![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
285 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Inclusion of SS inc in GI
|
The amount of social security benefits that is taxed is dependent on whether be combination income AGI plus interests on tax exempt bonds and 50% of the social security benefit is greater than the threshold amount if the combined income is less than the threshold amount the amount tax is the lesser of 1) 50% or of the benefit or 2) 50% of the excess of the combined income over the threshold. if the combined income is greater than a threshold the amount taxed is the lesser of 1) amount calculated above 85% of the excess of the combined income over the threshold or 2) 85% of the benefit thus 85% of the benefit is the maximum out of tax that may be included in gross income
|
|
|
Inclusion of SS inc in GI |
The amount of social security benefits that is taxed is dependent on whether be combination income AGI plus interests on tax exempt bonds and 50% of the social security benefit is greater than the threshold amount if the combined income is less than the threshold amount the amount tax is the lesser of 1) 50% or of the benefit or 2) 50% of the excess of the combined income over the threshold. if the combined income is greater than a threshold the amount taxed is the lesser of 1) amount calculated above 85% of the excess of the combined income over the threshold or 2) 85% of the benefit thus 85% of the benefit is the maximum out of tax that may be included in gross income |
|
|
Tax exempt awards |
Generally the fair market value of the prizes and awards is taxable income. However an exclusion from income for certain prizes and awards applies when the winner is selected for the award without entering into a contest [i.e. Without any action on the individual's part] and when they assigns the award directly to a Government or charitable organization |
|
|
Wages and unemployment compensation |
Gross income includes all income unless it is specifically excluded in the tax code. Wages and all unemployment compensation are not excluded from being taxable; therefore, there are included in the taxpayer's gross income for tax purposes .... |
|
|
Accruable expense |
one in Which the services have been received/performed but have not been paid for by the end of the reporting. .... |
|
|
Scholarships |
Scholarships are non taxable for degree seeking student to the extent that the proceeds are spent on tuition, fee, books and supplies. .... |
|
|
Series EE bond interest |
|
|
|
Property settlements |
Non taxable |
|
|
Ira withdraw |
|
|
|
Premature distribution |
Generally a premature distribution (prior to retirement or other allowable age) from an individual retirement account is subject to a 10% penalty tax. Certain exceptions allowed. |
|
|
Exceptions to 10% tax penalty |
|
|
|
Circular 230 |
|
|
|
Rules governing practice before the IRS apply to |
|
|
|
Circular 230 duties and restrictions |
The information to be furnished the time in which matter should be addressed with the IRSAssistance from or to disbarred or suspended persons and former IRS employees Practice by former government government employees, their partners, and their associates Fees Conflicts of interests Advertising Fee informacion Best practices for tax advisers Other various issues including client refunds, notary, practice of Law, referral agreements, and standard email disclaimer used in practice .... |
|
|
Agency |
An agency is a legal relationship in which the principal appoints an agent to act on his behalf |
|
|
Creation of the agency relationship |
The principal must have capacity (not a minor ) Writing is not generally required. Unless you buy or sell land or agency is last more than a year Agent (capacity not required)Minor can be an Agent Consideration is not required for an agency relationship |
|
|
Implied duties agency relationship |
|
|
|
Basis of a non taxable stock split dividend |
The receipt of a non taxable stock dividend will require the shareholder to spread the basis of his original share over both the original and new shares received resulting in the same total basis, but a lower basis per share of stick held. |
|
|
Property acquired as a gift |
Generally retains the rollover cost basis as it had in the hands of the donor At the time of the gift. Basis is increased By any gift tax paid Attributable to the appreciation In the value of the gift. There is exception to the General role: if the fair market value at the date of the gift Is lower than the roll over cost basis from the donor The basis for the donee depends upon the donee's future selling price of the asset |
|
|
Alternate evaluation date |
The executor can elect to use an alternate valuation date rather than the date the defendant died to value the property included in the gross estate . Generally 6 mths after decedants death or the earlier date of sale or distribution |
|
|
The de minimise rule |
Must have written policy to expense certain property as of the beginning of the year for financial stmts. Max $5k |
|
|
Dividend from unaffiliates |
Allowed a 70% div received deduction |
|
|
Meals and entertainment |
Only 50 percent deductible |
