![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
138 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
How is an ICU note written? |
By systems: - Neuro: GCS, MAE, pain control - Pulmonary: vent settings - CV: pressors, Swan numbers - GI - Heme: CBC - FEN: Chem 10, nutrition - Renal: urine output, BUN, Cr - ID: Tmax, WBC, antibiotics - Assessment - Plan
Note: physical exam is included in each section |
|
|
What is the best way to report urine output in the ICU? |
24 hours / last shift / last 3 hourly rate:
"Urine output has been 2L over last 24 hours, 350 last shift, and 45/35/40cc over last 3 hours" |
|
|
What are the possible causes of fever in ICU? |
- Central line infection - PNA/atelectasis - UTI, urosepsis - Intra-abdominal abscess - Sinusitis - DVT - Thrombophlebitis - Drug fever - Fungal infection, meningitis, wound infection - Endocarditis |
|
|
What is the most common bacteria in ICU pneumonia? |
Gram negative rods |
|
|
What is the acronym for the basic ICU care checklist? |
FAST HUG: - Feeding - Analgesia - Sedation - Thromboembolic prophylaxis
- Head of bed elevation (pneumonia prevention) - Ulcer prevention - Glucose control |
|
|
What is CO? |
Cardiac output = HR * Stroke Volume |
|
|
What is the normal CO? |
4-8 L/min |
|
|
What factors increase CO? |
- Increased contractility, HR, and preload - Decreased afterload |
|
|
What is CI? |
Cardiac Index = CO/BSA (body surface area) |
|
|
What is the normal CI? |
2.5-3.5 L/min/m^2 |
|
|
What is SV? |
Stroke Volume = the amount of blood pumped out of the ventricle each beat; simply, end diastolic volume minus the end systolic volume or CO/HR |
|
|
What is the normal stroke volume? |
60-100 cc |
|
|
What is CVP? |
Central Venous Pressure = indirect measurement of intravascular volume status |
|
|
What is the normal CVP? |
4-11 |
|
|
What is PCWP? |
Pulmonary Capillary Wedge Pressure = indirectly measures left atrial pressure, which is an estimate of intravascular volume (LV filling pressure) |
|
|
What is the normal PCWP? |
5-15 |
|
|
What is anion gap? |
Na+ - (Cl- + HCO3-) |
|
|
What are the normal values for anion gap? |
10-14 |
|
|
Why do you get an increased anion gap? |
Unmeasured acids are unmeasured anions in the equation that are part of the "counterbalance to the sodium cation |
|
|
What are the causes of increased anion gap acidosis in surgical patients? |
"SALUD": - Starvation - Alcohol (ethanol/methanol) - Lactic acidosis - Uremia (renal failure) - DKA |
|
|
What is MODS? |
Multiple Organ Dysfunction Syndrome |
|
|
What is SVR? |
Systemic Vascular Resistance = MAP - CVP / CO * 80 Remember, P = F*R |
|
|
What is SVRI? |
Systemic Vascular Resistance Index: SVR / BSA (body surface area) |
|
|
What is the normal SVRI? |
1500-2400 |
|
|
What is MAP? |
Mean Arterial Pressure = diastolic blood pressure + 1/3 (systolic - diastolic pressure)
Note: not the mean between diastolic and systolic BP because diastole lasts longer than systole |
|
|
What is PVR? |
Pulmonary Vascular Resistance = PA(mean) - PCWP / CO * 80
PA = pulmonary artery pressure and LA is left atrial or PCWP pressure |
|
|
What is the normal PVR value? |
100 ± 50 |
|
|
What is the formula for arterial oxygen content? |
Hemoglobin * O2 saturation (SaO2) * 1.34 |
|
|
What is the basic formula for oxygen delivery? |
CO * (oxygen content) |
|
|
What is the full formula for oxygen delivery? |
CO * (1.34 * Hgb * SaO2) * 10 |
|
|
What factors can increase oxygen delivery? |
Increased CO by increasing SV, HR, or both; increased O2 content by increasing the Hgb content, SaO2, or both |
|
|
What is mixed venous oxygen saturation? |
SvO2 = simply the O2 saturation of the blood in the RV or pulmonary artery; an indirect measure of peripheral O2 supply and demand |
