![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
60 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
What is it?
Who & When & How Sequela |
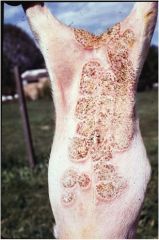
Dermatosis Vegetans
Who: Young Landrace pigs When: 2-3 months (could also be at birth) How: Auto Recessive Sequela: Hoof Malformation, Gian Cell Pneumonia |
|
|
What is it? AKA?
How? Sequela? |
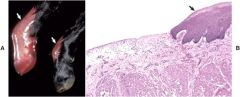
Epitheliogenesis Imperfecta
AKA: Aplasia cutis How: Inherited genetic mutation causes failure of stratified squamous epithelium of skin, adnexa & / or oral mucosa to fully develope Sequela: Death from infection of dehydration |
|
|

What (AKA) or What?
What's the difference? Standard in? |
Congenital Alopecia (AKA: Atrichia) = absence of hair from skin that is normally haired
Or Hypotrichosis = less than normal amount of hair Both can be standard in Sphinx cats |
|
|

Name an Integument condition found in this breed
|
Chinese Shar Pei
Mucinous Degeneration (Increased amount of amorphous, stringy, granular, basophilic material that separates, thins or replaces dermal collagen fibrils & surrounds blood vessels & appendages) |
|
|
|
What's characterized by increased amorphous, stringy, granular, basophilic material that separates, thins or replaces dermal collagen fibrils & surrounds blood vessels & appendages?
How would you demonstrate it? |
Mucinous Degeneration
Use Hale's or Alcian blue stains for mucin, b/c they stain the acid mucopolysaccharides. |
|
|
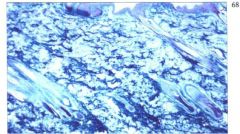
what is it?
what are the characteristics? what was it stained with? who is more prone to it? |
It is Mucinous Degeneration
Charcterized by: amorphous, stingy, granular, basophilic material separating, thinning or replacing dermal collagen fibrils & surrounds blood vessels & appendages Stain with: stains for acid mucopolysaccharide (Hale's & Alcian blue) Shar Pei |
|
|
|
Mucinous Degeneration AKA
|
Myxedema
Mucoid Degeneration Myxoid Degeneration Mucinosis |
|
|
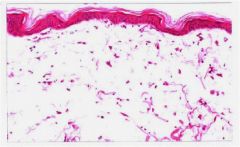
What is it?
Describe it Who is this normal in? |
Mucinous Degeneration
Dermal collagen separated by lightly basophilic ground substance representing increased glycosaminoglycan (mucin) Normal in Shar pei dog |
|
|
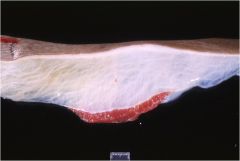
What is it?
how do you recognize it? |
Dermal Edema
Dilated lymphatics (not visible in normal skin) Widened spaces between blood vessels & perivascular (perivascular edema) or dermal collagen (interstitial edema) |
|
|
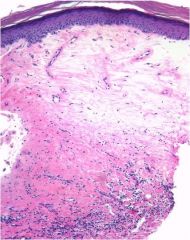
What is it?
How do you recognize it? |
Dermal Edema
Dilated lymphatics (not visible in normal skin) Widened spaces between blood vessels & perivascular (perivascular edema) or dermal collagen (interstitial edema) |
|
|
|
What is pigmentary incontinence?
|
Presence of melanin granules free w/in subepidermal dermis & w/in dermal macrophages (melanophages)
|
|
|
|
When would you see pigmentary incontinence?
|
Any process that damages stratum basal & basement membrane zones -especially hydropic degeneration of basal cells
|
|
|
|
List 3 Dermal Changes Secondary to Injury
|
1) Pigmentary Incontinence
2) Dermal Edema 3) Mucinous Degeneration |
|
|
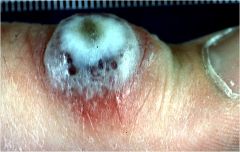
What is it?
What kind of lesion does it cause? |
Contageous Ecthyma
Causes crusts |
|
|
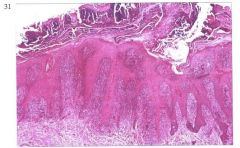
What is it?
What's it made of? Subclasses? Diagnostic for? |
Crust -a consolidated surface mass
Made of keratine, serum, cellular debris, microorganisms Subclasses: Serous -mostly serum Hemorrhagic -mostly blood Cellular -mostly inflammatory cells Exudative (serocellular) -mix of serum & inflammatory cells Dx for Dermatophilus congolensis |
|
|
|
What's crust?
|
A consolidated, surface mass.
