it worse. |
one or more, make and maintain contact with the subject. stabilize |
|
|
In a potential jumper rescue, extremely agitated subjects may not be approachable, and in that case establishing __________________ and ___________ __________ and a _________ _________ is appropriate. |
perimeters, fall zones, medical group
|
|
|
If the potential jumper is approachable and ffs have the opportunity to establish rapport, determine the subject's __________________, and possibly even talk the person into _________________________________. |
state of mind, coming down voluntarily. |
|
|
Tactical Rescue is generally assigned to the ____________ ___________ or _____________ ____________ ___________, with support of the other ffs. |
Rescue Company, Technical Rescue Team |
|
|
FFs should consider the potential need to attempt _____________________ if conditions warrant. |
tactical rescue |
|
|
Common industrial and construction incidents. |
Trench and Excavation Collapse |
|
|
Usually require technical rescue teams with specialized equipment and training. |
Trench and Excavation Collapse |
|
|
Crucial in stabilizing a Trench and Excavation Collapse incident. |
Initial response units |
|
|
En route to Trench and Excavation Collapse, consider special information from dispatchers; |
1. Location is at a construction site. 2. Number of victims. 3. Special Hazards. Any pre-planning that was done for the site in anticipation of potential collapse emergencies there. |
|
|
En route to Trench and Excavation Collapse, consider the need for additional resources: 1. __________ trailers 2. Units equipped with ___________ __________. 3. _____________ trucks. 4. Additional __________ __________, ___________, and ____________ ___________. |
1. Shoring trailers. 2. rescue vacuums 3. Hydrovac trucks. 4. rescue companies, lighting, utility companies. |
|
|
Request law enforcement response to assist in ____________ ___________ and other ____________________________ and ___________ ____________ measures required for working trench collapse incidents. |
traffic control, vibration-elimination, crowd control. |
|
|
On arrival at Trench and Excavation Collapse, park apparatus a safe distance from the collapse to reduce potential of _____________ causing a secondary collapse. |
vibration |
|
|
On arrival at Trench and Excavation Collapse, no vehicles should be within _______ ft of the trench, except possibly the ___________ or __________ _____________ if required for soil removal and as a high point for ____________ ___________. |
50ft hydrovac aerial ladder vertical extraction |
|
|
On arrival at Trench and Excavation Collapse, isolate and deny entry to ____________ collapse areas and ___________ trenches. |
unshored unshored
|
|
|
Generally, rescuers should not enter the unshored trenches and excavations more than _______ft in depth, even for rescue. |
5ft |
|
|
Alternatives for working outside the collapse area; 1. Using ___________ tools. 2. Lowering in __________ _________ _________ and other supplies to trapped victims. 3. Reaching in with __________________________. 4. Using ___________ __________. |
1. reaching tools 2. breathing apparatus masks 3. shovels to remove soil 4. rescue vacuums |
|
|
If construction workers, police, or others are digging in unshored areas to attempt rescue, they should be instructed to ____________________ until ___________ ___________ can be placed. |
exit to a safe zone, adequate shoring |
|
|
Failing to remove would-be-rescuers from unshored areas risks ______________ _____________ if there is a _____________ ______________. |
additional victims secondary collapse |
|
|
One alternative to help remove would-be-rescuers from unshored areas is to convince them to help you begin the process of _____________ the scene using plywood and/or timber as _________ __________ around the trench or excavation, and moving spoil piles at least _____ ft away from the edges. |
stabilizing edge protection 2ft |
|
|
Eliminate _________ ________, __________ ___________, and other causes of vibrations. Shut them all down, except for critical items like __________ _________. Do not forget to shut down nearby ________ ________. |
vehicle traffic, heavy equipment hydrovac trucks rail lines |
|
|
Locate the site supervisor to determine potential ___________________, their last ________ _________, and site-specific hazards like utilities, pipelines, water mains. |
number of victims known locations |
|
|
keep the site supervisor with the incident commander; do not allow the site supervisor to ____________ |
venture off |
|
|
place edge protection in the form of ________, _______, or even ______around all edges of trench?excavation.