|
|
Which lab values help assess adequate oxygen delivery? |
- SvO2 (low with inadequate delivery) - Lactic acid (elevated with inadequate delivery) - pH (acidosis with inadequate delivery) - Base deficit |
|
|
What is FENa? |
Fractional Excretion of Sodium (Na) = (Una * Pcr / Pna * Ucr) *100 |
|
|
What is the memory aid for calculating FENa? |
YOU NEED PEE = U (urine) N (Na+) P (Plasma)
Una * Pcr
For the denominator switch everything: Pna * Ucr |
|
|
What is the pre-renal FENa value? |
<1.0 = renal failure from decreased renal blood flow (eg, cardiogenic, hypovolemia, arterial obstruction, etc) |
|
|
How long does Lasix effect last? |
6 hours |
|
|
What is the formula for flow / pressure / resistance? |
P = F * R
Power FoRward |
|
|
What is the "10 for 0.08 rule" of acid base? |
For every increase of PaCO2 by 10 mmHg, the pH falls by 0.08 |
|
|
What is the "40, 50, 60 for 70, 80, 90 rule" for O2 sats? |
PaO2 of 40, 50, 60 corresponds roughly to an O2 sat of 70, 80, 90, respectively |
|
|
1L of O2 via nasal canula raises FiO2 by how much? |
~3% |
|
|
What is pure respiratory acidosis? |
Low pH (acidosis), increased PaCO2, normal bicarb |
|
|
What is pure respiratory alkalosis? |
High pH (alkalosis), decreased PaCO2, normal bicarb |
|
|
What is pure metabolic acidosis? |
Low pH, low bicarb, normal PaCO2 |
|
|
What is pure metabolic alkalosis? |
High pH, high bicarb, normal PaCO2 |
|
|
How does the body compensate for respiratory acidosis? |
Increased bicarb |
|
|
How does the body compensate for respiratory alkalosis? |
Decreased bicarb |
|
|
How does the body compensate for metabolic acidosis? |
Decreased PaCO2 |
|
|
How does the body compensate for metabolic alkalosis? |
Increased PaCO2 |
|
|
What does MOF stand for? |
Multiple Organ Failure |
|
|
What does SIRS stand for? |
Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome |
|
|
What is the site of action and effect for dopamine at a low dose (1-3 µg/kg/min)? |
++ dopa agonist, renal vasodilation (aka renal dose dopamine) |
|
|
What is the site of action and effect for dopamine at a intermediate dose (4-10 µg/kg/min)? |
+ alpha-1, ++ beta-1, positive inotropy and some vasoconstriction |
|
|
What is the site of action and effect for dopamine at a high dose (>10 µg/kg/min)? |
+++ alpha-1 agonist, marked afterload increase from arteriolar vasoconstriction |
|
|
Has "renal dose" dopamine been shown to decrease renal failure? |
NO |
|
|
What is the site of action of dobutamine? |
+++ beta-1 agonist ++ beta-2 agonist |
|
|
What is the effect of dobutamine? |
- Increased inotropy - Increased chronotropy - Decrease in systemic vascular resistance |
|
|
What is the site of action of isoproterenol? |
+++ beta-1 agonist +++ beta-2 agonist |
|
|
What is the effect of isoproterenol? |
- Increased inotropy - Increased chronotropy - Vasodilation of skeletal and mesenteric vascular beds |
|
|
What is the site of action of epinephrine? |
++ alpha-1 agonist ++ alpha-2 agonist ++++ beta-1 agonist ++++ beta-2 agonist |
|
|
What is the effect of epinephrine? |
Increased inotropy and chronotropy |
|
|
What is the effect of epinephrine at high doses? |
Vasoconstriction |
|
|
What is the site of action of norepinephrine? |
+++ alpha-1 agonist +++ alpha-2 agonist +++ beta-1 agonist
|
|
|
What is the effect of norepinephrine? |
- Increased inotropy and chronotropy - ++ Increase in BP |
|
|
What is the action of vasopressin? |
Vasoconstriction (increases MAP, SVR) |
|
|
What are the indications of vasopressin? |
Hypotension, especially refractory to other vasopressors (low-dose infusion - 0.01-0.04 units per minute) or as a bolus during ACLS (40 u) |