|
|
Schedule M-1 |
|
|
|
Premiums paid on key person life insurance policy |
Deductible for GAAP not book |
|
|
Schedule M-2 |
Reconciliation of unappropriated earnings |
|
|
Organizational cost in the year of organization |
Max $5k deductible remainder must be amortized over 180 months |
|
|
Agents power to contractually bind principle |
|
|
|
Actual Authority |
|
|
|
Apparent authority |
Power that a third party reasonably believes agent has, based on principle's conduct or communication toward 3rd party Holding agent out under a specific title(e.g., an agent held out ad a store manager has apparent authority to do whatever store managers in a similar business in the area do Failure to give notice of agents termination |
|
|
Ratification of a previously unauthorized act |
|
|
|
Disclosed principle |
If principle existence and identity are known to the third party agent is not liable |
|
|
Partially disclosed or undisclosed principle |
If third party does not know that agent is an agent or does not know principle's identity, agent is liable under contract along with principle |
|
|
Tort liability |
GR: principle is not liable for torts commited by agent; only agent is liable |
|
|
Respondeat superior |
|
|
|
Employee |
Uses employer tools Compensated on a timely basis Subject to supervision of employer in the details of the work |
|
|
Independent contractors |
|
|
|
Subagent |
Is one who assists the agent in the performance of his or her duties. Owes a duty to both the agent and principle |
|
|
Writing requirement for agency |
|
|
|
Simple trust |
|
|
|
Order that stock basis is changed |
|
|
|
Computing shareholder baisis (s corp) |
|
|
|
Capital Assets |
|
|
|
Netting rules for short term capital gain/loss |
1. First offset against ST gain that would be taxable at ordinary income rates 2. LT cap gains from 28% rate group 3. 25% rate group 4. Lower (15%) rate. |
|
|
Netting rules for long term capital gain |
1. If there any long term capital losses (this includes any long term capital loss carry overs) from the 28% rate group, they are 1st offset against any net gains from the 25% rate group and then against any net gains from the 15% rate group 2. If there any long term capital losses (this includes any long term capital loss carry overs) from the 15% rate group , they are offset first against gains from a 28% rate group and then against Net gain from the 25% rate group |
|
|
Section 1231 |
Depreciable business property |
|
|
Machinery and equipment |
|
|
|
Real estate |
Mid month convention |
|
|
IRC sec 179 |
Tangible property acquired from an unrelated party for use in the active conduct of trade or business |
|
|
Mid- Quarter convention |
One attacks pair of places 40% or more of its property (other than certain qualifying real estate properties ) Into service in the last quarter of the taxable year the corporation must use the mid quarter convention for macrs depreciation purposes. |
|
|
Nonresident property |
Depreciated over 39 years straight line if placed in service after 1993 |
|
|
MACRS 5 yr property |
|
|
|
MACRS 7YR property |
|
|
|
Chap 7 |
A discharge discharges most debts whether or not there is a bankruptcy estate. |
|
|
Chap 9 |
Municipal debt adjustment |
|
|
Chap 7 |
Provides for liquidation of debtor estate Debtor may not obtain another bankruptcy for 8 yrs |
|
|
Chap 11 |
|
|
|
Chap 13 |
Adjustment of debts of individuals with regular income |
|
|
Bankruptcy estates |
Includes property the debt receives from a bequest, devise, inheritance, property settlement, divorce decreeor beneficial interest in a life insurance policy or death benefit plan within 180 days after the filing of petition. Any income generated by estate property ( rent interest dividend) after petition is filed.
Earned income after the case is generally excluded |
|
|
Excluded from Bankruptcy estate |
|
|
|
Involuntary petition for bankruptcy |
If fewer than 12 creditors: One or more with unsecured and undisputed claims that aggregate at least $15,775 more than the value of any collateral securing the claim If more than 12 at least 3 must join
The filing of a petition in bankruptcy invokes an automatic stay against all attempts to collect on most debts |
|
|
Chap 7 proceeding events |
|
|
|
Preferential treatment |
A transfer of the debtors property to or for the benefit of a creditor for an antecedent debt ar a time when the debtors wad insolvent and within 90 dausbof filing the bankruptcy petition constitutes a preference if the transfer gives the transferee more the transferee more than they would have obtained under the bankruptcy code Not a preferential payment if it is made in the ordinary course of business, according to the ordinary business terms, and for the purpose of repaying a debt incurred in the ordinary course of business |
|
|
Corporation capital loss |
A corporation may not deduct any NOL from ordinary income instead they can carry it back 3 years or forward 5 years as a short term loss against capital gains or 1231 gains |
|
|
Liquidating distribution |
When a corp liquidates and distributes assets to shareholders, gain is recognized to the extent that the fair market value of assets distributed to a shareholder exceeds the shareholder basis |
