![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
25 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What brain region is affected by Alzheimer's Dementia?
|
Cortical Regions
Affect: Frontal, Temporal, Parietal Spares: Occipital |
|
|
What are the symptoms and course of Alzheimer's Dementia?
|
* Progressive cognitive impairment
2) Loss of formation of new memories 3) Progresses to multiple domains |
|
|
What are the pathologic hallmarks of Alzheimer's Dementia?
|
1) Excessive Aβ peptide production and deposition of amyloid
2) Tau changes with neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs) |
|
|
Are there genetic abnormalities associated with Alzheimer's Dementia?
|
* Most AD is sporadic
* Auto. dominant mutations in Presinilin 1 & 2 |
|
|
What are the symptoms and course of Parkinson's disease?
|
1) Progressive motor impairment
2) Bradykinesia 3) Resting Tremor 4) Rigidity 5) Late-stage dementia |
|
|
What are the neuronal systems affected in Parkinson's Disease?
|
Parkinson's results in
1) Loss of DOPAMINERGIC neurons in the Substantia Nigra 2) Degeneration of the Nigrostriatal Pathway |
|
|
What are the microscopic changes associated with Parkinson's?
|
Substantia Nigra neurodegeneration with LEWY BODY formation.
|
|
|
Is there a genetic component to Parkinson's?
|
Most cases are sporadic. Rare mutations in alpha-synuclein.
|
|
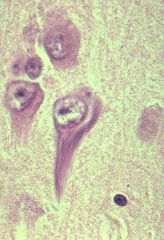
What's the pathology?!?
|
Neurofibrillary Tangles Associated with Alzheimer's Disease
|
|
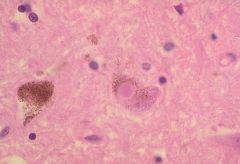
What's the pathology?!?
|
Lewy Body associated with Parkinson's Disease
|
|
|
What are the two major neurodegenerative diseases affecting the Basal Gangia?
|
1) Parkinson's
2) Huntington's |
|
|
What are the symptoms and course of Huntington's Disease?
|
SXS: Chorea (dance-like movements), dementia, and psychosis
Onset: variable, early-middle adulthood |
|
|
What are the gross changes in Huntington's?
|
1) Loss of the Caudate Nucleus
2) Secondary frontal lobe atrophy |
|
|
Describe the genetics of Huntington's Chorea
|
HC is an autosomal dominant disease, inherited with anticipation. Expansion of CAG trnucleotide repeats (>37) results in disease.
|
|
|
What is the typical microscopic appearance of Huntington's pts?
|
Gliosis
|
|
|
What is the most common motor neuron disease?
|
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
|
|
|
How does ALS present clinically?
|
ALS presents with both upper and lower motor neuron disability. There are several variants of the disease.
|
|
|
What is major feature of ALS?
|
Loss of descending upper motor neurons in the spinal cord
|
|
|
What are the microscopic features of ALS?
|
1) Loss of motor neurons and ASTROGLIOSIS in ANTERIOR HORN, motor cortex and brainstem
2) Bunina and Lewy-like Inclusions 3) Degeneration of the LATERAL CORTICOSPINAL TRACT |
|
|
Is there a genetic correlation with ALS?
|
* 10% caused by Cu/Zn Superoxide Dismutase Gene distruption
* 90% Sporadic |
|
|
What are the three sources of Creutzfeld-Jakob Disease?
|
1) Sporadic
2) Transmitted (iatrogenic) 3) Autosomal Dominant (mutation in Prion Precursor Protein) |
|
|
What's the clinical course of Creutzfeld-Jakob Disease?
|
Rapidly progressive dementia with movement disorders and myoclonus.
|
|
|
Are there diagnostic tests for CJD?
|
The diagnostic tests are ambiguous. Dx by pathology.
|
|
|
What are the three pathologic features of CJD?
|
1) Spongiform changes in neurons and processes
2) Astrogliosis 3) Amyloid Plaques of PrP fragments |
|
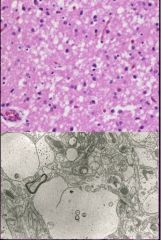
What's the pathology?!?
|
Spongiform Changes in CJD
|