|
|
What is the site of action of nitroglycerine? |
+++ venodilation + arteriolar dilation |
|
|
What is the effect of nitroglycerine? |
- Increased venous capacitance - Decreased preload - Coronary arteriole vasodilation |
|
|
What is the site of action of sodium nitroprusside? |
+++ venodilation +++ arteriolar dilation |
|
|
What is the effect of sodium nitroprusside? |
Decreased preload and afterload (allowing BP titration) |
|
|
What is the major toxicity of sodium nitroprusside? |
Cyanide toxicity |
|
|
What is preload? |
Load on the heart muscle that stretches it to end-diastolic volume (end-diastolic pressure) = intravascular volume |
|
|
What is afterload? |
Load or resistance the heart must pump against = vascular tone = SVR |
|
|
What is contractility? |
Force of heart muscle contraction |
|
|
What is compliance? |
Distensibility of heart by preload |
|
|
What is the Frank-Starling curve? |
Cardiac output increases with increasing preload up to a point |
|
|
What is the clinical significance of the steep slope of the Starling curve relating end diastolic volume to cardiac output? |
Demonstrates the importance of preload in determining cardiac output |
|
|
What factors influence the oxygen content of whole blood? |
Oxygen content is composed largely of that oxygen bound to hemoglobin, and is thus determined by the hemoglobin concentration and the arterial oxygen saturation; the partial pressure of oxygen dissolved in plasma plays a minor role |
|
|
What factors influence mixed venous oxygen saturation? |
Oxygen delivery (hemoglobin concentration, arterial oxygen saturation, cardiac output) and oxygen extraction by the peripheral tissues |
|
|
What lab test for tissue ischemia is based on the shift from aerobic to anaerobic metabolism? |
Serum lactic acid levels |
|
|
What is dead space? |
That part of the inspired air that does not participate in gas exchange (e.g., the gas in the large airways/ET tube not in contact with capillaries)
Think: space = air |
|
|
What is shunt fraction? |
That fraction of pulmonary venous blood that does not participate in gas exchange
Think: shunt = blood |
|
|
What causes increased dead space? |
- Overventilation (emphysema, excessive PEEP) - Underperfusion (pulmonary embolus, low cardiac output, pulmonary artery vasoconstriction) |
|
|
At high shunt fractions, what is the effect of increasing FiO2 on arterial PO2? |
At high shunt fractions (>50%), changes in FiO2 have almost no effect on arterial PO2 because the blood that does “see” the O2 is already at maximal O2 absorption; thus, increasing the FiO2 has no effect (FiO2 can be minimized to prevent oxygen toxicity) |
|
|
Define ARDS? |
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome = lung inflammation causing respiratory failure |
|
|
What is the ARDS diagnostic triad? |
CXR: - Capillary wedge pressure <18 - X-ray of chest with bilateral infiltrates - Ratio of PaO2 to FiO2 <200 |
|
|
What does the classic chest x-ray look like with ARDS? |
Bilateral fluffy infiltrates |
|
|
How can you remember the PaO2 to FiO2, or PE, ratio? |
Think: "PUFF" ratio: PF ratio = PaO2:FiO2 ratio |
|
|
At what concentration does O2 toxicity occur? |
FiO2 of >60% * 48 hours; thus, try to keep FiO2 below 60% at all times |
|
|
What are the ONLY ventilatory parameters that have been shown to decrease mortality in ARDS patients? |
Low tidal volumes (≤6 cc/kg) and low plateau pressures <30 |
|
|
What are the main causes of CO2 retention in ARDS? |
- Hypoventilation - Increased dead space ventilation - Increased CO2 production (as in hypermetabolic states) |
|
|
Why are carbs minimized in the diet/TPN of patients having difficulty with hypercapnia? |