|
|
Type b reorganization |
The acquisition of a controlling interest (80%) by one corp in then stock of Another company solely for stock is. Tax free reorganization Stock of target corporation is acquired solely for the voting stock either the acquiring corporation or its parent |
|
|
Complete liquidation |
Shareholder should treat property received in complete liquidation of a corp as a payment for their stock. Must recognize capital gain or loss |
|
|
Type A |
A+B=C Generally no gain or loss is recognized by shareholders of various corp except to the extent they receive cash or other consideration in addition to the stock or security. In addition neither corporation pursuant to a tax free re org |
|
|
gain realized |
the realized gain is claculated as the fair market value of the property contributed for value in corporation less the shareholder's basis in property |
|
|
gain recognized |
the gain recognized is the gain that is reported (recognized) on the tax return of the taxpayer. If there is a realized gain and boot (e.g. cash) gain may be recognized, but only to the extent of boot. If there is no boot received, no gain is recognized for tax purposes |
|
|
tax basis in shares |
the shareholder's tax basis in the shares is generally equal to the shareholder's net book value of the property immediately before the contribution plus any cash contributed. Remember the transfer of property is generally a non-taxable event, which means that basis is the net book value of the shareholder. |
|
|
Debt exceeds the basis of the contributed property |
if debt exceeds the basis of contributed property -> taxable boot stemming from the debt relief on the contribution |
|
|
Benefits received from a traditional non-dedicutible IRA |
the principal, which was not decutible when contributed, is non-taxable. the accumulated earnings on the principal are taxable when withdrawn |
|
|
Personal Residence exclusion |
the sale of the taxpayer's personal residence is subject to an exclusion from gross income for gain. For qualified single individuals, the exclusion from tgain is $250K. |
|
|
Legal liabilities |
|
|
|
Civil actions |
|
|
|
Contract principles |
contract principles impose the obligation to prepare the tax return diligently and competently |
|
|
Tort Principles |
Tort Principles provide that professional has a duty to exercise the level of care, skill, and diligence commonly exercised by other members of the profession under similar circumstances. |
|
|
prove malpractice |
|
|
|
Breach of contract |
best defense - client failure to cooperate can only be sued by people privity to contract |
|
|
privity |
client and named third party beneficiary |
|
|
Tort |
|
|
|
Fraud |
punitive damages |
|
|
Negligence(ordinary) |
|
|
|
Element to sue for ordinary negligence |
|
|
|
Negligence ( Who do you owe a duty to) |
generally only to clients and any person or limited foreseeable class of persons whom the CPA knows will be relying on the CPA's work ( current creditor/ investors more than just privity minority - Ultramares decision - negligence is just like breach of contract - so only privity ( name 3rd party and client ) |
|
|
Fraud ( constructive) |
bad faith - punitive damages as well and more people can sue |
|
|
element for intentional misrepresentations |
b |
|
|
"reasonable care" |
due care is taken = no negligence = not liable |
|
|
Lack of reasonable care |
|
|
|
Lack of even slight care |
gross negligence or constructive fraud |
|
|
Actual Fraud |
Actual intent to deceive |
|
|
criminal fraud |
actual intent to deceive |
|
|
Compensatory Damages |
|
|
|
Duty of confidentials |
|
|
|
CPA privilege |
|
|
|
IRC Sec 7525 |
|
|
|
Federally authorized tax practicioner |
|
|
|
tax shelter |
primary purpose tax avoidance or tax evasion |
|
|
S - corp stock basis |
adjusted annually, as of the last day of the year order: 1. increased for income items and excess depletion 2. decreased for distributions 3. decreased for non-deductible, non-capital expenses and depletion 3. decreased for items of loss and deduction |
|
|
taxability of a non-dividend distribution |
the shareholder looks solely to stock basis (debt basis is not considered) |
|
|
s corp election revocation |
s corp status can be revoked if shareholders owning more than 50% of the total number of issued and outstanding shares consent. The specific percentage of voting and nonvoting shareholders is not considered , just the total. |
|
|
qualifications to be a S Corp |
|
|
|
trusts allowed to be in S Corps |
|
|
|
Partnership termination |
|
|
|
Qualified Stock Options |
1. options granted under a plan approved by the shareholders 2. options granted within 10 years of earlier of the date when the plan was adopted or approved 3. the options were exercisable within 10 years of the grant date and employees do not own more than 10% of the combined voting power of the corporation, parent, or subsidiary as of the date of the grant employee's do not pick up any income on the grant date, or exercised date. All income is picked up on the date stock is sold as capital income |
|
|
non-qualified plan |
|
|
|
incentive stock option |
|
