![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
151 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
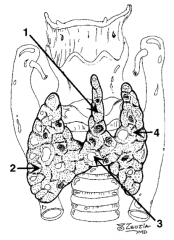
What is structure 1?
|
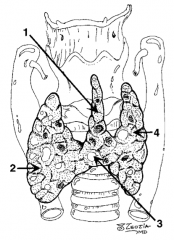
Pyramidal lobe |
|
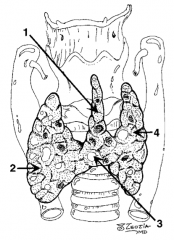
What is structure 2?
|
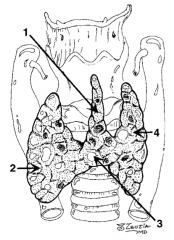
Right lobe |
|
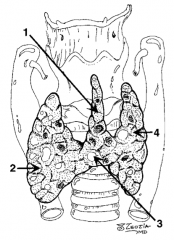
What is structure 3?
|
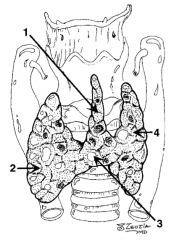
Isthmus |
|
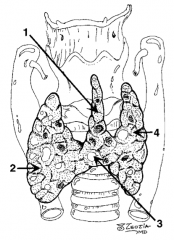
What is structure 4?
|
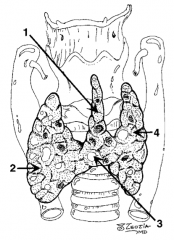
Left lobe |
|
|
What is the arterial blood supply to the thyroid? |
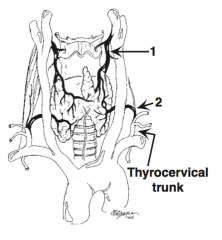
Two arteries: 1. Superior thyroid artery (first branch of the external carotid artery) 2. Inferior thyroid artery (branch of the thyrocervical trunk) (IMA artery rare)
|
|
|
What is the venous drainage of the thyroid? |
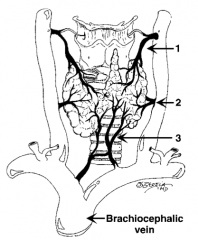
Three veins: 1. Superior thyroid vein 2. Middle thyroid vein 3. Inferior thyroid vein
|
|
|
Name the thyroid lobe appendage coursing toward the hyoid bone from around the thyroid isthmus? |
Pyramidal lobe |
|
|
What percentage of patients have a pyramidal lobe of the thyroid? |
~50% |
|
|
What veins do you see first after opening the platysma muscle when performing a thyroidectomy? |
Anterior jugular veins |
|
|
Name the lymph node group around the pyramidal thyroid lobe? |
Delphian lymph node group |
|
|
What is the thyroid isthmus? |
Mid-line tissue border between the left and right thyroid lobes |
|
|
Which ligament connects the thyroid to the trachea? |
Ligament of Berry |
|
|
What is the IMA artery? |
Small inferior artery to the thyroid from the aorta or innominate artery |
|
|
What percentage of patients have an IMA artery? |
~3% |
|
|
Name the most posterior extension of the lateral thyroid lobes? |
Tubercle of Zuckerkandl |
|
|
Which paired nerves must be carefully identified during a thyroidectomy? |
Recurrent laryngeal nerves, which are found in the tracheoesophageal grooves and dive behind the cricothyroid muscle
Damage to these nerves paralyzes laryngeal abductors and causes hoarseness if unilateral, and airway obstruction if bilateral |
|
|
What other nerve is at risk during a thyroidectomy and what are the symptoms? |
Superior laryngeal nerve - If damaged patient will have a deeper and quieter voice (unable to hit high pitches) |
|
|
What is the name of the famous opera singer whose superior laryngeal nerve was injured during thyroidectomy? |
Urban legend has it that it was Amelita Galli-Curci, but no objective data support such a claim |
|
|
What is TRH? Source? |
Thyrotropin-Releasing Hormone: released from hypothalamus, causes release of TSH |
|
|
What is TSH? Source? |
Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone: released by anterior pituitary, causes release of thyroid hormone from thyroid |
|
|
What are the thyroid hormones? |
T3 and T4 |
|
|
What is the most active form of thyroid hormone? |
T3 |
|
|
What is the most common site of conversion of T4 to T3? |
Peripheral (eg, liver) |
|
|
What is synthroid (levothyroxine): T3 or T4? |
T4 |
|
|
What is the half-life of synthroid (levothyroxine)? |
7 days |
|
|
What do parafollicular cells secrete? |
Calcitonin |
|
|
What percentage of people have a thyroid nodule? |
~5% |
|
|
What is the differential diagnosis of a thyroid nodule? |
- Multinodular goiter - Adenoma - Hyper-functioning adenoma - Cyst - Thyroiditis - Carcinoma / lymphoma - Parathyroid carcinoma |
|
|
Name three types of non-thyroidal neck masses? |
1. Inflammatory lesions (eg, abscess, lymphadenitis) 2. Congenital lesions (ie, thyroglossal duct [midline], branchial cleft cyst [lateral]) 3. Malignant lesions: lymphoma, metastases, squamous cell carcinoma |
|
|
What studies can be used to evaluate a thyroid nodule? |
- U/S: solid or cystic nodule - FNA --> cytology - 123-I scintiscan: hot or cold nodule |
|
|
What is the DIAGNOSTIC test of choice for thyroid nodule? |
