![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
16 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Introduction to Taxonomy: |

Classification of organisms. |
Taxonomy is the science of organizing organisms to their inferred natural relationship.There are five different ways to divide and analyze organisms; evolutionary relationships, biochemical relationships, homologous relationships and embryological relationships.
|
|
|
Evolutionary relationships: This classification shows how two or more organisms are related to a common ancestor. When comparing the organisms there is a recognizable common trait that makes one able to relate the two together. For example the okapi species,which is often thought to be related to the zebra family, is a cousin of the giraffe species. Although many dissimilarities are seen between the two, their ears and tongues share many similar like qualities. Their neck, which is a large difference in size, has evolved over time. In order to be able to navigate through the thick brush of the forest a longer lankier neck would not suffice for the okapi species. |

The okapi species related to the giraffe. |
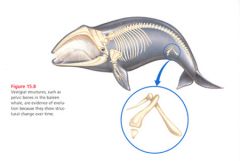
Vestigal: when a structure of an organism is reduced in size/function of a comparable structure from another species.( purpose is minimized or no longer needed) i.e. pelvis and femur bone in a whale |
|
|
Biochemical relationships: Scientists are able to explore and relate common aspects such as the numbers, types and counts of DNA, RNA, proteins, amino acids as well as chromosomes within an organism, showing their chemical relationship. |
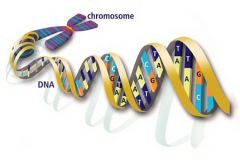
The structure of DNA that can help relate organisms to common ancestors. |
This allows biologists to further relate organisms together other than physical traits or functions. |
|
|
Homologous relationships: A homologous relationship is when two or more organisms have different parts that have evolved throughout time from the same ancestral body part. A common example of this is the similarity between human arms and those of a whale or bat. When first looking at the three, their is an evi dent external contrast being see between the three, however, the bone count is equal through out all body parts. All three share a different pur pose, such as flying, swimming or hold things, when in fact they all derive from the same ancestor. |
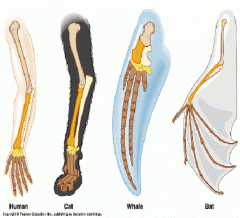
The bone structure of a human arm, dog leg, whale fin and bat wing. |
Further explanation of a homologous relationship: *This is when a certain part of an organism expands and matures over time away from the ancestral part to help aid them in survival their environment. |
|
|
Embryological relationship: Embryology is the study of embryos and their development. When looking at the embryos of vastly different organisms, in the early stages, there was a very common similarity shared between them.In comparing the human to a pigs embryo, scientists were able to recognize the commonality in the structure, during early development, were immensely a like. |
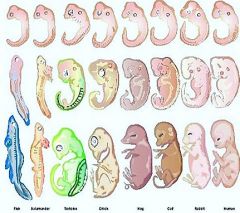
*similarities between the human embryo and other organisms in the early stages of development. |
Throughout the early development of the embryos, mutations or diversity to its structure of DNA presumably dies. Making the minor changes that occur to its DNA later on in development, have a higher possibility of survival thus able to pass on its genes. |
|
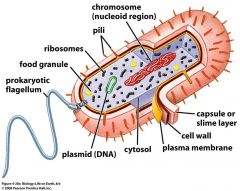
Prokaryotic Cell: *does not contain a membrane *structural shape is an oval, bean like shape *earliest form of life on earth *a tail(flagella) is attached to the cell to help move and guide it from on place to another *unicellular *commonly found amongst bacteria and archaea |
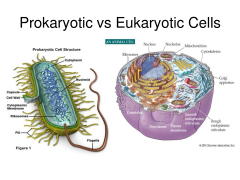
Similarities: *vacuoles present *cytoplasm; holds the cell together *vesicles *cell wall is present *both are able to reproduce asexually |
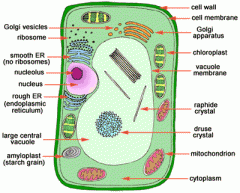
Eukaryotic: *has mitochondria *chloroplasts *multi-cellular *found in mostly animals and plants |
|
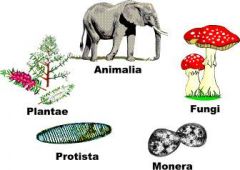
5 Kingdoms: There are five different kingdoms that organisms can be classified into. What differentiates them into the kingdoms is based on their cell structure, nu tritional requirements and their developmental pattern. |
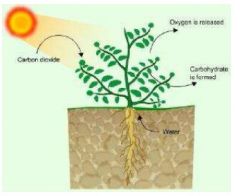
*an example of a autrophic organism |

