![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
22 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
How are inhaled dusts cleared from the lungs?
|
* Deposited dusts are cleared via macrophages and the mucociliary escalator
* Water-soluble stuff dissolves * Macrophages transport insoluble particles to the lymphatic system |
|
|
What are the 4 main types of occupational lung disorders?
|
1) Chemical Pneumonitis
2) Occupational Asthma 3) Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis 4) Pneumoconiosis |
|
|
What is the basic pathologic mechanism for Chemical Pneumonitis?
|
Chemical Pneumonitis is the direct injury of lung parenchyma by a toxic agent.
* SXS begin w/in HOURS of exposure |
|
|
What is the basic pathologic mechanism for Occupational Asthma?
|
Occupational Asthma is the inhalation of an antigen to which the person has been previously sensitized.
* IgE-driven response * Inflammation & Edema of the airway |
|
|
What is the basic pathologic mechanism for Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis?
|
Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis is a complex immunologic reaction involving months/years of exposure.
* Slowly progressive * May lead to diffuse interstitial fibrosis * Predominantly mononuclear infiltrate |
|
|
What is the basic pathologic mechanism for Pneumoconiosis?
|
Pneumoconiosis follows exposure to inorganic dusts
* Represents overwhelmed cellular response mechanisms * Months/years of exposure before clinically evident disease |
|
|
Where do pneumoconiotic lesions tend to accumulate?
|
1) Lymphatic origins
2) Near respiratory bronchioles 3) Beneath the pleura |
|
|
Name two dusts that may induce pulmonary fibrosis.
|
* Silicone dust
* Coal Dust * Asbestos |
|
|
What dust does NOT induce pulmonary fibrosis, but is simply a marker of exposure?
|
Inhalation of Iron Dust results in an asymptomatic reaction.
|
|
|
What size particles will penetrate into the alveoli and lodge, causing problems?
|
About 1 micron/micrometer.
|
|
|
Describe the characteristic pathologic features of siderosis.
|
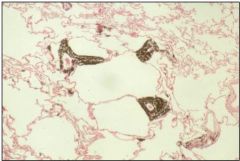
Iron accumulates in macules adjacent to respiratory bronchioles – can be visualized as fine nodules
|
|
|
escribe the characteristic pathologic features of silicosis.
|

* Nodular fibrosis in which the nodules are formed of dense, laminated collagen
* Nodules are also found in regional lymph nodes * Nodules are often partially calicified + visible on x-ray * Sometimes developes into progressive fibrosis |
|
|
Describe the characteristic pathologic features of asbestosis.
|
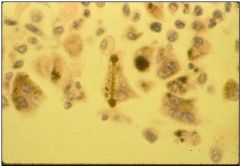
* Asbestosis is caused by exposure to fibrous silicates.
* Diffuse interstitial pulmonary fibrosis * Worse in lower lung zones + near pleura |
|
|
What's the difference between "simple" and "complicated" pneumoconioses?
|
Simple:
* Nodular fibrosis * Marker for exposure * Some risk of progression Complicated: * Conglomeration of nodules * Symptomatic w/restrictive physiology * May progress to pulmonary fibrosis |
|
|
Describe the natural history of Silicosis.
|
Silicosis:
* May be acute, typically over 20 years * 18% crystalline silica dust |
|
|
Describe the natural history of Asbestosis.
|
Asbestosis
* 10-25 year latency * High levels of exposure req'd. |
|
|
What are the two types of Asbestos particles? Which is more dangerous?
|
* Serpentine
* Amphibole (far more toxic) |
|
|
What's necessary to make the diagnosis of Asbestosis?
|
1) Pulmonary Fibrosis
2) Asbestos Particles |
|
|
On radiogram, pulmonary fibrosis looks like what other lesion?
|
Pulmonary neoplasm
|
|
|
How do mesotheliomas appear histologically?
|
Mesotheliomas recapitulate all stages of serosal development
|
|
|
What inhaled particle will really increase the risk of developing a mesothelioma?
|
Amphibole Asbestos
|
|
|
How do mesotheliomas progress?
|
The grow and spread across the pleural surfaces.
|