FNA |
|
|
What is the percentage of false negative results on FNA for thyroid nodule? |
~5% |
|
|
What is meant by a hot vs a cold thyroid nodule? |
Nodule uptake of IV 123-I or 99-mT - Hot: increased 123-I uptake = functioning / hyperfunctioning nodule - Cold: decreased 123-I uptake = non-functioning nodule |
|
|
What are the indications for a 123-I scintiscan for thyroid nodule? |
1. Nodule with multiple "non-diagnostic" FNAs with low TSH 2. Nodule with thyrotoxicosis and low TSH |
|
|
What is the role of thyroid suppression of a thyroid nodule? |
Diagnostic and therapeutic; administration of thyroid hormone suppresses TSH secretion, and up to 1/2 of the benign thyroid nodules will disappear |
|
|
In evaluating a thyroid nodule, what on history would suggest thyroid carcinoma? |
1. Neck radiation 2. Family history (thyroid cancer, MEN-II) 3. Young age (especially children) 4. Male > female |
|
|
In evaluating a thyroid nodule, what signs would suggest thyroid carcinoma? |
1. Single nodule 2. Cold nodule 3. Increased calcitonin levels 4. Lymphadenopathy 5. Hard, immobile nodule |
|
|
In evaluating a thyroid nodule, what symptoms would suggest thyroid carcinoma? |
1. Voice change (vocal cord paralysis) 2. Dysphagia 3. Discomfort (in neck) 4. Rapid enlargement |
|
|
What is the most common cause of thyroid enlargement? |
Multinodular goiter |
|
|
What are indications for surgery with multinodular goiter? |
- Cosmetic deformity - Compressive symptoms - Cannot rule out cancer |
|
|
What is Plummer's disease? |
Toxic multinodular goiter |
|
|
What percentage of cold thyroid nodules are malignant? |
~25% in adults |
|
|
What percentage of multinodular thyroid masses are malignant? |
~1% |
|
|
What is the treatment of a patient with a history of radiation exposure, thyroid nodule, and negative FNA? |
Most experts would remove the nodule surgically (because of the high risk from radiation) |
|
|
What should be done with thyroid cyst aspirate? |
Send to cytopathology |
|
|
What are the five main types of thyroid carcinoma and their relative percentages? |
1. Papillary carcinoma (80%) (P = Popular) 2. Follicular carcinoma (10%) 3. Medullary carcinoma (5%) 4. Hurthle cell carcinoma (4%) 5. Anaplastic / undifferentiated carcinoma (1-2%) |
|
|
What are the signs/symptoms of thyroid carcinoma? |
- Mass/nodule - Lymphadenopathy - Most are euthyroid |
|
|
What comprises the work up for thyroid carcinoma? |
- FNA - Thyroid U/S - TSH - Calcium level - CXR - +/- 123-I scintiscan |
|
|
What oncogenes are associated with thyroid cancers? |
Ras gene family and RET proto-oncogene |
|
|
What is papillary carcinoma's claim to fame? |
Most common thyroid cancer (80%) |
|
|
What is the environmental risk for papillary adenocarcinoma of the thyroid? |
Radiation exposure |
|
|
What is the average age of presentation of papillary adenocarcinoma of the thyroid? |
30-40 years |
|
|
What is the sex distribution for papillary adenocarcinoma of the thyroid? |
Female > Male; 2:1 |
|
|
What are the associated histologic findings of papillary adenocarcinoma of the thyroid? |
Psammoma bodies (remember P = Popular = Papillary = Psammoma) |
|
|
What is the route and rate of spread of papillary adenocarcinoma of the thyroid? |
Most spread via lymphatics (cervical adenopathy); spread occurs slowly |
|
|
What is the typical 123-I uptake in papillary adenocarcinoma of the thyroid? |
Good uptake |
|
|
What is the 10-year survival rate of papillary adenocarcinoma of the thyroid? |
~95% |
|
|
What are the treatment options for a papillary adenocarcinoma of the thyroid that is <1.5 cm and no history of neck radiation exposure? |
1. Thyroid lobectomy and isthmectomy 2. Near-total thyroidectomy 3. Total thyroidectomy |
|
|
What are the treatment options for a papillary adenocarcinoma of the thyroid that is >1.5 cm, bilateral, + cervical node metastasis OR a history of neck radiation exposure? |
Total thyroidectomy |
|
|
