![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
116 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Natural Selection |
Individuals of a species containing certain mutations are better able to survive and reproduce than other (survival of the fittest) |
|
|
|
Genes |
Stretches of DNA on a chromosome that provide information for an organism's characteristics which are responsible for heredity; genetic blueprint for the formation of proteins which make up the machinery of a cell |
|
|
|
Alleles |
Different forms of a gene |
|
|
|
Mutations |
Changes in DNA that affect the way a gene functions (permanent changes in DNA sequences), species variations that can be inherited |
|
|
|
Adaptation |
Increase from generation to generation of alleles of genes that allows a species to survive in their environment |
|
|
|
Name the Purine bases of nucleic Acids. How many rings do Purines have? |
Adenine and Guanine (A,G) Purines have two rings Adenine and Guanine have two rings (Purines) |
|
|
|
Name the pyrimidine bases of nucleic acids |
Pyrimidine have one ring. They include thymine in DNA, uracil in RNA and Cytosine in both RNA and DNA |
|
|
|
What is the job of nucleic acids? |
To store and transmit hereditary information. |
|
|
|
Describe the structure of DNA/RNA |
DNA is double helix. Two strands made up of chains of nucleotides. RNA is single stranded.
Nucleotides are composed of these components: 1. Pentose (sugar. Deoxyribose in DNA, Ribose in DNA) 2. Phosphate group "backbone" that link adjoining bases together 3. a nitrogenous base
Bonds between complementary bases are hydrogen bonds in DNA |
|
|
|
What elements make up nucleic acids? |
CHONP
Carbon Hydrogen Oxygen Nitrogen Phosphorous
|
|
|
|
What types of organisms have the most basic cell type? |
Bacteria (eubacteria and acrchaeabacteria) are prokaryotes |
|
|
|
What is the condensed DNA of a prokaryotic cell that contains genes? |
The nucleoid |
|
|
|
What are small, circular portions of DNA that are not associated with the nucleoid of prokaryotes? |
Plasmids |
|
|
|
What are pili? |
Pili allow communication between two bacterial cells |
|
|
|
Which are larger, eukaryotic or prokaryotic cells? |
Eukaryotic cells! |
|
|
|
Endoplasmic Reticulum |
Tubular network of flattened membranous sacs.
Rough ER - studded with ribosomes
Smooth ER - important metabolic processes
|
|
|
|
What eukaryotic organelle is responsible for moving proteins from one part of the cell to another and for secretion (moving proteins out of the cell)? |
The ER |
|
|
|
What is the function of the Golgi apparatus? |
The Golgi refines proteins that have been packaged by ribosomes, sorts proteins and prepares them for transport to other parts of the cell or for secretion. Works with ER. |
|
|
|
List three common types of vesicles |
Vacuoles - storage Peroxisomes - detox. Lysosomes - recycling (digestive enzymes) |
|
|
|
Peroxisomes |
Detox of hydrogen peroxide and more. Abundant in the liver due to buildup of toxic substances. Major sites of oxygen use and energy production. |
|
|
|
ATP is produced in what organelle? |
Cellular fuel (adenosine triphosphate) is produce in the Mitochondria., "powerhouses" |
|
|
|
What is the structure and function of the cristae of the Mitochondria? |
Folded membrane inside mitochondria. Contains enzymes that help convert sugar to ATP in the Mitochondria. |
|
|
|
What produces ribosomes? |
The nucleolus of the nucleus! |
|
|
|
What do the vacuoles of plant cells do? |
Maintain proper water pressure in the cell. |
|
|
|
Order call wall, capsule and cell membrane from innermost to outermost layer of a prokaryotic cell |
Cell membrane, cell wall, capsule |
|
|
|
What is the subunit of a chromosome? |
A gene! A chromosome consists of genes, which consist of DNA |
|
|
|
How does information flow in the cell? |
From DNA to RNA to proteins |
|
|
|
Differentiation produces a ___ cell from a ___ |