This helps ______weight of rescues and eliminate ___________collapse |
wooden planks, plywood sheeting, backboards
distribute, secondary |
|
|
Options for helping stabilize the area directly around the victim from secondary collapse and include placement of ________and _______ to prevent _______. |
ladders plywood wall failure
|
|
|
trench rescue operations eventually require the trench walls to be ____________in the shoring process, and these skills and equipment are generally ______the realm of the firefighter __ & __. |
pressurized outside firefighter I & II |
|
|
If the dirt pile is right on the edge of the trench, begin hand digging the pile back at least ___ from the edge |
2 feet |
|
|
consider requesting an _____for personnel for this labor intensive work |
additional alarm |
|
|
if possible, lower the ______and _______ to the victim with instructions to don both |
helmet and SCBA mask |
|
|
if possible, lower a _____to the victim with instructions to ________around the victim's body |
a rope, tie it |
|
|
do not allow the use of _________or other __________equipment to unbury victim |
backhoes heavy digging |
|
|
ensure that water mains, electrical and other utilities and pipelines are ____________in the collapse area |
shut down |
|
|
develop an ______________, including buckets and rope, shovels, rope rescue equipment, and so forth |
equipment pool |
|
|
assign at least ________to help the rescue company or technical rescue team unloading equipment on their arrival and transport tools to equipment pool |
two companies |
|
|
develop a _______________to store plywood, planks, and other shoring material |
materials pool |
|
|
consider potential ___________rescue options, in case rope systems are needed to pick the victim straight from the trench oven the victim is freed. |
high angle |
|
|
approach trenches from _________ to avoid secondary collapse and insert a ladder in _______ |
the ends each end |
|
|
a ladder should be placed every ____ft in the trench for emergency escape by rescuers once they are working in the collapse zone with shoring in place |
20 feet |
|
|
be prepared for unanticipated release of water or other substances in the collapse zone, caused by __________, ground movement |
rupturing pipes |
|
|
when hazmat or rescue companies arrive, monitor the ________________in the collapse zone |
atmosphere |
|
|
be mindful that apparatuses still running may create________ that could find its way into the trench or excavation |
carbon monoxide (CO) |
|
|
_________________into the trench and other collapse zones is advised under all circumstances to maintain a fresh atmosphere clear of contaminants |
Precautionary ventilation |
|
|
__________your findings to the incoming rescue company or technical rescue team |
Radio |
|
|
Identify the IC, operation section chief, and all other officers and team leaders for these incidents. For long term entrapment with potential for crush syndrome, compartment syndrome and other complications, consider requesting a _____________, or __ _______advise paramedics on treatment and a ___________to expedite patient transportation to trauma ctr after the victim is rescued |
medical director physician helicopter |
|
|
this is one of the most difficult and dangerous duties firefighters can respond to. |
confined-space rescue
|
|
|
there is a relatively high incidence of mortality among would be rescuers ____% |
50%
|
|
|
strict state and federal guidelines regulate ____can attempt rescue in confined spaces and ________is required |
who what equipment
|
|
|
classifications of confined spaces |
1. non-permit 2. permit
|
|
|
*Is large enough for an employee to bodily enter to perform work *has limited or restricted means of entry and egress *is not designed for continuous human occupancy |
Non -permit |
|
|
contains or has a known potential to contain, a hazardous atmosphere contains material with the potential for equipment has an internal configuration that may cause an occupant to become trapped or asphyxiated by inwardly converging walls, a floor that slopes and tapers to a smaller cross section, or other similar hazards contains any other recognized serious safety or health hazard. |
permit |
|
|
example of confined spaces |
tunnels storage tanks sewers boilers silos trenches manholes pits excavations pump wet wells degreasers tank trucks underground vaults |
|
|
1985 OSHA study showed _____confined space fatalities were in untested oxygen deficient atmospheres |
173 |
|
|
consumptions by fermentation, bacterial or chemical reactions absorption of hazardous substances into the lining of the shaft displacement by other gases formed withing the space or introduced from the outside purging operations oxidation from rusting steel casings or curing concrete shaft casings a result of respirations from a trapped victim |
oxygen deficient atmospheres |
|
|
combustible atmospheres may ignite or explode if a _________________is present or introduced |
source of ignition |
|
|
combustible agents may include __________gases, vapors from liquids such as fuels or solvents or dusts of combustible materials. |
naturally occurring |
|
|
combustible atmospheres are considered hazardous when they reach ___% of their _________________(LELs) |
10% lower explosive limits |
|
|