What is the treatment for papillary adenocarcinoma of the thyroid with lateral palpable cervical lymph nodes? |
Modified neck dissection (ipsilateral) |
|
|
What is the treatment for papillary adenocarcinoma of the thyroid with central palpable cervical lymph nodes? |
Central neck dissection |
|
|
Do positive cervical nodes affect the prognosis in papillary adenocarcinoma of the thyroid? |
No! |
|
|
What is a lateral aberrant thyroid in papillary adenocarcinoma of the thyroid? |
Misnomer - it is metastatic papillary carcinoma to a lymph node |
|
|
What post-op med should be administered to a patient with papillary adenocarcinoma of the thyroid? |
Thyroid hormone replacement, to suppress TSH |
|
|
What is a post-op treatment option for papillary adenocarcinoma of the thyroid? |
Post-op 123-I scan can locate residual tumor and distant metastasis that can be treated with ablative doses of 123-I |
|
|
What is the most common site of distant metastases from papillary adenocarcinoma of the thyroid? |
Pulmonary (lungs) |
|
|
What are the 7 P's of papillary adenocarcinoma of the thyroid? |
Papillary cancer: - Popular (most common) - Psammoma bodies - Palpable lymph nodes (spreads most commonly by lymphatics, seen in ~33% of patients) - Positive 123-I uptake - Positive prognosis - Post-op 123-I scan to diagnose/treat metastases - Pulmonary metastases |
|
|
What percentage of thyroid cancers are follicular adenocarcinomas? |
~10% |
|
|
What is the consistency of a follicular adenocarcinoma of the thyroid? |
Rubbery, encapsulated |
|
|
What is the route of spread of follicular adenocarcinoma of the thyroid? |
Hematogenous, more aggressive than papillary adenocarcinoma |
|
|
What is the male:female ratio in follicular adenocarcinoma of the thyroid? |
1:3 (male:female) |
|
|
What is the 123-I uptake in follicular adenocarcinoma of the thyroid? |
Good uptake |
|
|
What is the overall 10-year survival rate of follicular adenocarcinoma of the thyroid? |
~85% |
|
|
Can the diagnosis of follicular adenocarcinoma of the thyroid be made by FNA? |
No - tissue structure is needed for a diagnosis of cancer |
|
|
What histologic findings define malignancy in follicular adenocarcinoma of the thyroid? |
Capsular or blood vessel invasion |
|
|
What is the most common site of distant metastasis from follicular adenocarcinoma of the thyroid? |
Bone |
|
|
What is the treatment for follicular adenocarcinoma of the thyroid? |
Total thyroidectomy |
|
|
What is the post-op treatment option if follicular adenocarcinoma of the thyroid is malignant? |
Post-op 123-I scan for diagnosis/treatment |
|
|
What are the 4 F's of follicular adenocarcinoma of the thyroid? |
Follicular cancer: - Far-away metastasis (spreads hematogenously) - Female (3:1 ratio) - FNA...NOT (FNA cannot diagnose cancer) - Favorable prognosis |
|
|
What is Hurthle cell thyroid cancer? |
Thyroid cancer of the Hurthle cells |
|
|
What percentage of thyroid caners does Hurthle cell thyroid cancer comprise? |
~5% |
|
|
What is the cell of origin of Hurthle cell thyroid cancer? |
Follicular cells |
|
|
What is the 123-I uptake in Hurthle cell thyroid cancer? |
No uptake |
|
|
How do you diagnose Hurthle cell thyroid cancer? |
FNA can identify cells, but malignancy can be determined only by tissue histology (like follicular cancer) |
|
|
What is the route of metastasis of Hurthle cell thyroid cancer? |
Lymphatic > Hematogenous |
|
|
What is the treatment for Hurthle cell thyroid cancer? |
Total thyroidectomy |
|
|
What is the 10-year survival rate of Hurthle cell thyroid cancer? |
80% |
|
|
What percentage of all thyroid cancers are medullary carcinoma? |
~5% |
|
|
What other condition is medullary carcinoma of the thyroid associated with? |
MEN type II: autosomal dominant genetic transmission |
|
|
What is the histologic appearance of medullary carcinoma of the thyroid? |
Amyloid (aMyloid = Medullary) |
|
|
What does a medullary carcinoma of the thyroid secrete? |
Calcitonin (tumor marker) |
|
|
What is the appropriate stimulation test of medullary carcinoma of the thyroid? |
