![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
17 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Translation |
Slid right or left |
|
|
Symmetry |
A symmetry of an object is a rigid motion of the plane that leaves the object apparently unchanged. |
|
|
Reflection |
To flip an object |
|
|
Identity |
A 0 degree rotation or a 360 degree rotation. |
|
|
Proper Rigid Motion |
If the object reserves orientation (right hand is still a right hand) (rotations) |
|
|
Improper Rigid Motion |
When the object reverses orientation (right hand is now a left hand) (reflections) |
|
|
Bounded Object |
If the object is fully contained in a square in the plane. |
|
|
Unbounded Object |
If it is not contained within a square in the plane. |
|
|
Regular N-sided Polygon |
Is the shape in the plane enclosed by n equals length straight sides, assembled so that all n angles are equal. |
|
|
Orientation |

If the object has no improper symmetries (no reflections) |
|
|
Oriented Polygon |
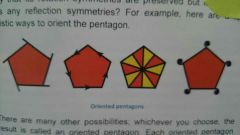
A oriented shape that have rotation symmetries but no reflection symmetries. |
|
|
Border Pattern |

If all translations are parallel to a single line. Continues forever right and left |
|
|
Wallpaper Pattern |
Infinitly stretches in all directions. |
|
|
Glide Relfection |
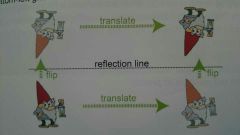
Performing a translation (slide) then a reflection (flip) |
|
|
The Center Point Theorem |
Any bounded Object in the plane has a "center point" such that: (1) every proper symmetry is a rotation about this center point, and (2)every improper symmetry is a flip over a line through this center point. |
|
|
Composition |
The addition of symmetry. A*B this means do B then A. |
|
|
Cayley Table |

The composition chart |