combustible atmospheres may flow into deep shafts naturally or be introduced by ___________into the space accidentally. |
workers |
|
|
an oxygen-enriched atmosphere (_____%) ___________the potential for ignition |
23.5% + increases |
|
|
different gases, heavier or lighter than air, seek _________or ________levels (__________) in a deep confined space |
lower or higher stratification |
|
|
____________of chemicals from the walls of the confined space may cause a combustible atmosphere |
desorption |
|
|
__________may become combustible in certain concentrations, |
dusts |
|
|
dusts are considered combustible when particulates reduce visibility to less than ____ft. |
5 feet |
|
|
confined spaces containing asphyxiates and irritants can cause____, ___, _____. |
disease, illness, injury or death |
|
|
what are two types of gases in confined spaces containing asphyxiates and irritates |
carbon monoxide (CO) Hydrogen sulfide |
|
|
An incomplete product of combustion colorless and odorless can reach lethal levels in confined spaces |
carbon monoxide
|
|
|
produced from natural decomposition of sulfur bearing organic matter. raw sewage can create hydrogen sulfide. exposure to low concentrations can cause breathing complications higher concentrations can cause unconsciousness and death it has a rotten egg smell that can prevent the rescuer or victim from being able to smell |
hydrogen sulfide |
|
|
Mechanical hazards: if power goes out, machines must be _____and __________and security posted |
isolated and locked out/tagged out |
|
|
Mechanical hazards: ____________entry and egress can contribute to confined space dangers |
restrictive |
|
|
with little or no light, ______ _________is a major concern. |
getting lost |
|
|
OSHA requires ____separate and intrinsically safe light sources be carried by each member of an entry team |
3 |
|
|
establishing _____ ______ for interior and exterior of the incident is recomended |
floor lighting |
|
|
confined spaces should be considered an _____atmosphere until proven differently |
IDLH |
|
|
is should be assumed that IDLH hazard exist _________the duration of the entry |
throughout |
|
|
Hazards of performing the rescue include ___, _____,____ operations |
cutting, shoring and lifting |
|
|
OSHA requires all employees involved in confined space rescue must be protected from all existing and potential hazard through _____,_______,and ____ |
training, equipment and procedures |
|
|
only _________personnel can attempt rescues in confined spaces |
certified |
|
|
Confined spaces En route interview |
witnesses the responding party site supervisor
|
|
|
confined spaces En route Determine |
what happened number of probable victims probability of victim survival potential hazards to rescuers
|
|
|
confined spaces En route Request |
entry permit MSDS sheets victim information 1. number of entrants 2. their location 3. age 4. sex 5. general health 6. special health conditions 7. what they are doing in the space 8. what protective clothing and equipment was being used
|
|
|
factors to consider for rescue or recovery
this considers a serious _________versus________ equation when developing an action plan |
IDLH environment Length of exposure
risk versus benefit |
|
|
On arrival at confined spaces, goals to assist the rescue teams, establish an ___________. Should be _____ft around the space opening . Establish an ___________. A ____ft perimeter around the exclusion zone. _______and _____entry team operations and support operations are conducted here |
exclusion zone 50 feet operational zone 100 feet primary and backup
|
|
|
Initial efforts prevent _____victims establish an _____ consider ways for rescuers to initiate ___rescue operations without entering the confined space |
additional ICS indirect |
|
|
lowering harnesses, wristlet, ropes and ladders to victims to aid in self rescue |
indirect support |
|
|
provide respiratory support to victims, if possible by :
also provide air sampling and monitoring |
SCBA lowering air hoses using fresh air blowers provide fresh air ventilation |
|
|
conduct _______/_____procedures on machinery or industrial processes that may contaminate the work arez |
lockout/tagout |
|
|
all electrical, mechanical and other forms of energy must be _____and ______prior to entry |
shut down and de-energized |
|
|
all valves, switches, gates or other control devices must be locked out with a keyed padlock and tag that reads ____________________, _______ |
DO NOT REMOVE, DO NOT TOUCH |
|
|
Post a guard to make sure no one __________these safety measures |
circumvents |
|
|
_________and __________must be blanked or blinded by disconnecting or using a provided steel plate blank out system. the system should then be ____to assure deactivation |
hydraulic lines and pipelines bled |
|
|
if the device cannot be secures and locked out it is necessary to _________and station an entry team member at the device or switch to prevent activation |
tag the switch |
|
|
locate a responsible party who is ___________ _________ with the systems to assist with this process and give any necessary technical advice about the facility and equipment |
intimately familiar |
|
|
safety considerations no one enters confined space unless they are ____and ______to do so |
trained and certified |
|
|
make sure _________ ___________ is conducted initially and on a regular schedule around the hazard area.
