![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
37 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
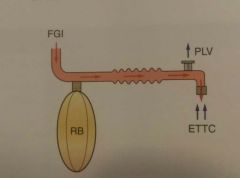
Magill Circuit Mapleson A Uses low fresh gas flow Expired gas may be breathed with manual ventalation |
|
|
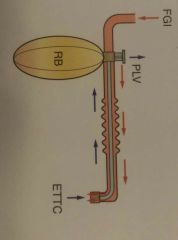
Lack Circuit Modified Mapleson A Uses low fresh gas flow Seperate tube for expired gas |
|
|
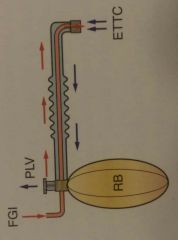
Bain Coaxial Circuit Modified Mapleson D Requires high fresh gas flow Freash gas inlet surrounded by corrugated tube. Tube within tube design for warming |
|
|
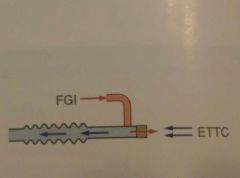
Ayre's T-piece Mapelson E No reservoir bag Very high flow rate 2-3 times RMV |
|
|
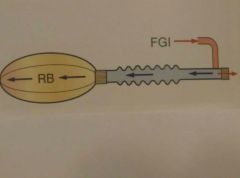
Jackso-Rees Circuit Fresh gas at patient end High fresh flow (2-3 times RMV) |
|
|
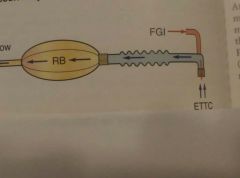
Norman Mask Elbow Mapleson F Same as Jackson-Rees but elbow possibly reduces dead space |
|
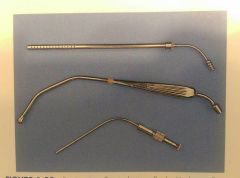
Names and uses |
Suction tips: Poole - large volumes Yankauer - single tube, bulky, general purpose Frazier/Adson - small hole, thumb hole to control pressure, for ortho and Neuro procedures |
|
|
Instrument components |
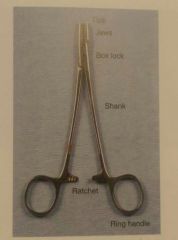
|
|
|
Scissors |
Operating - inanimate objects Mayo - large tissues Metzenbaum dissecting - delicate tissues Suture removal - suture |
|
|
Hemostats |
Halstead mosquito - small vessels Kelly - medium vessels, small masses Crile - medium vessels, small masses Rochester-Carmalt - large vessels, large tissues Rochester-Pean - longer than Crile, large muscles, tissues or vessels Ferguson angiotribe (not true) - traumatic forceps, any vessel or tissue not needed by the body. |
|

Left to right |
Halsead mosquito Crile Kelly |
|
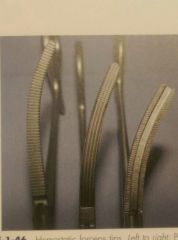
Left to right |
Rochester-Pean Rochester-Carmalt Ferguson angiotribe |
|

Top to bottom |
Operating scissors Blunt Sharp-blunt Sharp |
|
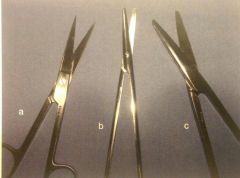
|
A. Operating B. Metzenbaum C. Mayo |
|
|
Needle Holders |
Short jaw, only tool for holding metal Derf - small, extraocular procedures Olsen-Hegar - scissors built in Mayo-Hegar - variety of lengths, general purpose Crile-Wood - finer, delicate jaw |
|
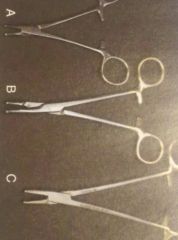
|
A. Derf B. Olsen-Hegar C. Mayo-Hegar |
|