|
|
employee stock purchase plan |
|
|
|
readily ascertainable value |
|
|
|
Employee taxation: readily ascertainable value of nonqualified stock |
|
|
|
Employee taxation: readily not ascertainable value of nonqualified stock |
|
|
|
employer taxation ( nonqualified option) |
deduct expense that employee reports income |
|
|
Employee taxation: ISO |
|
|
|
Employer taxation: ISO |
no tax deduction |
|
|
Employee taxation: ESPP |
not taxable as comp when granted or exercised capital gain/loss when sold stock basis is exercise price plus any amount paid for the option
|
|
|
Individual Income Tax Formula |
|
|
|
Filing requirement for individuals |
generally, a taxpayer must file return if his or her income is greater than:
|
|
|
Filing Status |
GR: use the status as of Dec 31 ( except in case spouse dies) |
|
|
Qualifying widow |
|
|
|
Multiple support |
|
|
|
Gross income |
all income whatever the source unless specifically excluded |
|
|
Wages |
also includes FMV of property received for services |
|
|
Life insurance proceeds |
Generally not taxable however the interest portion of deferred payout is taxable |
|
|
Interest Income |
Interest on state and federal tax refunds are taxable |
|
|
Dividends |
if distribution is from Earnings and profit it is considered a dividend * tax rate - 15% for most tax payers * tax free distirbutions: stock dividends, and life insurance dividends * maximum rate of tax 20% for qualified dividends |
|
|
state tax refunds |
taxable only if itemized in prior tax return |
|
|
annuities |
partially taxable ( interest), and partially not taxable (principle) Exceptions: annuitant outlives life expectancy |
|
|
unemployment comp |
taxable |
|
|
worker's comp |
nontaxable |
|
|
SS Income |
0 to 85 percent is taxable at various levels |
|
|
Schedule C |
* Sole proprietor
* Meals and Entertainment 50% deduct ( also applies to employee unreimbursed expenses) * prepaid interest can be deducted; but accural method must be used * bad debt actually written off maybe deducted only if accrual basis taxpayer * nondeductible expenses: personal expenses, federal taxes, and salaries paid to sole proprietor * self employment taxes are not deductible ( adjustment to AGI) * NOL - 2 years back/ 20 yrs forward |
|
|
Farming Income |
* income from farming activities treated similar to income from other business
* Schedule F |
|
|
Rent Income |
* passive
* prepaid rent or nonrefundable deposit is taxable when received Included on Sch E |
|
|
Individual txpyr: Capital Loss |
limited to capital income + $3K |
|
|
Trust |
Separate income tax paying entities Distributions made by trust are deductible to the trust - but taxable to the recipient |
|
|
Guaranteed pymts |
made by partnership to partners for services rendered to the partnership, that are deductible business expenses: * deductible on form 1065, Line 10 to arrive at partnership ordinary income * Included on schedule K-1 to be taxed as ordinary income to the partners |
|
|
Partnership NOL |
Ordinary losses are limited to basis and any at risk amount |
|
|
S Corp "at risk" Rule |
limit the deductiblity of t distributive shares of losses of an S corp to the amount the taxpayer has at risk as opposed to non recourse loans and could loss from activity |
|
|
Form 1120S |
Gain or loss from S corporation's sale of collectibles is separately reported on the Schedule K-1 of IRS form 1120S |
|
|
Form 141 |
if grantor is does not retain beneficial enjoyment of the corpus or the power to dispose of the trust income without approval or consent of any adverse party they are a separate entity for tax purposes and must file a Form 1041and issue K-1 to their beneficiaries |
|
|
Teachers adjustment to Gross income |
teachers can take a $250 adjustment to Gross income if two teacher they both get $250, so $500 in total. |
|
|
Regular IRA |
If you are rich and in a plan you can't participate in a regular IRA |
|
|
+/- Adj items to Income |
Adjustments for gain/loss Long-Term Contracts Installment Sales Excess Depreciation |
|
|
add-back PREFERENCES (increase income) |
Percentage depletion Private Activity -- Issued post 1986 ( tax exempt interest income) Pre-1987 ACRS excess deprecation |
|
|
Adj Current Earnings -/+ ( negative adjustment limited to past positive) |
Municipal Interest Organizational expense amortization Life insurance proceeds on key employees Difference between AMT and ACE depreciation Dividends received deduction under 20% |
|
|
AMT summary |
Regular taxable Income ALIE PPP MOLDD Alternative Minimum taxable income (AMTI) Alternative mini tax base x 20% Gross alternative mini tax Tentative mini tax Alt Mini Tax |
|
|
Intercompany gain/ losses |
are eliminated with consolidation original basis is maintained |
|
|
affiliated group |
means that a common parent owns
an affiliated group of corporations may elect to be taxed as a single unit, thereby eliminating intercompany gains and losses. |
|
|
Rules for consolidated returns |
|
|
|
Corporations that cannot file Consolidated tax return |
|
|
|
Home equity indebtedness |
Debt other than acquisition debt that is secured by a qualified residence to the extent that it does not exceed the fmv of residence less acquisition debt |