differentiation produces a more specialized cell from a less specialized cell. |
|
|
|
What is a zygote? |
A fertilized egg |
|
|
|
What is an organism in the early stages of development after fertilization? |
An embryo |
|
|
|
What's the process of cells differentiating to form tissue layers? |
Gastrulation |
|
|
|
Stem cells |
Totipitent - can give rise to an entire organism and any tissue type
Pluripotent - can give rise to any tissue type but not a whole organism
Multipotent - most differentiated stem cell. Can give rise to one of a few kinds of cells
|
|
|
|
Interphase |
A process that occurs prior to mitosis when the cell must duplicate its DNA, increase the amount of organelles and cytoplasm, and synthesize protein in preparation for cell division. Consists of G1, S phase and G2 |
|
|
|
G1 phase |
DNA forms messenger RNA, mRNA exits nucleus and carries information to the ribosome |
|
|
|
S phase |
DNA unwinds. DNA polymerase synthesizes new complementary strands of DNA, resulting in two identical copies of the cel's DNA |
|
|
|
G2 |
Continued protein synthesis, and cell growth in preparation for division. |
|
|
|
What organisms carry out photosynthesis? |
Autotrophs! Green plants, green algae and some bacteria. |
|
|
|
What two processes comprise cellular respiration? |
Glycolsis and the citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle) |
|
|
|
What is responsible for the expression of genetic traits? |
Proteins |
|
|
|
How many codons code how many amino acids? |
64 different codons code for 20 different amino acids |
|
|
|
What is a mutagen? |
A substance that induces mutations such as harmful chemicals, u.v. light from the sun. |
|
|
|
Repair mechanisms for DNA replication and damage |
DNA polymerase enzyme speeds up replication.
1. DNA polymerase performs proofreading of the newly synthesized strand, inserts proper base pair if it finds a mistake
2. Mismatch repair removes incorrect base pairs, replaces with correct ones
3. Excision repair inspects DNA for damage from mutagens, cuts out defective DNA and enlists DNA polymerase to create a new correct piece of DNA |
|
|
|
How frequently do errors occur in human DNA replication |
Before repair mechanisms: 1/1000 genes or up to 5% of genes. After repair: less than .3% or less than one DNA base in 10^9 to 10^12 bases. |
|
|
|
Example of incomplete dominance |
Sickle-cell |
|
|
|
Atoms |
Smallest parts of elements that still retain the properties of that element |
|
|
|
Which organ system supports the distribution of oxygen, hormones and nutrients? |
The cardiovascular system |
|
|
|
What system helps regulate blood pressure through the release of hormones? |
Endocrine |
|
|
|
What system helps regulate blood volume and pressure by adjusting urine volume? |
Urinary system |
|
|
|
What system controls blood pressure, heart rate, and distribution of blood to various parts of the body? |
Nervous system |
|
|
|
What hormone helps preserve vascular health in women? |
Estrogen |
|
|
|
What system allows heat to escape by dilating superficial blood vessels? |
The integumentary system |
|
|
|
Where are blood cells formed? |
In the bone marrow of the skeletal system |
|
|
|
The liver and pancreas function in what organ system and how? |
Digestive system! The liver produces bile which helps break down fat. The pancreas delivers enzymes to the small intestine that aide in digestion |
|
|
|
What system controls body functions, growth and metabolism and secretes hormones? |
The endocrine system |
|
|
|
Name the organs of the endocrine system |
Pituitary Thalamus Hyperthalamus Thyroid Thymus Pineal Adrenal
Pancreas, testis and ovaries also have endocrine funtionality Pancreas, testis and ovaries also have endocrine funtionality
|
|
|
|
Which system provides a means of transport for some hormones of the endocrine system? |
Lymphatic system |
|
|
|
Which system controls the secretion of hormones from the pituitary gland? |