Made of keratine, serum, cellular debris, & microorganisms |
|
|
|
What are the different kinds of crusts?
|
Serous -mostly serum
Hemorrhagic -mostly blood Cellular -mostly inflammatory cells Exudative (serocellular) -inflammatory cells & serum |
|
|

What is it?
|
Leukotrichia -decreased pigment of hair
Why not leukoderma? |
b/c leukoderma = decreased pigment of skin. Dog's skin is black.
|
|
|
Leukoderma?
|
Decreased pigment of skin
|
|
|
|
What are the ordinary parts or elements of worship?
|
• Reading of Scripture, preaching and hearing the Word, singing, prayer, administration of the sacraments.
• "The reading of the Scriptures with godly fear, the sound preaching and conscionable hearing of the Word, in obedience unto God, with understanding, faith and reverence, singing of psalms with grace in the heart; as also due administration and worthy receiving of the sacraments instituted by Christ, are all parts of the ordinary religious worship of God: beside religious oaths, vows, solemn fastings, and thanksgivings upon special occasions, which are, in their several times and seasons, to be used in an holy and religious manner. "-WCF 21.5 |
|
|
|
Pigmentary incontinence
|
loss of melanin from basal layer due to damage and accumulation of macrophages in superficial dermis
|
|
|
|
Possible causes of pigmentary incontinence
|
Lupus Erytheatosus or Vitiligo
|
|
|
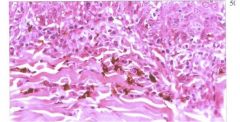
What is it?
How is it caused? |
Pigmentary incontinence
Loss of melanin from basal layer due to damage & accumulation of macrophages in superficial dermis |
|
|
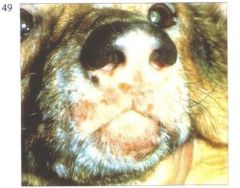
what is it?
|
Depigmentation
|
|
|

What is it?
What causes it? |
Familial Vitiligo
-immune cells attack melanocytes |
|
|
|
Types/Causes of Hypopigmentation
|
Lupus Erythematosus (AutoImmune, characterized by hydropic degeneration of basal cells)
Vitiligo Toxic -monobenzyl ether of dihydroquinone damaging melanocytes Inflammatory disorder affecting melainization or destroys melanocytes Hormonal Disorder |
|
|
|
Lentigo
|
Typer of Hypermelanosis with increased number of melanocytes in epidermis
Can be Focal or Diffuse Confined to Stratum Basale or Found Throughout Epidermal Layers Common, non-Dx in chronic inflamm & hormonal dermatoses & some developmental & neoplastic disorders |
|
|
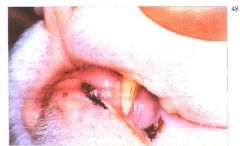
What is it?
|
Hypermelanosis (Lentigo)
|
|
|
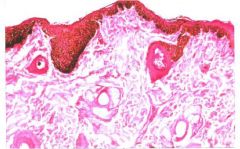
What is it?
|
Hypermelanosis (Lentigo)
Increase number of melanocytes confined to epidermis |
|
|
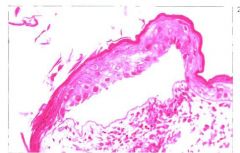
What is it?
Charcteristics? |
Vesicle (<1cm)
Bullae (>cm) Microscopic & Macroscopic fluid filled, relatively acellular space within or below epidermis |
|
|
|
Acantholysis AKA
|
Dyshesion
Desmolysis Desmorrhexis |
|
|
|
What is Acantholysis?
|
Loss of cohesion btw epidermal cells resulting in intraepidermal clefts, vesicles & bullae
|
|
|
|
What are Acantholytic cells?
|
Free Epidermal cells in the vesicle
|
|
|
|
What is it?
What's at the red arrow? |
Acantholysis
Acantholytic cell (free floating epithelial cell/keratinocyte) entering bullae/vessicle |
|
|
|
Acantholysis AKA
|
Dyshesion
Desmolysis Desmorrhexis |
|
|
|
What is Acantholysis?
|
Loss of cohesion btw epidermal cells resulting in intraepidermal clefts, vesicles & bullae
|
|
|
|
What are Acantholytic cells?
|
Free Epidermal cells in the vesicle
|
|
|
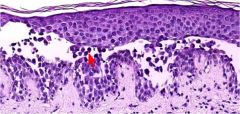
What is it?