secure the scene |
atmospheric monitoring |
|
|
maintain a ___________group within the ICS
support the ______team |
medical
rescue |
|
|
have all rescue and support team members properly _________ when working near the opening to the confined space, especially if its a __________confined space |
harnessed vertical |
|
|
prevent possible collapse by placing _________or other _________material around the opening |
plywood or decking |
|
|
for many urban and suburban fire dpts a response to an office bldg or apart. bldg to rescue someone trapped in an __________ is a common occurrence |
an elevator |
|
|
some of the common emergencies responded to are: passengers in an elevator who are ___________.
repair technicians, bldg mainteance personnel and kids performing elevator hopping who are ________ by the elevator |
trapped between floors
injured |
|
|
other responses that are not as common but involve elevators are: |
high-rise fire earthquakes hurricanes terrorist attacks
|
|
|
a vertical shaft where the elevator car travels. there are ______________at each floor level |
Hoist way Hoist way doors |
|
|
device that travels up and down the hoist way and each car has its own set of doors |
elevator car |
|
|
it uses and electric motor and a cable or rope to raise and lower the elevator car controls are found in an elevator equipment room at the top of hoist way. can be found in bldgs of any height. |
traction elevators |
|
|
it uses a hydraulic piston to raise and lower the car. power units for the elevator are typically found at or near the lowest level typically found in bldgs up to five floors in height. |
hydraulic elevators |
|
|
make sure an elevator_______________has been dispatched. |
service mechanic |
|
|
Initial actions in Elevator rescues contact the occupants using the _______________. use ______________. if they have cell phones with service, contact them using the_____. |
elevator phone or intercom direct voice contact cell phone
|
|
|
determine the immediate life safety issue 1. what is the ____________________ 2. is there an immediate ______________ 3. is the _______ on in the elevator? 4. is there adequate ______,_________,_____? |
1. condition of the occupants? 2. medical issue? 3. lighting 4. ventilation, heating or air conditioning?. |
|
|
determine the exact location of the elevator by asking the occupants what the __________ in the elevator show |
floor indicator light |
|
|
if no contact is made: send firefighter to _________or ________look up or down and see where the car is located. |
pit area or elevator room |
|
|
contact with occupants: if no life safety issue exists, the best action is wait for arrival of __________ maintain ___________with occupants ________the situation in the elevator |
elevator mechanic communications monitor
|
|
|
perform a lockout/tagout of the elevator a good idea is to use bldg _____________ to assist in this. This prevents an ______________of the system. |
maintenance personnel unattended starting |
|
|
Usually stored in equipment room, sometimes on apparatus |
Hoist way keys |
|
|
Accessing the elevator= force doors using |
halligan tool rabbit tool wedges small air rescue bags
|
|
|
make sure safety interlocks are ___________. if not sure of condition, perform a ___/_________ |
operational lockout/tagout |
|
|
____________are metal bars that prevent the hoist way doors from opening if car is outside the "landing zone" which is ____inches above or below the floor level of the lobby |
Door restrictors 18 inches |
|
|
Removing occupants will be based on |
condition of occupants relationship of elevator to landings access |
|
|
car above the landing block the ____in the hoist way to prevent falls place a ladder from the ____to the ____. send firefighter into the car to aid in ___________the occupants |
gap landing , car removing |
|
|
place a ladder into the car. send firefighter into the car to assist occupants up the ladder
|
car below the landing |
|
|
Send firefighter down a ladder from the above landing to the roof of the elevator open the emergency roof panel send a ff down into the car via an attic ladder send occupants up the ladder to the landing. |
accessing through the emergency roof hatch |
|
|
bring another elevator car alongside the stuck elevator and transfer occupants to that car. planks or ladders can be used a walkways between the elevators |
accessing from an adjacent elevator |
|
|
attempts to lower the car should only be performed by a trained and certified technician it is best to shut off the power to the elevator. perform lockout/tagout remove occupants using previously discussed methods |
hydraulic elevators |
|
|