|
|
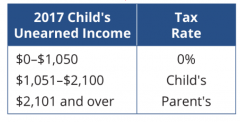
Kiddie Tax |
|
|
|
Alternative minimum tax ( individuals) Adjustments |
|
|
|
Credits that can reduce AMT |
Foreign tax credit Adoption credit Child Tax credit Contributions to retirement plans credit Residential energy credit |
|
|
Net Investment Income Tax |
|
|
|
political contributions |
are not charitable donations and are not deductible |
|
|
Wash Sale |
|
|
|
Like-Kind |
Same type of investment (e.g. realty for realty, personalty for personalty, assuming the personal property falls within the same asset class for tax depreciation purposes) |
|
|
Calculation for " Recognized Gain with no Boot" |
Gain/loss realized: Amount realized= Fair market value of auto received -- Adjusted basis of auto given up Gain/loss recognized: amount recognized = the less of gain realized or boot received Basis of new property: New basis = adj basis of property given up + gain recognized |
|
|
Homeowner's exlusion |
|
|
|
Involuntary conversion |
Gains realized on involuntary conversion of property. Tax payers reinvestment of the involuntarily received proceeds restores him to position he held prior to the conversion if you don't spend all of the proceed it is considered boot. must recognize gain on it |
|
|
Divorce settlement |
when divorce settlements provide for lump sum payments or property it is a non-taxable event |
|
|
Exchange of like kind property |
property used in trade or business or held for investment ( except inventory, stock securities, partnership interests, goodwill/going concern value, and real property in different country) |
|
|
Installment method |
is a tax method of reporting gains for sales made by a "non-merchant" in personal property and "non-dealer" in real estate when part of the payments are received in a tax year after the year of the sale. Under the installment method, revenue is reported over the period in which cash payments are received. |
|
|
Treasury stock |
when a corp issues, buys back and reissues stock transaction is exempt from gain/loss recognition |
|
|
Related party gain/loss |
disallowed |
|
|
personal losses |
non losses is recognized on nonbusiness disposal or loss. An itemized deduction maybe available in the category of casualty and theft |
|
|
Gain realized on Like Kind Exchanges |
|
|
|
Basis of new asset on like kind exchanges |
|
|
|
inherited property |
|
|
|
Individual tax payer estimated taxes |
in computing the amount of estimated payments due, an individual taxpayer may choses between the annualized method or the prior year method unless the taxpayer's AGI exceeds $150,000 then they must use 110% of last year's tax |
|
|
annualized method |
90% of current year's tax |
|
|
Foreign Tax Credit |
A taxpayer may claim a credit against federal income taxes due for foreign income taxes paid to a foreign country or a US possession. There is a limitation on the amount of the credit an individual can obtain. |
|
|
Adoption Tax credit |
|
|
|
Child and dependent Care Credit |
|
|
|
Child and dependent care credit computation |
the credit is computed by using the lowest of :
|
|
|
Eligible expenses |
|
|
|
Child and dependent care credit computation |
) if the taxpayer has two or more qualifying dependents |
|
|
Credit for ederly and/or permanently disabled |
15% of eligible amount S - 7.5K MFJ-10K MFS- 5K |
|
|
Refundable Credits |
|
|
|
Earned income tax credit |
|
|
|
Earned income tax credit Requirements |
|
|
|
Taxation of a C corp |
|
|
|
Corporate Alternate Mini Tax |
|
|
|
Contributions to a corporation in exchange for stock |
Formations are generally nontaxable if the 80% rule is met |
|
|
Corporate distribution |
|
|
|
Stock dividends |
generally not taxable to the shareholder ( it depends on whether the shareholder had a choice of receiving cash or other property) |
|
|
Corporate liquidation |
|
|
|
Basis of property contributed to corporation in exchange for stock |
There is no gain or loss to the corp issuing stock in exchange for property for the issuance of stock. the general rule is that the basis of the property received from the transferor/SH is the greater of:
|
|
|
Accrual method |
will be required by tax shelters, large C corps and manufactures. |
|
|
Charitable Contribution deduction for Corp |
|
|
|
Cost of organizing corporation |
|
|
|
Cost of selling stock |
are not expensable/amortizable |
|
|
Accuracy-related penalties |
apply to the portion of tax underpayments attributable to negligence or disregard of tax rules and regulations as well as to any substantial understatement of income tax |
|
|
The negligence penalty |
with respect to understatement of tax is an accuracy based penalty for negligence or for disregard of tax rules and regulation |
|
|
Exempt property |
an individual debtor is entitled to exempt certain property under the bankruptcy code, but states can opt out and supply their own exemptions |
|
|
Preferential payment |
a transfer for the benefit of a creditor or account of an antecedent debt made within 90 days ( or one year for insiders) prior to filing the petition while the debtor was insolvent and the creditor received more than the creditor would receive under the bankruptcy code. Contemporaneous exchanges for new value are excluded, as are payments of ordinary business bills and payments by consumer debtors of less than $600 |