Pentagastrin (causes an increase in calcitonin) |
|
|
What is the route of spread of medullary carcinoma of the thyroid? |
Lymphatic and hematogenous distant metastasis |
|
|
How do you diagnose medullary carcinoma of the thyroid? |
FNA |
|
|
What is the 123-I uptake in medullary carcinoma of the thyroid? |
Poor uptake |
|
|
What is the associated genetic mutation with medullary carcinoma of the thyroid? |
RET proto-oncogene |
|
|
What is the female/male ratio with medullary carcinoma of the thyroid? |
Female > Male; 1.5:1 |
|
|
What is the 10-year survival rate of medullary carcinoma of the thyroid? |
80% without LN involvement 45% with LN spread |
|
|
What should all patients with medullary carcinoma of the thyroid also be screened for? |
MEN II: pheochromocytoma, hyperparathyroidism |
|
|
If medullary carcinoma of the thyroid and pheochromocytoma are found, which one is operated on first? |
Pheochromocytoma |
|
|
What is the treatment for medullary carcinoma of the thyroid? |
- Total thyroidectomy and median lymph node dissection - Modified neck dissection, if lateral cervical nodes are positive |
|
|
What are the M's of medullary carcinoma of the thyroid? |
Medullary cancer: - MEN II - aMyloid - Median lymph node dissection - Modified neck dissection if lateral nodes are positive |
|
|
What is anaplastic carcinoma of the thyroid also known as? |
Undifferentiated carcinoma |
|
|
What is anaplastic carcinoma of the thyroid? |
Undifferentiated cancer arising in ~75% of previously differentiated thyroid cancers (most commonly, follicular carcinoma) |
|
|
What percentage of all thyroid cancers does anaplastic carcinoma of the thyroid comprise? |
~2% |
|
|
What is the gender preference for anaplastic carcinoma of the thyroid? |
Women > Men |
|
|
What are the associated histologic findings of anaplastic carcinoma of the thyroid? |
Giant cells, spindle cells |
|
|
What is the 123-I uptake in anaplastic carcinoma of the thyroid? |
Very poor uptake |
|
|
How do you diagnose anaplastic carcinoma of the thyroid? |
FNA (large tumor) |
|
|
What is the major differential diagnosis for anaplastic carcinoma of the thyroid? |
Thyroid lymphoma (much better prognosis) |
|
|
What is the treatment of small anaplastic carcinoma of the thyroid? |
Total thyroidectomy + XRT/chemotherapy |
|
|
What is the treatment of anaplastic carcinoma of the thyroid if there is airway compromise? |
Debulking surgery and tracheostomy, XRT/chemotherapy |
|
|
What is the prognosis for anaplastic carcinoma of the thyroid? |
Dismal, because most patients are at stage IV at presentation (3% alive at 5 years) |
|
|
What lab value must be followed post-op after a thyroidectomy? |
Calcium - decreased 2/2 to parathyroid damage - During lobectomy, the parathyroids must be spared and their blood supply protected - If blood supply is compromised intraoperatively, they can be autografted into the sternocleidomastoid muscle or forearm |
|
|
What is the differential diagnosis of post-op dyspnea after a thyroidectomy? |
- Neck hematoma (remove sutures and clot at bedside) - Bilateral recurrent laryngeal nerve damage |
|
|
What is a "lateral aberrant rest" of the thyroid? |
Misnomer: it is a papillary cancer of a lymph node from metastasis |
|
|
What is the most common cause of hyperthyroidism? |
Graves' disease |
|
|
What is Graves' disease? |
Diffuse goiter with hyperthyroidism, exophthalmos, and pretibial myxedema |
|
|
What is the etiology of Graves' disease? |
Caused by circulating antibodies that stimulate TSH receptors on follicular cells of the thyroid and cause deregulated production of thyroid hormones (ie, hyperthyroidism) |
|
|
What is the female:male ratio with Graves' disease? |
6:1 |
|
|
What specific physical finding is associated with Graves' disease? |
Exophthalmos |
|
|
How do you diagnose Graves' disease? |
- Increased T3, T4, and anti-TSH receptor antibodies - Decreased TSH - Decreased global uptake of 131-I radionuclide |
|
|
