![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
15 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Strep suis
a. epidemiology b. pathogenesis |
a. ubiquitous: cultured from vagina of normal sows
survives in environment: dust, feces, biofilms; also spread by flies **mostly a nursery dz (5-6 wks of age)** **risk factors**: crowding, co-mingling, PRRS virus b. clinical dz can occur w/o other agents, but PRRS, PCV-2, & pseudorabies --> ↑ morbidity & mortality **bacteria enter thru crypts of tonsils** MP carry bacteria --> mandibular lymph nodes --> systemic (CSF, meninges, brain, lungs, joints) |
|
|
Strep suis
a. lesions b. clinical signs |
a. pigs that die acutely have fibrinous meningitis
often rapid onset: may appear normal w/in hr. of death any serosal membrane may be affected: polyserositis, polyarthritis, myocarditis, endocarditis, pericarditis, bronchopneumonia **lesions indistinguishable from those of Haemophilus parasuis** b. pigs often appear scruffy & malnourished **CNS signs: opisthotonus, nystagmus, paddling, +/- convulsions |
|
|
Strep suis
a. dx b. tx c. control |
a. culture: gold standard
b. β-lactam ABs (mostly still sensitive, definitively sensitive to ceftiofur) c. commercial, autogenous vaccines marginally effective elimination of PRRS: very difficult strategic AB use in water, feed, & parenterally |
|
|
Haemophilus parasuis
a. epidemiology b. lesions & signs c. dx d. tx |
a. can see in nursery & grow/finish pigs
b. same as Strep suis c. culture: gold standard d. β-lactam ABs tx difficult when PRRS, PCV-2, or influenza also active |
|
|
What is the etiology & pathogenesis of edema dz?
|
F-18 or F-4 strains of E. coli
α-hemolytic & produces Shiga-like enterotoxin toxins produced in SI after attachment to brush border: receptor for fimbrial Ag must be present on brush border cells: genetically determined toxin damages small arteries & arterioles --> localized edema in several organs (colon, SI, eyelids, brain) acute & typically fatal |
|
|
edema dz
a. epidemiology b. dx |
a. not seen in baby pigs while nursing: lactogenic protection & absorbed Abs
changes in gut environment assoc. w/ weaning favor enteropathogenic E. coli buildings become contaminated & colonized co-mingling of pigs may ↑ risk of clinical dz change from milk to corn/soy ration survives in biofilms & fecal contaminated trucks b. clinical signs, hx, gross lesions labs can ID both F-18 & F-4 adhesion Ag & specific toxin **histopath: typical vascular lesions, brain stem malacia ddx: S. suis, H. parasuis |
|
|
edema dz
a. tx b. prevention |
a. unrewarding once signs appear
b. may prevent in non-affected pigs sanitation & biosecurity: dry rooms before filling **oral inoculums w/ non-toxin producing strains of F-18 (autogenous oral vaccine) |
|
|
salt poisoning (water deprivation)
a. etiology b. epidemiology |
a. sodium ion toxicosis d/t water deprivation of at least 48 hrs
b. most common in nursery, can also occur in grow/finish |
|
|
salt poisoning (water deprivation)
a. signs b. dx |
a. usually high morbidity & mortality in affected groups
refusal to eat, commotion/squealing at water source **CNS signs begin w/in hours after resumption of water availability: “dog sitting” w/ convulsions common b. **hx of water deprivation **histopath (pathognomonic): cerebral perivascular cuffing by eosinophils dog sitting --> convulsions |
|
|
edema dz
|
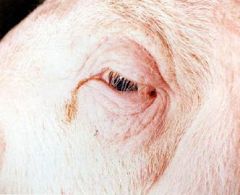
What neuro dz is consistent with this clinical appearance?
|
|
|
water deprivation (salt poisoning)
|

What neuro dz might you suspect in this pig?
|
|
|
edema dz
|
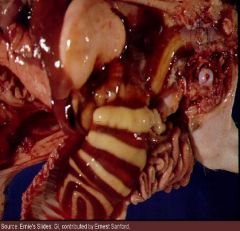
What neuro dz might you suspect based on these lesions?
|
|
|
edema dz
|
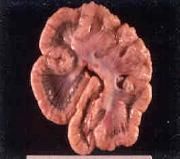
What neuro dz might you suspect based on these lesions?
|
|
|
Strep suis or Haemophilus parasuis
|
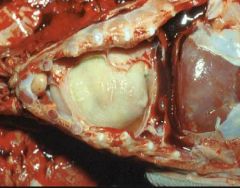
What neuro dz might you suspect based on these lesions?
|
|
|
Strep suis or Haemophilus parasuis
|
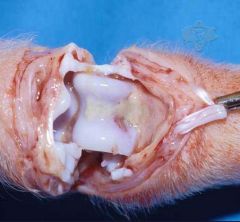
What neuro dz might you suspect based on these lesions?
|