|
|
Fraudulent transfers |
any transfer for less than equivalent value made with the intent to hinder, delay or defraud creditors. The Trustee has the power to set aside fraudulent transfers made within two years of the filing date. |
|
|
Claims against the estate |
|
|
|
Miscellany |
The trustee can serve as a professional ( e.g. tax preparer) for the estate if the court approves and may receive compensation |
|
|
Donation of services |
Value of services donated not deductible |
|
|
Exoneration |
Is the right of a surety prior to payment To get a court order demanding the debtor pay |
|
|
Contribution |
The right of a co surety to demand pro rata payment from other co surities not available prior to payment |
|
|
Reimbursement |
The right of a surety to recover from the debtor payments made to the creditor. Not available prior to payment |
|
|
Charitable contributions of property |
if proerty is capital asset help for over a year before being contributed, it qualifies to be deducted at the higher FMV without capital gains being recognized 30% of AGI limitation applies |
|
|
Fraud penalties |
For the IRS to prevail in a case with a criminal penalty, the IRS must prove beyond a reasonable doubt that taxpayer willfully and deliberately attempted to evade tax |
|
|
FICA Taxes |
are fully deductible on a schedule C |
|
|
Passive activity |
activity that tax payer does not materially participate in |
|
|
passive activity losses |
|
|
|
mom and pop exception |
taxpayers who own more than 10% of rental activity, have modified AGI of under 100K and have active participation may deduct up to 25K of net passive losses phase out provision from 100-150K |
|
|
Chapter 7
|
Gives debtor a fresh start
|
|
|
Chapter 7 - Objection to discharge
|
Reason to deny a discharge of all debts. the reasons that commonly appear on the exam: the debtor is not an individualfraudulent transfers of propertyunjustifiably failed to keep adequate booksreceived a prior discharge within eight years commision of bankruptcy crim
|
|
|
Chapter 7 - Execptions to discharge
|
There are a few execeptions to discharge: debt arising from willful and malicious injury, alimonydebts arising from fraudtaxeseducational loansdebt undisclosed at bankruptcy
|
|
|
Chapter 7 - Reaffirmation of discharged debts
|
Allowed if the agreement to reafffirm was made before the granting of discharge
|
|
|
Chapter 7 - revocation of discharge
|
creditor or trustee may request a revocation if the debtor obtained the discharge fraudulently, the debtor acquired property that would consititute property of the estate and fraudulently failed to disclose, the debtor failed to obey a court order, or debtor could not explain why the debotr failed to make documents available to the auditor
|
|
|
Chapter 7 - Distribution of debtor's estate
|
1. Secured claiments - paid first to the exent of the value of collateral2. priority claim - paid next in specific order3. General creditior - paid last
|
|
|
Chapter 7 - priority claimants
|
1. Support obligations to spouse and child2. Adminstrative expenses3. Involuntary cas Gap claims4.Wage claims of each employee up to $12,850 earned within 180 days prior to bankruptcy 5. Employee benefit plan contributions for each employee arising within 180 days prior to bankruptcy, up to $12,850 redced by wage claims6. Grain farmers' and fishermen's claim against storage/ processing facilities up to $6,3257. Consumer deposits up to $2,8508. Tax claims9. Personal injury claims arising from intoxicated drivers
|
|
|
Chapter 11
|
Create a creditor committee or a stockholder's committeeTrustee generally is not appointed, but can be when there is fraud, dishonesty, incompetence or gross mismanagement by debtor
|
|
|
Chapter 11 - reorganization plan
|
unless a trustee is appointed, the debtor has an exclusive right to file a plan during the first 120 days afte rthe order for relief is effectiveCreditors may file a plan if a trustee has been appointed; the debtor has not filed a plan within 120 days; or the debtor has filed a plan but has not obtained acceptance of the plan by every impaired class within 180 days of the entory of the order of relief
|
|
|
Chapter 15
|
US court can recognize as a foreign main proceeding ( ie a country where the debtor's main interest are located) or a foreign non-main proceeding ( ie a country other than one whre the debtor's main interest are locatedAutomatic stay takes effect upon recognition of foreign main proceeding prohibits discrimination against foreign creditors and requires cooperation with foreign courts and representatives
|
|
|
Attachment
|
Creditor forwarns debtor that if they default they will "reposses" property in a oeaceful mannerprotect yourself from the debtorallows creditor to seize property from debtor without getting a court order
|
|
|
perfection
|
notice to the world that creditor has security interest in collateral and because of this notice, give the creditor the right in the collateral superior certain 3rd parties
|
|
|
types of collateral
|