The nervous system |
|
|
|
What regulates hair growth and hydration? |
Hormones from the endocrine system |
|
|
|
What system activates vitamin D? |
The urinary system |
|
|
|
What system regulates the production of sweat, interprets stimuli and adjusts the diameter of blood vessels in the skin |
The nervous system |
|
|
|
What structures compose the lymphatic system? |
Lymph Lymph nodes Lymphatic vessels Thymus Spleen Tonsils Thoracic duct |
|
|
|
What system supports the immune system by housing and transporting wbc's to and from lymph nodes and also returns fluid to the cv system? |
Lymphatic system |
|
|
|
Acidic secretions prevent bacterial growth in which two systems? |
Reproductive and integumentary system |
|
|
|
What does structures is the muscular system composed of? |
Skeletal muscle Ligaments - attach bones to bones to form joints Tendons - attach muscles to bones |
|
|
|
Which two muscle types are NOT part of the muscular system? |
Smooth and cardiac |
|
|
|
What system serves as the body's control system? |
The nervous system |
|
|
|
What system provides storage for minerals such as phosphorous and calcium? |
The skeletal system Ligaments, joints, bones, cartilage |
|
|
|
What is necessary for calcium absorption into the bones? |
Vitamin D (provided by the integumentary system, activated by the urinary system) |
|
|
|
What is the primary function of the lungs? |
Inhale oxygen, exhale carbon dioxide |
|
|
|
What is the path of air? |
Nose to trachea to bronchial tubes to alveoli |
|
|
|
When the diaphragm contracts |
Inspiration occurs |
|
|
|
What decreases pulmonary function? |
Age, smoking, pollutants and irritating chemicals |
|
|
|
What structures make up the Central Nervous System (CNS) |
Brain and spinal cord |
|
|
|
What structures make up the Peripheral Nervous System? |
PNS - cranial and spinal nerves that extend beyond the the CNS PNS is divided into the sensory - somatic nervous system and the autonomic nervous system. |
|
|
|
What structures make up the sensory somatic nervous system |
12 pairs of cranial nerves; 31 pairs of spinal nerves and associated ganglia |
|
|
|
How fast does transmission from neuron to neuron happen? |
90 meters/second |
|
|
|
What does intrinsic factor do? |
Increases stomach's absorption of vitamin B12 |
|
|
|
Which remains in the stomach longer, fat or carb - laden chyme? |
Fat stays in the stomach longer |
|
|
|
Which hormones do the small intestine secrete? |
Secretin, which triggers bicarbonate release from the pancreas to neutralize the acidity of the stomach And cck which initiates bile release from the gallbladder, decreasing motility and acid production in the stomach |
|
|
|
Natural Killer cells are part of what line of defense and do what? |
Innate, nonspecific, second line of defense. Produce perforins (pore-producing proteins), that target cancer and virus cells, causing them to lyse. |
|
|
|
The body's response to viral infection which prevents replication of virus after 7 to 10 days |
Interferons |
|
|
|
What activates NK cells and macrophages? |
Interferons |
|
|
|
Diapedesis |
WBC'S slide through capillary slits in response to cytokines and are guided to site of injury by CAMs |
|
|
|
Adaptive Reponses |
3rd line of defense. Specific. Includes humoral/antibody mediated immunity and cellular immunity |
|
|
|
What kinds of light (primarily) reach earth from the sun? |
Visible lig jt, ultraviolet and xray |
|
|
|
What are electomagnetic waves and what's the spectrum |
Waves of radiation characterized by electric and magnetic fields
Long to short:
Radio Microwave Infrared Roygbiv Ultraviolet Xray Gamma |
|
|
|
What drives weather and climate conditions on earth? |
The sun |
|
|
|
What is a major source of biomass on earth? |
Organic (carbon based) compounds which are products of photosynthesis, driven by solar energy |
|
|
|
Formula and units for kinetic energy |