Left to right |
Olsen-Hegar Mayo-Hegar |
|
|
Scalpel Blades, common sizes |
Small animal: 10,11,12,15 Large animal: 20-22 |
|
|
Thumb Tissue Forceps |
DeBakey thoracic - atraumatic, delicate tissue, ridge instead of teeth Tissue thumb forceps - straight shaft, 1x2 or 3x4 teeth Russian thumb tissue forceps - traumatic, bulky tip, for tissue being removed Adson's (3) - narrow tip to wider handle Adson dressing - no teeth, flat serrations Adson-Brown - 2 parallel rows, 9 teeth Adson 1x2 - 1x2 teeth, can be traumatic Allis tissue forceps - not hemostat or thumb forcep, traumatic tissue grasping |
|
|
Retractors |
Handheld Senn Self-retaining: Gelpi - hooks Weitlaner - blunt or sharp jaws Balrour - abdomen |
|
|
Bone tools |
Bone rongeurs - cupped tip Bone cutters - rongeurs with cutting edge tip Bone curettes - single handle, sharp edges Hand chuck - hold and drive pins |
|
|
Grip for scalpel or thumb forcep |
Pencil |
|
|
Grip for ring handle instruments |
Index and ring finger in rings |
|
|
Reservoir bag calculation |
60 ml/kg |
|
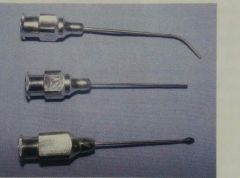
|
Lacrimal cannulas |
|
|
Anatomy of suture needles |
Point Body Suture attachment end |
|
|
Suture attachment ends |
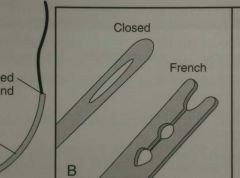
Single eye - closed around eye French-eyed - eye and second slit Swagged - no eye, suture crimped on |
|
|
Needle point types |
Taper - sharp point and rounded, less traumatic and well sealed suture line Reverse cutting - 3 edges, one cutting edge on outside curve, maintains shape and very strong Cutting - 3 cutting edges, one cutting edge on inside curve/toward wound edges, can compromise tissue strength of incision |
|
|
Needle types |
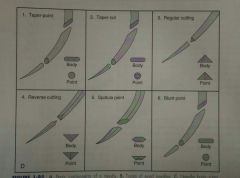
|
|
|
Suture characteristics |
Tensile strength Memory Flexibility Absorbability Capillarity Knot security Structure Color |
|
|
Endotracheal tubes |
Murphy Cole |
|
|
Endotracheal tube anatomy |
Patient end Bevel Murphy eye Cuff Pilot balloon and valve Machine end Connector |
|
|
Gas tanks |
Green large - H tank - O2 Green small - E tank - O2 Blue - Nitrous oxide |
|
|
Tubing for anesthesia machine |
Traditional - Y-tubing - corrugated - over 7 kgs Universal F tubing - tube in tube - exhaled air warms inhaled Pediatric tubing - 2.5-7 kgs (under 2.5 pgs use non-rebreather) |
|
|
Parts of anesthesia machine (tank to scavenge) |
Oxygen source Pressure reducing valve (40-45 psi) Flow meter (15 psi) Float Fast flush valve Vaporizer (precision or non-) Unidirectional inspiratory valve Negative pressure release valve Pop-off valve Unidirectional expiratory valve Manometer Rebreathing bag/reservoir bag CO2 absorber Scavenging system |
|
|
Miscellaneous surgical equipment |
Warming devices Lights Surgery table Electrosurgery (monopolar or bipolar) Suction tips (Poole, Fraser/Adson, Yankauer) |
|
|
Anesthesia machine areas out of circuits |
Oxygen source Pressure reducing valve Flow meter Fast flush valve |