perform lockout/tagout devise a plan for committing resources to a rescue attempt get assistance from an elevator mechanic consider the following: use of air bags cribbing field surgical intervention |
`=Victim trapped between car and landing |
|
|
Less common than elevator emergencies |
escalator rescues |
|
|
Escalators situations: fingers caught where handrail glides into the underside. Use a ______ or ________saw to cut the plate end expose the innards. cutting through the ____________may allow access to free the fingers |
whizzer or reciprocating handrail |
|
|
Fingers caught beneath the handrails Can usually be freed by cutting the ___________. Feet caught where stairs dive beneath the landing plate. Lift the _____and determine action based on gears and motors. |
handrail belt. plat |
|
|
make sure that medical care is available for ____and ______ _______treatment |
trauma and crush syndrome |
|
|
have ____________ ______ available to an appropriate medical facility |
rapid transportation
|
|
|
More than ____firefighters have been killed by electricity over the past ___years |
25 20 years |
|
|
Use ___________ ___________to see potential hazards at an emergency scene |
situational awareness |
|
|
always consider all electrical lines and conductors as ___________ until told they are ___ |
ENERGIZED COLD |
|
|
when approaching the scene drivers need to ______any possible electrical hazards. |
size up |
|
|
responding units should not travel or position beneath any wires that are ____________ |
compromised. |
|
|
avoid parking near or in ___________ that may become energized |
puddles of water |
|
|
Exiting the apparatus: ff need to examine the area around the apparatus prior to exiting the apparatus for any _________. |
downed wires. |
|
|
Apparatus is grounded by the rubber tires, but any part of aerial ladder of pumper that touches high voltage lines energizes the _____________ |
entire apparatus. |
|
|
carefully ____as far away as possible land with ___________without losing balance do not touch the ground with ________ do not _____forward or backward once on the ground, _________while walking away to maintain contact with the ground and to prevent ________. |
jump both feet together your hand fall shuffle feet arcing
|
|
|
_______or __________touches or gets to close to live wires |
aerial ladder or tower bucket |
|
|
Any operating, erecting, and handling of tools or apparatus over energized high voltage lines should be _______ |
prohibited
|
|
|
aerial ladders are required to maintain a distance of ____ft from wires and components of __________volts or more. |
10 feet 600 volts |
|
|
Alternate methods of reaching upper floors |
using wooden ground ladders fire escapes interior stairs adjacent roofs in extreme cases the use of a helicopter is possible
|
|
|
care must be taken when moving, raising, and lowering ladders. even wood ladders can conduct electricity due to metal parts |
ground ladders |
|
|
power lines make the IC aware of any electrical hazards request a utility representative to the incident scene |
sizing up the scene |
|
|
common natural hazards |
windstorms hurricanes floods
|
|
|
Assume power lines will be _____as a result of these occurrences. Many times these hazards can ____electrical hazards and make the scene a ____event due to the risks involved victim search and rescue efforts may have to be ______until_____hours |
down hide, high-risk suspended daylight |
|
|
Other electrical hazards: _______electrical hazards are found at fires in structures. ____in walls __________ |
internal wiring drop loops
|
|
|
Determining if electricity is present |
flip switches at electric panel have utility company shut down power and confirm use hot sticks and voltage meters to detect electrical current
|
|
|
if victims are present and either trapped or in contact with electrical lines, the IC should have a _____________ __ respond in an expedited manner. IC should upgrade the incident type to a ___________to ensure the appropriate response. |
utility reprensentative technical rescue |
|
|
firefighters should wear __________and ____protection
________gloves should be used if available |
full PPE and eye
lineman's gloves |
|
|
One of the more common tasks involving electricity. |
De-energizing a building |
|
|
the standard procedure of cutting power to the bldg may not always be the most______ . Why: Plunges the entire bldg in to ________ _________of occupants hinders ______________working in the bldg |
appropriate darkness hinders evacuation firefighters |
|
|
Methods of De-energizing a bldg __________ it will ______the bldg and reduce the hazard to firefighters
|
open main switch or breaker at main electrical panel. de-energize |
|
|