Respiratory Quotient (RQ) is the ratio of CO2 production to O2 consumption and is highest for carbohydrates (1.0) and lowest for fats (0.7) |
|
|
Why are indwelling arterial lines for BP monitoring in critically ill patients? |
Because of the need for frequent measurements, the inaccuracy of frequently repeated cuff measurements, the inaccuracy of cuff measurements in hypotension, and the need for frequent arterial blood sampling / labs |
|
|
Which pressures / values are obtained from a Swan-Ganz catheter? |
- CVP - PA pressures - PCWP - CO - PVR - SVR - Mixed venous O2 saturation |
|
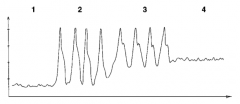
What is the Swan-Ganz waveforms in #1? |
CVP / R atrium |
|
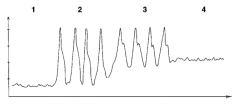
What is the Swan-Ganz waveforms in #2? |
Right ventricle |
|
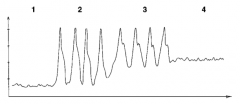
What is the Swan-Ganz waveforms in #3? |
Pulmonary artery |
|
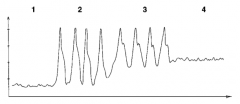
What is the Swan-Ganz waveforms in #4? |
Wedge |
|
|
What are the other names for PCWP? |
Wedge or wedge pressure, pulmonary artery occlusion pressure (PAOP) |
|
|
What is PCWP? |
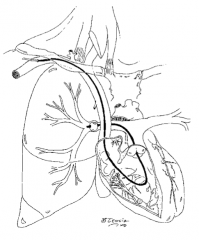
- Pulmonary capillary pressure after balloon occlusion of the pulmonary artery, which is equal to left atrial pressure because there are no valves in the pulmonary system - Left atrial pressure is essentially equal to left ventricular end diastolic pressure (LVEDP): left heart preload, and, thus, intravascular volume status. |
|
|
What is the primary use of the PCWP? |
As an indirect measure of preload = intravascular volume |
|
|
Has the usage of a Swan-Ganz catheter been shown to decrease mortality in ICU patients? |
NO |
|
|
What is ventilation? |
Air through the lungs; monitored by PCO2 |
|
|
What is oxygenation? |
Oxygen delivery to the alveoli; monitored by O2 sats and PO2 |
|
|
What can increase ventilation to decrease PCO2? |
Increased respiratory rate (RR), increased tidal volume (minute ventilation) |
|
|
What is minute ventilation? |
Volume of gas ventilated through the lungs (RR tidal volume) |
|
|
What is tidal volume? |
Volume delivered with each breath; should be 6 to 8 cc/kg on the ventilator |
|
|
Are ventilation and oxygenation related? |
Basically no; you can have an O2 sat of 100% and a PCO2 of 150; O2 sats do not tell you anything about the PCO2 (key point!) |
|
|
What can increase PO2 (oxygenation) in the ventilated patient? |
- Increased FiO2 - Increased PEEP |
|
|
What can decrease PCO2 in the ventilated patient? |
- Increased RR - Increased tidal volume (ie, increase minute ventilation) |
|
|
What is the IMV mode of mechanical ventilation? |
Intermittent Mandatory Ventilation: mode with intermittent mandatory ventilations at a predetermined rate; patients can also breathe on their own above the mandatory rate without help from the ventilator |
|
|
What is the SIMV mode of mechanical ventilation? |
Synchronous IMV: mode of IMV that delivers the mandatory breath synchronously with patient’s initiated effort; if no breath is initiated, the ventilator delivers the predetermined mandatory breath |
|
|
What is the A-C mode of mechanical ventilation? |
- Assist-Control ventilation: mode in which the ventilator delivers a breath when the patient initiates a breath, or the ventilator “assists” the patient to breathe; if the patient does not initiate a breath, the ventilator takes “control” and delivers a breath at a predetermined rate
- In contrast to IMV, all breaths are by the ventilator |
|
|
What is the CPAP mode of mechanical ventilation? |
Continuous Positive Airway Pressure: positive pressure delivered continuously (during expiration and inspira- tion) by ventilator, but no volume breaths (patient breathes on own) |
