![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
78 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Which of the following are common approaches for abdominal surgery in the horse?
a) Ventral Midline b) Paramedian c) Paralumbar Fossa d) Parainguinal e) Inguinal |
a) Ventral Midline is most common (although the others are used sometimes)
|
|
|
Which of the following are common approaches for abdominal surgery in the cow?
a) Ventral Midline b) Left paralumbar fossa c) Right paralumbar fossa d) Caudal paramedian e) Right paramedian |
b) Left paralumbar fossa
c) Right paralumbar fossa e) Right paramedian |
|
|
Which approach is useful for rumenotomy? Abomasopexy? C-section?
|
Rumenotomy (Left paralumbar fossa)
Abomasopexy (L. paralumbar fossa; R. paramedian) C-section (L. paralumbar, R. paramedian, Caudal paramedian, ventral midline) |
|
|
T or F:
In equine abdominal surgery, you always exteriorize the cecum. |
True!
|
|
|
Which structures should be exteriorized in ruminant abdominal surgery?
|
Only what is abnormal
|
|
|
Choose simple vs. strangulating obstruction...
...enterolith |
simple
|
|
|
Choose simple vs. strangulating obstruction...
...lumenal obstruction without vascular compromise. |
simple
|
|
|
Choose simple vs. strangulating obstruction...
...simultaneous vascular and lumenal occlusion. |
strangulating
|
|
|
Which type of strangulating obstruction involves complete loss of blood supply?
|
Ischemic strangulating bowel obstruction (ISO)
|
|
|
Which type of strangulating obstruction involves thickening of bowel wall?
|
Hemorrhagic strangulating bowel obstruction (HSO)
|
|
|
Intravascular obstruction of the bowel without bowel incarceration is known as...
|
...Nonstrangulating infarction
|
|
|
What are parameters used to clinically assess bowel wall integrity?
|
Color of bowel wall
Color of mucosa Palpation of arterial pulse Presence of intestinal motility Return of normal bowel wall color |
|
|
What are some ancillary methods for evaluating bowel integrity?
|
Histopath
Fluorescein dye Surface oximetry Doppler ultrasound Luminal pressure |
|
|
What procedure is used when removing material from an impacted cecum? How would this be closed to provide the best blood supply to edges of incised tissue?
|
Typhlotomy;
Closed w/appositional followed by inverting (Lembert is best for blood supply) |
|
|
What is the strongest layer of bowel wall?
|
SUBMUCOSA
|
|
|
Which of the following procedures DOES NOT prevent abdominal contamination?
a) change gown/gloves before closing b) exteriorize segment to be incised or resected c) lavage before anastomosis to remove all surface contamination d) use separate instruments for clean and dirty portions of procedure |
c) lavage before anastomosis to remove all surface contamination is NOT correct. Lavage should be done AFTER anastomosis
|
|
|
What is the most common approach to a c-section in cattle? In horses? In camelids?
|
Cattle (left paralumbar fossa)
Horses/camelids (ventral midline) |
|
|
What is the linea alba?
|
where aponeurosis of transverse, internal, and external oblique muscles connect to midline
|
|
|
Which structure must ALWAYS be included when closing a linea alba incision?
|
External sheath of the rectus abdominus
|
|
|
Which two monofilament suture materials are NOT recommended in abdominal closure?
|
Gut
Monocryl (poliglicaprone) |
|
|
T or F:
Subcutaneous fat has little effect on suture integrity when closing a linea alba incision. |
False! You should clean the linea of fat first!
|
|
|
What are the borders of the epiploic foramen?
|
Vena cava
Portal v. Hepatic a. |
|
|
What are indications for tearing the omentum when performing an exploratory laparotomy?
|
To visualize the left limb of pancreas, splenic vessels, some lymph nodes
|
|
|
Which organs are in the gutter?
|
Kidneys
Vessels to the gonads adrenals Ureters |
|
|
What do you use as your "handle" to examine the right gutter? The left gutter?
|
Right (mesoduodenum)
Left (descending colon) |
|
|
Choose decerebrate, decerebellate, or Schiff-Sherrington...
...extension of thoracic limbs. |
Decerebellate AND Schiff-Sherrington
|
|
|
Choose decerebrate, decerebellate, or Schiff-Sherrington...
...extension of all limbs. |
Decerebrate
|
|
|
Choose decerebrate, decerebellate, or Schiff-Sherrington...
...paralysis of pelvic limbs. |
Schiff-Sherrington
|
|
|
Choose decerebrate, decerebellate, or Schiff-Sherrington...
...associated with a T2/T3 lesion. |
Schiff-Sherrington
|
|
|
What is the nerve associated with the following reflexes? From which segments does each arise?
