![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
45 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Proponent of conditions of learning |
Torres 1994 |
|
|
enumerate the conditions of learning |

|
|
|
(condition of learning) the almost simultaneous occurence of stimilus and cue |
contiguity |
|
|
(condition of learning) It is the procedure of encouraging of correct response |
reinforcement |
|
|
(condition of learning) the repetition of the correct response |
practice |
|
|
(condition of learning) the ability to identify similarities among different things and identify differences among similar things |
generalization/discrimination |
|
|
proponent of laws of learning |
Thorndike 1932 |
|
|
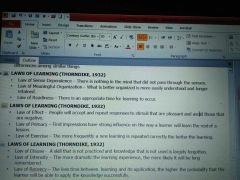
enumerate the laws of learning |
|
|
|
(laws of learning) There is nothing in the mind that did not pass through the senses |
law of sense dependence |
|
|
(laws of learning) what is better organized is more easily understood and longer retained |
law of meaningful organization |
|
|
(laws of learning) there is an appropriate time for learning to occur |
law of readiness |
|
|
(laws of learning) People will accept and repeat responses to stimuli that are pleasant and avoid those that are negative |
law of effect |
|
|
(laws of learning) first impressions have strong influence on the way a learner will learn the rest of the lesson |
law of primacy |
|
|
(laws of learning) The more frequently a new learning is repeated correctly the better the learning |
law of exercise |
|
|
(laws of learning) a skill that is not practiced and knowledge that is not used is largely forgotten |
law of disuse |
|
|
(laws of learning) the more dramatic the learning experience the more likely it will be long remembered |
law of intensity |
|
|
(laws of learning) the less Time between learning and its application the higher probability that the learner will be able to apply the knowledge successfully |
law of recency |
|
|
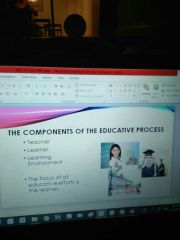
enumerate the components of the educative process |
|
|
|
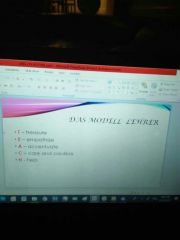
enumerate the das model lehrer |
|
|
|
enumerate bloom's taxonomy of behavioral objectives in order (cognitive) |

|
|
|
enumerate bloom's taxonomy of behavioral objectives in order (affective) |

|
|
|
enumerate bloom's taxonomy of behavioral objectives in order (psychomotor) |

|
|
|
(Bloom's taxonomy of behavioral Objevtives-cognitive) recognition and recall of facts and specifics |
knowledge |
|
|
(Bloom's taxonomy of behavioral Objevtives-cognitive) interprets, translates, summarizes, or paraphrases given information |
comprehension |
|
|
(Bloom's taxonomy of behavioral Objevtives-cognitive) uses information in a situation different from original learning context |
application |
|
|
(Bloom's taxonomy of behavioral Objevtives-cognitive) separates whole into parts until relationship among elements is clear |
analysis |
|
|
(Bloom's taxonomy of behavioral Objevtives-cognitive) combines elements to form new entity from original one |
synthesis |
|
|
(Bloom's taxonomy of behavioral Objevtives-cognitive) involves acts of decision making, judging or selecting based on criteria and factors |
evaluation |
|
|
(Bloom's taxonomy of behavioral Objevtives-affective) aware of; passively attending phenomena and stimuli |
receiving |
|
|
(Bloom's taxonomy of behavioral Objevtives-affective) complies to a given expectations by attending or reacting to stimuli or phenomena |
responding |
|
|
(Bloom's taxonomy of behavioral Objevtives-affective) displays behavior consistent with single belief or attitude where he is not forced to comply or obey |
valuing |
|
|
(Bloom's taxonomy of behavioral Objevtives-affective) committed to set of values as displayed by behavior |
organizing |
|
|
(Bloom's taxonomy of behavioral Objevtives-affective) total behavior is consistent with values internalized |
characterizing |
|
|
(Bloom's taxonomy of behavioral Objevtives-psychomotor) observes skill and attempts to repeat it |
imitation |
|
|
(Bloom's taxonomy of behavioral Objevtives-psychomotor) performs skill according to instruction rather than observation |
manipulation |
|
|
(Bloom's taxonomy of behavioral Objevtives-psychomotor) reproduces a skill with accuracy, proportion and exactness; usually performed independent of original source |
precision |
|
|
(Bloom's taxonomy of behavioral Objevtives-psychomotor) combines more than one skill in sequence with harmony and consistency |
articulation |
|
|
(Bloom's taxonomy of behavioral Objevtives-psychomotor) completes one or more skills with ease and becomes automatic with limited physical or mental exertion |
naturalization |
|
|
enumerate anderson & krathwohl's taxonomy of behavioral objectives (2001) |
remember, understand, apply, analyze, evaluate, create |
|
|
lower order thinking skills |
remember, understanding, applying |
|
|
higher order thinking skills |
analyzing, evaluating, creating |
|
|
proponent of different types of objective |
dwyer 1991 |
|
|
1991different types of objective |
facts concepts rules/principles problem solving |
|
|
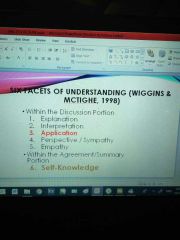
proponents of six facets of understanding |
wiggings & mctighe 1998 |
|
|
six facets of understanding |
|