What's at the red arrow? |
Acantholysis
Acantholytic cell (free floating epithelial cell/keratinocyte) entering bullae/vessicle |
|
|
|
Primary causes of Acantholysis
|
Production of autoantibodies against intercellular cement substance
|
|
|
|
Secondary causes of Acantholysis
|
Severe Spongiosis/Intercellular Edema (any acute or subacute inflammatory dermatosis)
Ballooning degeneration/Intracellular Edema (viral infection) Proteolytic enzymes released by neutrophils (bacterial & fungal dermatoses) Neoplastic transformation (squamous cell carcinoma) |
|
|
What is it?
|
Acantholysis
|
|
|
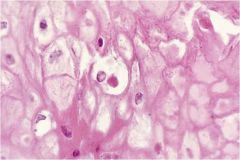
What is it?
What's it characteristic of? |
Ballooning Degeneration
Characteristic of Pox viruses |
|
|
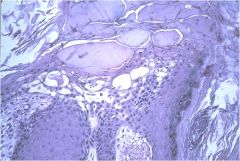
What is it?
What's it characteristic of? |
Ballooning degeneration
characteristic of Pox virus |
|
|
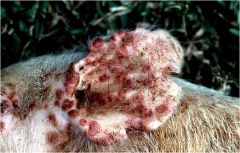
What is it?
What are some characteristics of it? |
Swine Pox
Ballooning degen & intracytoplasmic inclusions |
|
|
|
What's ballooning edema?
|
Type of epidermal edema
Intracellular fluid accumulates in superficial keratinocytes Cells swell & lose intercellular adhesions Characteristic in Pox & ParaPox viruses |
|
|
|
Intracellular edema AKA
|
Hydropic degeneration
Vacuolar degeneration |
|
|
|
Characteristics of Intracellular edema
|
Increased size, cytoplasmic pallor, displacement of nucleus to periphery of affected cells
Specific to basilar layer If severe -intraepidermal vesicles Common, nonDx feature of any acute or subacute inflammatory dermatosis |
|
|
|
What looks similar to Intracellular Edema?
|
Freezing artifact & delayed fixation artifact can be confused for intracellular edema
|
|
|
|
Intracellular edema AKA
|
Hydropic degeneration
Vacuolar degeneration |
|
|
|
Characteristics of Intracellular edema
|
Increased size, cytoplasmic pallor, displacement of nucleus to periphery of affected cells
Specific to basilar layer If severe -intraepidermal vesicles Common, nonDx feature of any acute or subacute inflammatory dermatosis |
|
|
|
What looks similar to Intracellular Edema?
|
Freezing artifact & delayed fixation artifact can be confused for intracellular edema
|
|
|
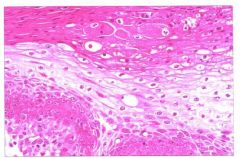
What is it?
Characteristics? |
Intracellular edema
Swollen cells Nucleus in periphery In basilar layer Cytoplasmic pallor |
|
|
|
Intercellular edema AKA
|
Spongiosis
|
|
|
|
Intercellular edema/Spongiosis Characteristics
|
Widened intercellular spaces with accentuation of intercellular bridges
Severe may lead to rupture of intercellular bridges & form spongiotic vesicles w/in epidermis Severe spongiotic vesicle formation may "blow out" basement membrane to look like subepidermal vesicles Common, NonDx of any acute/subacute inflammatory dermatosis |
|
|
|
Common cause of Intercellular edema/Spongiosis
|
Staphylococcus or Malassezia
|
|
|
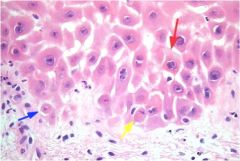
What is it?
|
Intercellular edema / Spongiosis
|
|
|
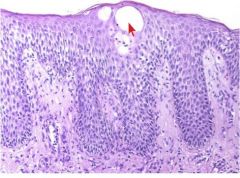
What is it?
What is it from? |
Spongiotic vesicle
Severe intercellular edema / spongiosis that lead to rupture of intercellular bridges & form spongiotic vesicle w/in epidermis |
|
|
|
2 Hormones that Promote hair growth
|
Thyroid & Growth Hormones
|
|
|
|
What are the Epidermal Responses to Injury?
|
Edema (Intraepidermal or Interepidermal)
Acantholysis Hypomelanosis Hypermelanosis Crusting |
|
|
|
What are the Dermal Responses to Injury?
|
Pigmentary incontinence
Edema Mucinous Degeneration |
|