goodsintangible/ semi intangibleinvestment propertyproceeds
|
|
|
Consumer goods
|
depends on what the debtor is using it for. Automatic perfection if there is a PMSI creditor
|
|
|
Investment property
|
You have to controll it
|
|
|
Purchse money security Interest
|
Has priority over all other types of security in the same collateral, if PMSI is properly perfected\
|
|
|
Alt Min Tax exemption
|
$40Kit must be reduced by 25% of the amout by which AMTI exceeds 150K Exemption is completely phased out at $310K
|
|
|
personal holding company tax
|
paid in addtion ot its regular and alt min taxes
|
|
|
amt calculation
|
AMTI base * 20%compare tentitive mini tax to regular tax liability
|
|
|
tentative min tax credit
|
can only be used to offset a corporation's regular income tax liabilityamt liabilities will result in additional minim tax credit carryforward
|
|
|
personal holding company
|
|
|
|
Additional tax assessed on PHC
|
addtional 20% on net income not distributedtaxable income must be reduced by federal income taxes and net long term capital gain net of tax to determine the undistributed personal holding company income prior to the div paid deduction
|
|
|
Chapter 11 Plan confirmation
|
only the court can confirm a plan creditiors and security interest vote whether to accept the plan unimpaired parties such as secured creditors are presumed to have affirmed, so their vote is not necessary
|
|
|
Chapter 11 Plan affirmation
|
plan needs to be affirmed by 2.3 of the interests ( e.g. 2/3 of the oustanding shares) through the cram down provision of . the Bankruptcy Code (BC) a plan may be confirmed by a court even if only impaired class votes to affirm the plan
|
|
|
Alimony
|
can not be discharged in bankruptcy
|
|
|
Dischargeable in bankruptcy
|
Contract claimsdebt owed to secured creditors beyond the value of the collateral ( treated like any other unsecured debt) Debts arising from negligent conduct are dischargeable in bankruptcy ( if the auto accident arose from drunk driving or injuries were willful, debt would not be discharged)
|
|
|
Bankruptcy Code Section 727
|
sets out the reasons for revoking a discharge. the grounds include failing to answer material questions on the bkrpty petition if the question has been approved by the court, unless the fifth amendment privilege against self incrimination is appropriately claimed
|
|
|
Foreign enity
|
May file an ancillary proceeding under chap 15, and may also file a proceeding under chapt 7 and 11 the automatic stay arises after a petiion for recognition is granted by the court
|
|
|
Limited Partnership
|
Limited partners generally have no liability beyond their investment and unpaid capital commitments. Limited partners generally have no right to participate in management of the businessIn some states if they manage or control, they are liable to any party who reasonably beleive that they were a general partner must have at least one GP
|
|
|
Partnership
|
partners have unlimited personal liability for all contracts of the partnerships and all torts commited y other partnerships within the scope of partnership business. also absent agreement to the contrary, partners have equal rights to manage the business
|
|
|
Limited liability Partnership
|
Unless otherwise agreed, patnership have the right to participate in the management of the business, just as partners in a general partnership have the right to manage Partner in LLP is generally not liable for the debt or contracts of business. A business liabilty partnership does not pay federal income tax. the limited partnership has " flow through taxation"
|
|
|
Limited Liability Company
|
|
|
|
Sole Proprietorship
|
unlimited liability for obligations of the business
|
|
|
Corporation
|
Pays federal income taxshareholders have no liability beyon their investment and unpaid captial commitments. Shareholders generally have no right to manage the corporationshareholders do have the right to elect and remove directorsright to vote for fundamental changes in corporation ( dissolution, amendments to the artivles, mergers, consolidations, compulsory share exchanges, and sale of substantially all the corproations assets outside the ordinary course of business
|
|
|
Required to file with state
|
Limited partnershipLimited liability company Corporation
|
|
|
Joint venture
|
an association of persons or entities with the intent of engagaing in a single business ventrue for profit.The legal requirement and consequence and advantages and disadvantages of forming a joint venture generally idential to those of a general partnership
|
|
|
Cumulative preferred stockholder
|
entitled to receive a dividend for the current year and all prior years for which the preferred dividend was not paid before any dividend is paid to the common stockholders
|
|
|
business manager
|
|
|
|
Termination of actual authority
|
Actual authority automatically terminated by law if:
|
|
|
Create a contract under Common Law
|
Identity of offeree and subject matterprice to be paidtime of performancequantity involvednature of work to be performed
|
|
|
Common law
|
Services or real property
|
|
|
Statute of Fraud: Contracts that requiring a writing
|