Name treatment option modalities for Graves' disease. |
1. Medical blockade: iodide, propranolol, propylthiouracil (PTU), methimazole, Lugol's solution (potassium iodide) 2. Radioiodide ablation: most popular therapy 3. Surgical resection (b/l subtotal thyroidectomy) |
|
|
What are the possible indications for surgical resection of Graves' disease? |
Suspicious nodule; if patient is non-compliant or refractory to medicines, pregnant, a child, or if patient refuses radioiodide therapy |
|
|
What is the major complication of radioiodide or surgery for Graves' disease? |
Hypothyroidism |
|
|
What does PTU stand for? |
Propyl-Thio-Uracil |
|
|
How does PTU work? |
1. Inhibits incorporation of iodine into T4/T3 (by blocking peroxidase oxidation of iodide to iodine) 2. Inhibits incorporation of iodine into T4/T3 (by blocking peroxidase oxidation of iodide to iodine) |
|
|
How does methimazole work? |
Inhibits incorporation of iodine into T4/T3 only (by blocking peroxidase oxidation of iodide to iodine) |
|
|
What is toxic multinodular goiter also known as? |
Plummer's disease |
|
|
What is toxic multinodular goiter? |
Multiple thyroid nodules with one or more nodules producing thyroid hormone, resulting in hyperfunctioning thyroid (hyperthyroidism or a "toxic" thyroid state) |
|
|
What medication may bring on hyperthyroidism with a multinodular goiter? |
Amiodarone (or any iodine-containing med/contrast) |
|
|
How is the hyperfunctioning toxic multinodular goiter localized? |
131-I radionuclide scan |
|
|
What is the treatment of toxic multinodular goiter? |
Surgically remove hyper-functioning nodule(s) with lobectomy or near total thyroidectomy |
|
|
What is Pemberton's sign? |
Large goiter causes plethora of head with raising of both arms |
|
|
What are the features of acute thyroiditis? |
- Painful, swollen thyroid - Fever - Overlying skin erythema - Dysphagia |
|
|
What is the cause of acute thyroiditis? |
Bacteria (usually Strep or Staph), usually caused by a thyroglossal fistula or anatomic variant |
|
|
What is the treatment of acute thyroiditis? |
- Antibiotics - Drainage of abscess - Needle aspiration for culture - Most patients need definitive surgery later to remove the fistula |
|
|
What are the features of subacute thyroiditis? |
- Glandular swelling - Tenderness - Often follows URI - Elevated ESR |
|
|
What is the cause of subacute thyroiditis? |
Viral infection |
|
|
What is the treatment of subacute thyroiditis? |
Supportive: NSAIDs +/- steroids |
|
|
What id De Quervain's thyroiditis? |
Just another name for subacute thyroiditis caused by a virus (think: De QuerVain = Virus) |
|
|
How can the differences between etiologies of ACUTE and SUBACUTE thyroiditis be remembered? |
Alphabetically: - A before S - B before V
Acute before Subacute Bacterial before Viral |
|
|
What are the common causative bacteria in acute suppurative thyroiditis? |
Streptococcus or Staphylococcus |
|
|
What are the two types of chronic thyroiditis? |
1. Hashimoto's thyroiditis 2. Riedel's thyroiditis |
|
|
What are the features of Hashimoto's (chronic) thyroiditis? |
Firm and rubbery gland, 95% in women, lymphocyte invasion |
|
|
What is the claim to fame of Hashimoto's disease? |
Most common cause of hypothyroidism in the US |
|
|
What is the etiology of Hashimoto's disease? |
Auto-immune |
|
|
What lab tests should be performed to diagnose Hashimoto's disease? |
Anti-thyroglobulin and microsomal antibodies |
|
|
What is the medical treatment for Hashimoto's thyroiditis? |
Thyroid hormone replacement if hypothyroid (surgery is reserved for compressive symptoms and/or if cancer needs to be ruled out) |
|
|
What is Riedel's thyroiditis? |
- Benign inflammatory thyroid enlargement with fibrosis of thyroid - Patients present with painless, large thyroid - Fibrosis may involve surrounding tissues |
|
|
What is the treatment for Riedel's thyroiditis? |
Surgical tracheal decompression, thyroid hormone replacement as needed - possibly steroids/tamoxifen if refractory |

