![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
35 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the difference between a Layer 2 and Layer MPLS VPN?
|
Layer 2 CPE routers peer directly and think of each CPE as neighbors. It looks like that the MPLS cloud is transparent
Layer 3 VPN the CPE routes to see the SP routers. So the CPE routers peer with SP routers. Exchanges OSP messages directly. The SP router keeps a private table that aggregates the other CPE devices and advertises these routes to the CPE router |
|
|
What is a VF CEF table?
|
?
|
|
|
What is the exterior routing protocol used between CPE routers?
|
BGP. This allows the CPE routers to get notifications on new networks at the customer sites.s.
|
|
|
If a private addresses are used on the enterprise network, what prevents problems associated with the same network id being used multiple times by different customers
|
Route Distinguish-er. An RD value consist of two 32 bit numbers that is unique for this particular customer. By convention the first number is the Autonomous System and the second number is unique number that identifies this particular customer.
|
|
|
What happens when an Ingress PE router receives packet from CE router of VPN customer
|
Ingress PE router receives packet from CE router of VPN customer
Pushes VPN label for associated VPN Pushes LDP label for LSP corresponding to Loopback0 address of Egress router Sends packet over LDP LSP to Egress router (LDP label popped by PHP router). Egress router receives packet Pops VPN label and forwards to customer |
|
|
What is a VPN?
|
A virtual private network (VPN) is a network that emulates a private network over a common infrastructure.
“Private Network” = Layer 1 (leased line) or Layer 2 (Frame Relay or ATM virtual circuit) connection. “Common infrastructure” = IP |
|
|
What is a multi-site virtual private network (VPN) is a service offered by an ISP to its customers that includes some or all of the following elements:
Inter-site Intranet Peering: Private network peering and prefix advertising between customer edge (CE) routers at different sites within the same VPN. |
A multi-site virtual private network (VPN) is a service offered by an ISP to its customers that includes some or all of the following elements:
Inter-site Intranet Peering: Private network peering and prefix advertising between customer edge (CE) routers at different sites within the same VPN. Inter-site Extranet Peering: Private network peering and controlled prefix advertising between CE routers at sites on different VPNs. Secure transport of data Performance guarantees via Service Level Agreement (SLAs) |
|
|
What are the two types of VDN's?
|
There are actually two types of VPN service.
Remote Access VPN service Remote users utilize VPN client software to connect into a VPN server to provide secure Intranet connection to VPN site. Remote user gains a new virtual interface connecting to VPN site, with IP address allocated from VPN site. Multi-site VPN service Direct peering between routers via tunneling. |
|
|
What is an unmanaged VPN?
|
Unmanaged VPNs
A customer can implement VPN services between their sites without ISP involvement. These are unmanaged VPNs. CE routers peer directly with each other. Typically done via secure Generic Record Encapsulation (GRE) tunneling (adds another IP header to IP packet) on CE routers. IPSec Tunnel Mode: Encrypt packet, add IP header with address of remote VPN/IPSec server. Remote IPSec server (CE router) receives, decrypts, forwards. |
|
|
What are the advantages of a managed VPN?
|
With Managed VPN services, ISP routers provides VPN services.
Managed VPN advantages to customers: No VPN processing on CE routers Network-based routing and security Performance guarantees via Service Level Agreements (SLAs) |
|
|
What is the architecture issue with the Overlay Layer 2 model?
|
Scalability.
|
|
|
What is the difference between the overlay and peer-to-peer VPN models?
|
Overlay VPN Model
Carrier provides L1/L2 connections between sites. Direct peering between CE routers. Peer-to-Peer VPN Model Each CE router peers with a directly connected Provider Edge (PE) router. PE routers maintain a private routing table (VRF = Virtual Route Forwarding table) for customer VPN routes. |
|
|
Each customer CE router peers only with a
|
Each customer CE router peers only with a connected ISP PE router
Single peering connection per CE router rather than many. |
|
|
Provider PE router determines which
|
Provider PE router determines which VPN IP subnets get advertised to which CE routers.
Advertisement of subnets from multiple VPNs allows Extranet implementation |
|
|
(Cisco) PE router utilizes __________ on CE interfaces to provide customized routing.
|
(Cisco) PE router utilizes Virtual Routing / Forwarding instances (VRFs) on CE interfaces to provide customized routing.
|
|
|
Each VRF instance has its own:
|
Each VRF instance has its own:
Routing Table CEF Table Routing protocol process (PE-CE peering) |
|
|
Each VRF must be associated with a
|
Each VRF must be associated with a router interface.
|
|
|
Each interface can be associated with at most one
|
Each interface can be associated with at most one VRF.
|
|
|
What is a Route Distinguisher
|
When VPN prefixes are advertised via BGP between PE routers, a 64-bit Route Distinguisher (RD) is added to each VPN IP prefix.