KE (joules) = (1/2) mv^2 M is mass in kg V is velocity in m/s |
|
|
|
Potential energy, formula and units |
PE (joules) = mgh M is mass in kg G is gravity constant (use 10m/s^2) H is height in meters |
|
|
|
Symbolic 4-step process of catalystic reactions |
1) X + C > XC 2) XC + Y > XYC 3) XYC > CZ 4) CZ > C + Z |
|
|
|
Examples of catalytic reactions in nature |
Biological processes Fusion within a star's core Production of 90% of commercial chemical processes |
|
|
|
The breakdown of hydrogen peroxide uses what kind of catalyst? |
A manganese dioxide catalyst. 2(H2O2) > 2 (H2O) + O2 |
|
|
|
Describe a reaction in catalytic converters |
Carbon monoxide is broken down using rhodium and platinum. CO + 2NO > 2(CO2) + N2 |
|
|
|
How is ozone broken down? |
Ozone is broken down by chlorine ions from chlorofluorocarbons in the upper atmosphere. Cl + O3 > ClO + O2 |
|
|
|
What is the basis of petroleum feul? |
Saturated hydrocarbons |
|
|
|
What is the basis of organic chemistry? |
The study of hydrocarbon structure |
|
|
|
Hydrocarbons are abundant... |
Food, feul, plastic, even in the solar system. Lakes of liquid methane and Ethane have been discovered on Saturn's largest moon. |
|
|
|
What are 3 important types of redox reactiona? |
Metabolism (cellular respiration) Photosynthesis Combustion |
|
|
|
When oxygen forms water it is ____ |
When oxygen forms water it is reduced. reduced. reduced. |
|
|
|
When propane is burned (propane plus oxygen) to form water and carbon dioxide, which reactants is oxidized and which reduced? |
Propane is oxidized to form carbon dioxide Oxygen is reduced to form water |
|
|
|
In photosynthesis, carbon dioxide and water form glucose and oxygen. Redox? |
Yes, carbon dioxide is reduced to glucose and water is oxidized to form oxygen |
|
|
|
A base and an acid neutralize each other and produce what? |
Water and a salt.
NaOH + H2SO4 > H2O + Na2SO4 |

An example |
|
|
What is the result of electrolysis on water? |
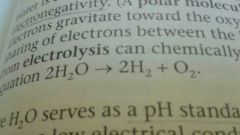
Water splits into its gaseous components |
|
|
|
At what temperature is the maximum density of water? What is its density at that point? |
4 celcius. 1g/mL
Water has a 0 C melting point and a 100 C boiling point at standard pressure. |
|
|
|
At higher than sea level, the boiling point of water is... |
Lower. At 29000 above sea level it is 68 degrees celcius |
|
|
|
Kelvin Scale |
Defined by an absolute zero reference point. 0K = -273 C Standardized by the triple point of water (273.16K = 0.01C), the temperature and pressure at which ice, water and steam coexist |
|
|
|
What has the second highest specific heat after ammonia. |
Water at 4.184j/gC (the amount of energy needed to raise one gram of water one degree celcius) |
|
|
|
What allows water to undergo minor temperature changes relative to its environment? |
The high specific heat of water. |
|
|
|
What acts to moderate Earth's climate? |
Water due to its high heat of vaporization |
|
|
|
What is a biproduct of star formation? |
Water! It is heavily concentrated on comets and other planets |
|
|
|
Latent heat |
The amount of energy necessary for a phase transition at a fixed temperature. Generally more energy is required to go from liquid to gas than solid to liquid |
|
|
|
Heat |
Flow of energy due to a difference in temperature |
|
|
|
Evaporation |
Conditions: high heat, low humidity, fast movement of surrounding air mass Cause: physical collisions at the surface layer, removing more energetic atoms from the liquid Result: cooler system |
|
|
|
Vaporization |
Phase transition from liquid to gas by breaking physical bonds within the liquid. Heat of vaporization (H) necessary depends on the mass and latent heat (L). Adding H will cause a phase transition from liquid to gas through boiling. |
|
|
|
Heat of vaporization |
H = M × L Mass (g) Latent heat (cal/g) Liquid to gas H is positive Gas to liquid H is negative (remove heat from the system) |
|