Feeding Differences:
heterotrophic: an organism that is unable to fix carbon and uses biological or organic carbon for growth. i.e.animals, fungi, bacteria, protist Eutrophic: an organism that accumulates complex organic compounds to produce energy for food i.e. plants, bacteria, moss |
|
|
Monera: A kingdom that contains unicellular organisms with prokaryotic cells, mostly which are bacteria. These cells are believed to be one or the oldest of life forms on this planet today. Spore formation and bionary fission is how these cells reproduce. |
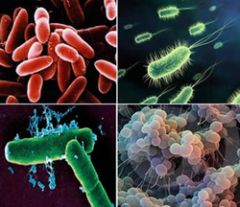
monera: microscopic cells |
*These cells are present in both living and non-living environments *unicellular organisms *found in hot springs, under ice, in deep ocean floors, deserts and on or inside the body of plants and animals. *they are separated in eutrophic and heterotrophic groups |
|
|
Protista: A protistan is any organism that is not a plant, animal or fungus. They are mostly unicellular cells, some however may be multicellular. These cells can be either heterotrophic or autotrophic, while most of them live in water some live in moist soil or even in the human body. All of these cells are eukaryotic (have a nucleus). |
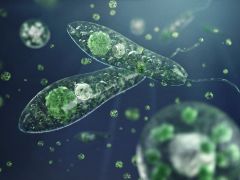
Protist cells
|
These cells are classified on how they obtain nutrition and how they move. VIDEO: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UOfY26qdbU0 |
|
|
Fungi: The fungi kingdom is a very diverse group. They are compelled of eukaryotic cells aswell as microorganisms such as yeasts and molds. They release enzymes out of their bodies in order to break down the nutrients into smaller pieces that make it easier to absorb the nutrients. |

there are said to be 5.1 million different species of fungi |
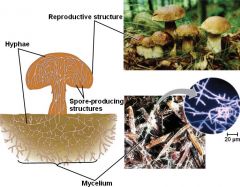
Fungi are able to reproduce by releasing spores that are able to travel and scatter around to great distances
|
|
|
Plantae: Is made up of eukaryotic, multicellular,photosynthetic plants.All of the plants within this kingdom are considered autrophs. They are able to obtain their energy from the sun, allowing them to produce their own food. |
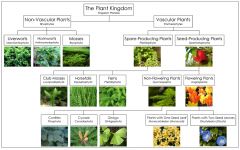
This shows the division of the plantae kingdom. |

This kingdom includes all types of plants such as herbs, shrubs,
trees,creepers,climbers,aquatic plants,desert plants, mountain plants,flowering and non flowering plants,etc. |
|
|
Animalia: *all multicellular *made of eukaryotic cells *around 9-10 million species of animals *scientists have identified 36 groups of animals *made up of the nervous, circulatory, digestive, excretory, skeletal, and reproductive system *all animals in the kingdom have the ability to move |
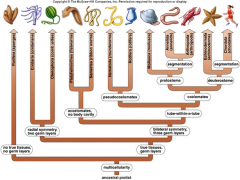
an example of the kingdoms |
All of the organisms that classify as a part of the animalia kingdom are heterotrophs. |
|
|
7 Levels: Kingdom: grouping together all living organisms with similar traits and characteristics Phylum: A smaller group of organisms that share a similar trait i.e backbone Class: A group or set (of things or entities) with common characteristics, attributes, qualities or traits Order: A taxonomic rank used in classifying organisms, generally below the class, and comprised of families sharing a set of similar nature or character i.e mammalia |
*an acronym can help aid you in memorizing the 7 levels king Philip came over for great spaghetti |
Family: Organisms belonging to the same family would have evolved from the same ancestors and share relatively common characteristics. Genus: group(s) of species that are structurally similar or phylogenetically related. Species:An individual belonging to a group of organisms having common characteristics and are capable of mating with one another to produce fertile offspring. |
|
|
Full seven level name: KINGDOM: insect bird pig horse buffalo cow snake cat ox PHYLUM: bird pig horse buffalo cow snake cat ox CLASS: pig horse buffalo cow ox ORDER: horse buffalo cow ox FAMILY: buffalo cow ox GENUS : buffalo ox SPECIES: buffalo |
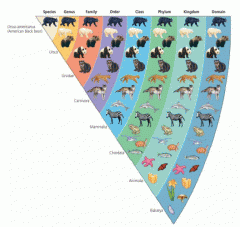
This is an example of the bear being classified in the seven levels.
|
|
|
|
Binomial nomenclature: * this labels the act of naming species based on two parts, their genus name and their species name. The names are usually formed or descended by Latin words. i.e homo sapiens meaning "the same" and "wise" |
These names are given to different species so that it is easier to distinguish them a part. These names are also universally know. This allows scientists to share information about a common species without a language barrier or simple confusion.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