Usually 1 RD per VPN, but more for multi-homing. |
|
|
Why use RDs?
|
To differentiate IP prefixes that may be identical within different VPNs (private IPs, for example)
|
|
|
RD format:
|
X:Y, where X is usually ASN.
|
|
|
Route Target are tied to __________ so that with mulithoming there would be more than one route target.
|
Route Target are tied to an interface so that with mulithoming there would be more than one route target.
|
|
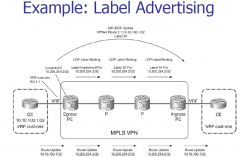
In this example why are there two labels
|
The BGP label is used by the CE routers and are associated to a particular VRF table for the customer networks. The VPN label is used with the core by the SP to move a packet through the P routers to the PE and ultimately to the CE router.
|
|
|
What if you want to use OSPF as routing protocol between each CE router and its peer PE VRF?
|
CE router: configure OSPF as usual.
The MPLS VPN backbone can be considered an OSPF superbackbone – higher than area 0. |
|
|
How to provide public Internet access to VPN customers?
|
Dual interface: a separate CE-PE link could be used for Internet. Easy, but expensive unless you can do subinterfaces.
Static route through global routing table can be placed in VRF routing table. |
|
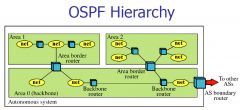
What the important points for OSPF Hiearchy
|
•Backbone router: connect only to networks in the backbone area (Area 0)
•Area border router: attaches to multiple areas. •Internal router: all interfaces connected to networks in the same area. •AS boundary router (Also known as Border Router): connect to other ASes |
|
|
Regarding Area 0 depending on OSPF area design at the customer sites, the MPLS-VPN backbone can
|
Depending on OSPF area design at the customer sites, the MPLS-VPN backbone can
Act as area 0 Act as a Super Backbone connecting multi-site split backbone (area 0) |
|
|
What are the five types of Link State Advertisements flooded to announce the state of links
|
Link State Advertisements
Each OSPF LSA packet is flooded to announce the state of links connected to a router Five types of LSAs: Type #1: Router Link LSA, Floods intra-area prefixes. Sent by internal/backbone routers. Type #2: Network Link LSA Floods intra-area prefixes. Sent by designated routers Type #3: Summary Link LSA Floods inter-area prefixes. Sent by Area Border Routers (ABR) Type #4: Summary Link to ASBR LSA Floods prefix for ASBR. Sent by AS Border Routers (ASBR) Type #5: External Link LSA Floods external (outside of AS) prefixes. Sent by ASBRs |
|
|
What type of LSA should VPN PE router flood to CE router to advertise remote VPN site prefixes?
|
PE is doing BGP-to-OSPF redistribution. Normally this would mean Type #5 External Link LSAs.
In this case, PE would be ASBR. Remote VPN prefixes would be marked as External links in the CE routing table. But, VPN default is for site prefixes should be internal, so VPN PE routers flood Type #3 Summary Link LSAs. So PE acts as ABR. Remote VPN prefixes are marked as internal Inter-Area links in the CE routing table. |
|
|
What is Traffic Engineering?
|
Traffic Engineering (TE) techniques provide network operators with more control of the path taken by IP packets across a network.
Operators may not want all packets to follow “shortest path” determined by the IGP routing protocol. Different paths may be used for load balancing, network maintenance, traffic prioritization, private services (like VPN), peering agreements, etc. |
|
|
Why do we need TE:
|
Lack of control w/ IP routing
|
|
|
What was the technique to perform load balancing prior to MPLS
|
Before MPLS - one way to address this IP routing problem would be to permit bandwidth reservations and then do routing based on “available bandwidth”. (Cisco: RRR)
|
|
|
Note that “available bandwidth” is a ____ property, not a path property.
|
Note that “available bandwidth” is a Link property, not a path property.
Must use Link-State protocol (Extended OSPF) to keep all routers informed about ABW for all links. Can use resource reservation protocol (RSVP) to do bandwidth reservations. |
|
|
How does Original RSVP Protocol work
|
RSVP signals one-way resource reservations across IP routers.
Flow Destination router sends RSVP RESV message along path back to Flow Source LSR to warn all routers on path about resource reservation. Source router sends RSVP PATH message at regular intervals to reserve resources on routers along the path to the Flow Destination. If path changes then New routers on path get notified to reserve bandwidth by new PATH messages. Routers who are no longer on path eventually time out because they stop seeing PATH messages, and free up resource reservation. |
|
|
What additional capabilities are provided by RVSP over MPLS
|
MPLS TE supports ABW routing and more!
New RSVP-TE distributes labels. New OSPF-TE advertises additional link metrics. Administrator configures MPLS TE Tunnel LSPs between Head-End LSRs and Tail-End LSRs. Configuration done on Head-End LSR. Head-End LSR chooses complete path for tunnel – RSVP PATH msg is source routed. RESV distributes labels. Head-End can take ABW, delay, jitter, hops, admin metrics into account in best path calculation (PCALC). The LSP path for a TE tunnel can change over time as conditions change and new tunnels are established. Head-End LSR re-routes tunnel at regular time intervals. |