must be signed by to be enforacable1.marriage2. cannot be performed in a year3. Land ( real property for sale/ lease) 4. Contracts ny executors or similar rep to pay estate debts out of personal funds5. goods more than $5006. Contracts to act as surety ( pay the debt of another)
|
|
|
Death of offeror
|
death of an offer prior to acceptance terminates the offer by operation of law without notice to the offeree
|
|
|
unilateral contract
|
promise is exchanged for an act
|
|
|
statue of limiation for an alleged breach of contract
|
generally begins on the date of alleged breach. refers to the time period in whcih case must be filed time period varies from state to state depending on type of case
|
|
|
Material breach of contract
|
generally discharge the nonbreaching party
|
|
|
novation
|
the agreement is unchanged but one of the orignal parties is released and a new party is substituted int heir place
|
|
|
substituted contract
|
the orginal parties are both released from orginal agreement, but both are bound to new agreement
|
|
|
Consequential damages
|
recoverable for breach of contract only to the extent the are foreseeable. In every case, a nonbreaching party has a duty to mitigate damages- a duty to make reasonable effort to cut down on losses resulting from breach. failure to do so will preclude party from collecting damages that may have been avoided
|
|
|
unilateral mistake
|
a defense to a contract if the nonmistaken party knew or should have known of the mistake
|
|
|
parol evidence rule
|
prohibits introduction of prior written statements to vary the terms of a fully intergrated contract, but it does not bar the introduction of subsequent oral or written agreements
|
|
|
Contract conditions
|
Can be precedent, subsequent, or concurrent
|
|
|
undue influence
|
a person in a position of trust or confidence takes unfair advantage of the relationship such that the other party's free will to contract is overcome
|
|
|
Domestic Production Deduction(DPD)
|
Overview: a business may deduct a specific %-age of their qualified production activities income.
|
|
|
Domestic Production Deduction limitation
|
the deduction may not exceed 50% of the w-2 wages paid by the corporation for the year
|
|
|
Calc for DPD
|
the deduction is 9% of the less of : 1 - qualified production activties income(QPAI) 2 - Taxable income (disregarding the QPAI deduction)
|
|
|
QPAI
|
Domestic production gross receipts --------------------------------------------------------------Qualified production activities income
|
|
|
Domestic production gross receipts
|
derived in the US manufactured, produced, grown, extracted, constructed, engineering services, architecutral services
|
|
|
Charitiable Contribution for C corp
|
max deduction of 10% of adjusted taxable income limitationcarried forward for 5 yrs any accural must be paid by april 15thno political gifts
|
|
|
Adjusted taxable income limiation
|
Chartiable contributions for C corps Calculated before the deduction of : chartiable contribution deductiondiv-received deductionany NOL carrybackcapital loss carrybackU.S. production activities deduction
|
|
|
Business Losses casualty losses related to business C corp
|
100% Deductible as ordinary loss or capital loss depending on asset type Partially destroyed : loss is limited to lesser ofthe decline in the value of the propertythe adjusted basis of the property immediately before the casuality Fully destroyed (NBV) amount of loss is the adjust basis of the proporty
|
|
|
Organizational Expenditures and Start up Costs
|
$5K deductionExcess is amortized over 180 mths
|
|
|
Allowable Org and start up costs
|
fees paid for:Legal servicesdrafting the corp charter, bylaws, minutes of org meetingsaccounting servicesincorporation fees
|
|
|
Disallowed Org and start up costs
|
issuing and selling stockcommisionsunderwriter feescost incurred in transfer of assets to corp
|
|
|
Purchased good will
|
amortized on straight line basis over 15 years
|
|
|
Dividends- received deduction
|
First corp must be taxed owned 45 days before or after
|
|
|
personal service corporation
|
accounting, law, consulting, engineering, architecture, health and actuarial science
|
|
|
regulated investment company
|
registared under the investment compay act of 1940some venture capital companiesat least 90% of gross income must be qualified investment source incomemust distribute 90% of dividends and interest incomecorporation is not taxed on amounts distributed to shareholders
|
|
|
accumulated earnings tax
|
imposed on corporations whose accumulated (retained) earnings is in excess of $250K if improperly retained instead of being distributed to shareholders. personal service corps are only entitled to $150K
|
|
|
Elements of Constructive fraud
|
|
|
|
Ultramares
|
limits accuontant's liability for negligence to (1) parties in privity(2) intended 3rd party beneficiaries parties who ware merely "foreseen" cannot recover
|
|
|
scienter
|
knew that the statement was wrong or recklessly disregarded the truth
|
|
|
Non residential real property using MACRS
|
straight line method over 39 years
|
|
|
MACRS 5 year property
|
Autombileslight truckscomputerstypewriterscopiesduplicating equipment
|

