![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
13 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- Premature closing of the cranial sutures leads to:
- Brachycephaly (short head) - Trigonocephaly (triangle-shaped head) - These Pt's are NOT mentally deficient |
Crouzon's Disease (Craniofacial Dysostosis)
- 1 out of 25,000 to 65,000 births - Autosomal dominant, some spontaneous - Ocular proptosis (protruding eyeballs due to shallow orbits) - Hypertelorism (widely spaced eyes) - Hypoplastic maxilla with short upper lip - Mal occlusion (crowding, 2/3 have cross bite) - Possible "cloverleaf" skull (broad looking forehead, most severe cases) - Anterior open bite - 50% or more have poor vision and hearing deficits Treatment: multiple surgeries |
|
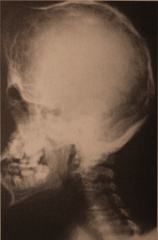
- Acrobrachycephaly (tower skull)
|
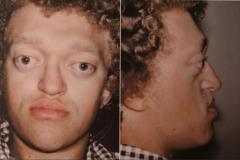
Apert Syndrome
- One out of 65,000-160,00 births - Autosomal dominant - Possible "cloverleaf" skull in severe cases - Ocular proptosis - Hypertelorism - Down slanting of lateral palpebral fissures |
|
|
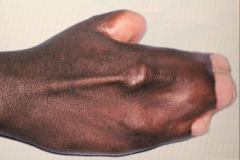
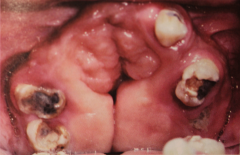
Apert Syndrome
- Syndactyly of hands and feet - Possible mental retardation - Hypoplastic maxilla - Mandibular prognathism (maxillary crowding with class III map occlusion) - Possible cleft soft palate - Gingival thickening w/ possible delayed eruption - Shovel Shaped incisors in 1/3 of pts. |
|
|
Apert Syndrome
|
|
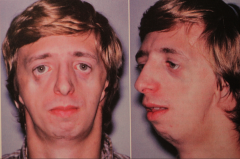
- Autosomal Dominant w/ irregular pattern (1/2 of cases spontaneous)
- Affects structures developing from the 1st and 2nd branchial arch |
Treacher Collins Syndrome (Mandibulofacial Dystosis)
- One out of 10,000 to 50,000 births - Mandibular micrognathia due to condylar and coronoid hyperplasias - "Bird-like" appearance - Zygomatic atrophy (depressed cheeks) - Coloboma (notch lower eyelid) (75%) - Downward slanting of lower eyelid - External and internal ear defects (possible hearing loss, including deafness) (Microtia) - Preauricular hair growth - Malocclusion - Cleft palate in 1/3 of cases Treatment: possible cosmetic surgery. |
|
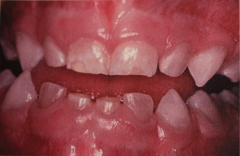
|
Osteogenesis Imperfecta (Lobstein's Disease)
- Opalescent dentin in a pt. w/ osteogenesis imperfecta. - Inherited disorder of collagen maturation that results in bone w/ thin cortex, fine trabeculation and diffuse osteoporosis - Bone fracture easily, w/ inability of the matrix to fully mineralize which leeds to exaggerated caller formation. - 1 in 8,000 births. |
|
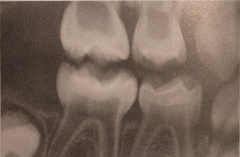
|
Osteogenesis Imperfecta (Lobstein's Disease)
- Bite-wing radiograph of the same pt. showing shell teeth w/ thin dentin and enamel of normal thickness - Bone deformities and fragility (pts confined to wheelchair) - Dentinogenesis imperfecta-like teeth in 25% of cases - Possible malocclusion due to maxillary hypoplasia |
|
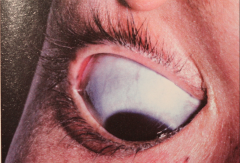
- Possible Blue sclera
|
Osteogenesis Imperfecta (Lobstein's Disease)
- Four major types (mild to severe forms; I, II, III, & IV) - Lethal types occur in 10% of cases - Sever non-lethal types occur in 20% of cases - Mild form may not be apparent at birth and fractures decline at puberty - Possible hearing loss. - No specific treatment. |
|
|
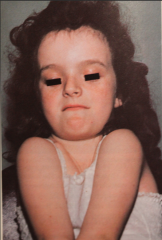
Cleidocranial Dysplasia
- Autosomal dominant and spontaneous - Clavicles are absent or hypoplastic - Skull deformities, brachycephaly, hypertelorism, frontal and occipital bossing that produces enlarged and abnormally shaped head. - Short stature, cardiac anomalies. |
|
|
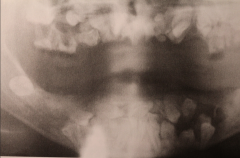
Cleidocranial Dysplasia
- Lacks secondary cementum - Increased cleft palate and high palate - Over-retained primary teeth, delayed eruption of permanent teeth, supernumerary teeth (some distorted crowns) No known treatment |
|
|
- Sporadic or may occur w/ other syndromes
- 5 to 22 per 100,000 births ( or 1 per 4,545 to 20,000 births) - Cleft Palate (leads to feeding and speech problems) - Mandibular micrognathia - Glossoptosis (airway obstruction due to posterior displacement of tongue) (lack of tongue musculature) - Respiratory and feeding problems common |
Pierre Robin Syndrome
|
|
|
- Autosomal dominant disease
- 23,000 americans affected w/ This syndrome - Abnormally soluble collagen (problem w/ connective tissue protein) |
Marfan Syndrome (Arachnodactyly)
- Tall, slender stature, large hands and fingers, chest deformities - Long narrow skull and bones, cardiovascular defects (mitral valve prolapse, aortic regurgitation, aneurysms, etc.) |
|

|
Marfan Syndrome (Arachnodactyly)
- High arched palate, bifid uvula, malocclusion - Possible early death (has occured in undiagnosed athletes) - Need annual medical exam and possible limit physical activity. |