considerations when de-energizing bldg. inspect the condition of the panel for ___ or ___damage. avoid standing in ____ stand to the ____of the panel do not reach ____your body to disconnect switches turn ____when disconnecting switches to protect your upper extremeties use _________or ________to protect your face never pull the ____________ |
fire or water water side across away SCBA mask or face shield electrical meter |
|
|
Turning off breakers mark or remember any ____breakers turn off _____switch first if panel is not accessible, contact the local |
tripped main power company |
|
|
downed wires inspect ____in the immediate area identify all wires and their _________points. follow wire to determine if they contacting: |
other wires termination fences structures trees brush |
|
|
Establish a safety perimeter at least _____ ___ of the pole in all directions set up _______________control use ______________or fire line tape assign ______to limit access |
one span incident access traffic barriers law enforcement
|
|
|
request ________company to respond Avoid moving or cutting ________________wires that have not been de-energized |
utility high voltage
|
|
|
Electrical rescues request an urgent response of ____company to the scene. have an _____unit standing by Have a ________standing by moving the wire" Use ________with proper ____and ________ Dont _____/ |
utility ALS RIT/RIC hot stick, gloves, PPE TOUCH |
|
|
Fire at the base of an electrical pole. If the cause was not underground, electrical sources or a downed wire it can be considered a Class ___ and extinguished using water |
CLASS A |
|
|
if fire is near the top or involves electrical wires and or equipment, it is considered a Class ___fire. notify the utility company via the ___ protect ____ Establish a perimeter _____ the span of the pole |
CLASS C the IC exposures one times |
|
|
Vehicle with life hazard situation |
Fire flooding |
|
|
For a conscious victim direct the victim to __________ have the victim stand on the _______of vehicle have victim jump to the ground with both feet together instruct them to remain balanced and not to touch the ground with their hands have the victim shuffle away from the vehicle to a safe area at least ____ from the vehicle or downed wire |
open the vehicle door rocker panel 30 feet |
|
|
Unconscious victim - no life hazard wait for ____company to arrive _______the wires or equipment make patient _____ |
utility de-energize contact |
|
|
life hazard IC must consider ____________ consider ____before committing to a rescue attempt alternate means of accessing the vehicle use a ____to knock down the fire use _____to push the vehicle ways from the downed wire |
risk versus gain all hazards deck gun another vehicle |
|
|
Extinguishing the vehicle fire with unconscious victim- do not use ____ or _______ consider fire a Class _ Fire' have the utility company _____the wires before extinguishment protect ____________ isolate area and deny entry within ____ of affected area |
water or foam Class C de-energize exposures 30 feet |
|
|
Safety considerations for electrical vaults and manholes: Keep apparatus ______of any manholes. set up a perimeter of at least ____ft in all directions. do not remove the cover if _____or ____are showing. do not enter the _____or ____until utility company confirms it is safe rescue attempts area ____ entry and should be done with proper protocols in place establish a _____/____and ____unit |
clear 150 feet flames or smoke manhole or vault confined space RIT/RIC and ALS |
|
|
Fires in transformers are considered Class ___ fires once the equipment is de-energized |
Class B
|
|
|
be aware of older transformers, they may contain____________. This is hazardous material and a known _______ |
polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) carcinogen |
|
|
Newer transformers contain _______ |
mineral oil
|
|
|
_____can affect electrical power towers and poles. maintain a safe distance equal to ____times the height of the tower or pole |
wild fires 1 1/2 times |
|
|
fires at base of pole or tower can be considered Class ____. Extinguish smoldering pole fire only _____the electrical lines to maintain pole or tower integrity. Avoid establishing a safe zones or escape routes ______or ____or ____ |
A. below below wires, or towers, or poles |
|
|
persons trapped on high voltage towers or trees near electrical lines may be considered a ____ _____rescue with special circumstances. IC needs to have the ______ ________dispatched. Provide a _____ ____and crisis negotiation team |
high angle appropiate response fall bag |
|
|
Entrapment on towers and billboards 1. consider ___ _____ 2. contact ______company 3. Develop and action plan for rescue once the wires have been __________. |
fall bags utility de-energized |