|
|
What is the pressure support mode ofmechanical ventilation? |
Pressure is delivered only with an initiated breath; pressure support decreases the work of breathing by overcoming the resistance in the ventilator circuit |
|
|
What is the APRV mode of mechanical ventilation? |
Airway Pressure Release Ventilation: high airway pressure intermittently released to a low airway pressure (shorter period of time) |
|
|
What is the HFV mode of mechanical ventilation? |
High Frequency Ventilation: rapid rates of ventilation with small tidal volumes |
|
|
What are the effects of positive pressure ventilation in a patient with hypovolemia or low lung compliance? |
Venous return and cardiac output are decreased |
|
|
Define PEEP? |
Positive End Expiration Pressure: positive pressure maintained at the end of a breath; keeps alveoli open |
|
|
What is "physiologic PEEP"? |
PEEP of 5 cm H2O; thought to approximate normal pressure in normal nonintubated people caused by the closed glottis |
|
|
What are the side effects of increasing levels of PEEP? |
Barotrauma (injury to airway pneumothorax), decreased CO from decreased preload |
|
|
What is the typical initial ventilator mode setting? |
Intermittent mandatory ventilation |
|
|
What is the typical initial ventilator tidal volume setting? |
6-8 ml/kg |
|
|
What is the typical initial ventilator rate setting? |
10 breaths / min |
|
|
What is the typical initial ventilator FiO2 setting? |
100% and wean down |
|
|
What is the typical initial ventilator PEEP setting? |
- 5 cm H2O - From these parameters, change according to blood-gas analysis |
|
|
What is a normal I:E (inspiratory to expiratory time)? |
1:2 |
|
|
When would you use an inverse I:E ratio (eg, 2:1, 3:1, etc)? |
To allow for longer inspiration in patients with poor compliance, to allow for "alveolar recruitment" |
|
|
When would you use a prolonged I:E ratio (eg, 1:4)? |
COPD, to allow time for complete exhalation (prevents "breath stacking") |
|
|
What clinical situations cause increased airway resistance? |
Airway or endotracheal tube obstruction, bronchospasm, ARDS, mucus plugging, CHF (pulmonary edema) |
|
|
What are the presumed advantages of PEEP? |
Prevention of alveolar collapse and atelectasis, improved gas exchange, increased pulmonary compliance, decreased shunt fraction |
|
|
What are the possible disadvantages of PEEP? |
Decreased cardiac output, especially in the setting of hypovolemia; decreased gas exchange; T compliance with high levels of PEEP, fluid retention, increased intracranial pressure, barotrauma |
|
|
What parameters must be evaluated in deciding if a patient is ready to be extubated? |
Patient alert and able to protect airway, gas .exchange (PaO2 >70, PaCO2 <50), tidal volume (5 cc/kg), minute ventilation (<10 L/min), negative inspiratory pressure (<-20 cm H2O, or more negative), FiO2 ≤40%, PEEP 5, PH >7.25, RR <35, Tobin index <105 |
|
|
What is the Rapid-Shallow Breathing (aka Tobin) index? |
Rate: Tidal volume ratio
Tobin index <105 is associated with successful extubation (Think: Respiratory Therapist = RT = Rate: Tidal volume) |
|
|
What is a possible source of fever in a patient with an NG or nasal endotracheal tube? |
Sinusitis (diagnosed by sinus films / CT) |
|
|
What is the 35-45 rule of blood gas values? |
Normal values: - pH = 7.35 - 7.45 - PCO2 = 35 - 45 |
|
|
What meds can be delivered via an endotracheal tube? |
"NAVEL" - Narcan - Atropine - Vasopressin - Epinephrine - Lidocaine |
|
|
What conditions should you think of with increased peak airway pressure and decreased urine output? |
1. Tension pneumothorax 2. Abdominal compartment syndrome |