Patellar Gastrocnemius Bicipital Triceps Cutaneous trunci |
Patellar (Femoral; L4-L6)
Gastrocnemius (Tibial/Sciatic; L7-S1) Bicipital (Musculocutaneous; C6-C8) Triceps (Radial; C7-T2) Cutaneous trunci (lateral thoracic n.; C8-T1) |
|
|
If you shine a light into a patients left eye and there is a lesion affecting the AFFERENT fibers of CN III, what happens? How about if the efferent fibers are affected?
|
Afferent (no pupillary constriction)
Efferent (contralateral pupillary constriction) |
|
|
What is the TLC of cancer surgery?
|
Tumor type
Location of tumor Condition of patient |
|
|
Regarding surgery (or most anything)...."Proper Planning Prevents ________ _________ ________."
|
Piss Poor Performance!
|
|
|
Which drug inhibits osteoclasts?
|
Bisphosphonates
|
|
|
What is the difference between single-modal and multi-modal surgical oncology?
|
Single-modal (cut big, cut wide, live forever)
Multi-modal (cytoreduction and chemo) |
|
|
Which procedure is best to diagnose a round cell tumor?
a) biopsy b) FNA c) Skin scrape |
b) effin' A!
|
|
|
What are some examples of things NOT to biopsy?
|
Masses in the brain, testis, lung, spleen, thyroid
|
|
|
A biopsy in which the entire mass is removed is called a(n) _____________ biopsy.
|
EXCISIONAL
|
|
|
What anatomic structures are natural barriers to cancer?
|
Fascial layers!
|
|
|
When should drains be placed during a biopsy?
|
NEVA!
|
|
|
Which tool is good for deep, ultrasound-guided biopsies? Which is good for superficial tumors? For bone biopsies?
|
Deep (needle-core; tru-cut instrument)
Superficial (punch) Bone (Jamshidi) |
|
|
What are the goals of the histological exam of a biopsy sample?
|
Neoplasia vs. non-neoplasia
Benign vs. malignant Histologic type Grade Status of margin |
|
|
Identify the following as neuro or ortho signs (or both)!
Shortened stride Ataxia Limb circumduction Head bob Weakness Toeing in/out Crepitus |
Shortened stride (both)
Ataxia (neuro) Limb circumduction (ortho) Head bob (ortho) Weakness (both) Toeing in/out (ortho) Crepitus (ortho) |
|
|
Choose AAEP lameness grade 1 - 5...
...constant lameness only under certain conditions. |
Grade 2
|
|
|
Choose AAEP lameness grade 1 - 5...
...very obvious lameness. |
Grade 4
|
|
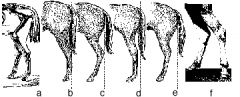
Which of these images displays "sickle hock"? What is the cause of this?
|
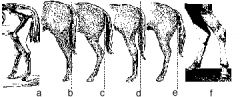
Image C; caused by crushing of cuboidal bones
|
|
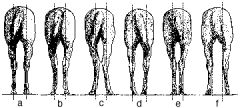
Which of these displays "cow hocks"? What is the medical term for this?
|
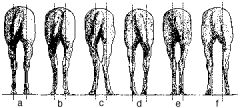
B and C are both cow-hocked (C is worse); bilateral tarsal valgus
|
|
|
Which nerves are blocked in a heel block? In an abaxial sesamoid block?
|
Palmar/plantar digital nerves (heel)
Palmar/plantar digital + lateral/medial brs. of metacarpal/tarsal nerves (sesamoid) |
|
|
Which nerves are blocked in a low 4-point block? In a high 4-point block?
|
Low (palmar/plantar nn., palmar/plantar metacarpal/tarsal nn.)
High (same as low but just higher up; can get it with one stick by getting the palmar n. near accessory carpal) |
|
|
Which ligament do you wanna miss when performing an intra-articular fetlock joint block?
|
collateral sesamoidean ligament
|
|
|
In the horse, flexing the stifle without flexing the hock indicates a ruptured ________________.
|
Peroneus tertius
|
|
|
T or F:
There is no such thing as veterinary physical therapy. |
True! Stupid human medicine has trademarked or copyrighted this or something retarded like that...
|
|
|
What does articular cartilage depend on for nutrition?
|
Synovial fluid
|
|
|
Compare/contrast heat and cold therapy.
|
Both reduce swelling; cold better for acute (post-op every 4-6hrs for 48hrs) while heat is better for chronic
|
|
|
What happens if a cold pack is applied for too long?
|
Hunter's reflex. Cyclical rebound vasodilation; can change temp by 10 to 15 degrees C!!
|
|
|
What are advantages of passive range of motion exercises?
|
Maintains joint mobility
Prevents muscle shortening Increase joint nutrition Stimulate cartilage regeneration |
|
|
T or F:
TENS units stimulate the muscles in their natural progression of fast twitch followed by slow twitch. |
False!
While TENS does stimulate fast b4 slow, normal muscle has slow before fast! |
|
|
What are some specific tendon injuries where ultrasound therapy is indicated?
|
Bicipital tenosynovitis
Flexor tendon contractions Tendon calcifications |
|
|
How does pulsed ultrasound and continuous wave ultrasound differ?
|
Pulsed (no heat, increases cell membrane permeability, used for chronic conditions)
Continuous (heat, used for acute injury) |
|
|
Water buoyancy at the level of the epicondyle reduces apparent body weight of a dog by what factor?
a) 5% b) 9% c) 12% d) 15% e) 62% |
d) 15%
|
|
|
What stretching regimen improves canine spinal flexibility and is a great warm-up for sporting dogs?
|
Cookie stretch
|
|
|
T or F:
Acupuncture cannot be practiced without a veterinary degree. |
True
|
|
|
What are the major resident bacteria that can be opportunistic pathogens of dogs and cats?
|
Staph aureus for both;
penicillin-resistant in dogs usually |
|
|
What are the major resident bacteria that can be opportunistic pathogens of cattle and horses?
|
Strept zooepidemicus for both
|
|
|
T or F:
If you are performing surgery on a dog and it ends up with a surgical site infection with S. aureus, it is YOUR FAULT!! |
False. Dogs and humans both have S. aureus (but it doesn't mean it WASN'T you)
|
|
|
T or F:
If you are performing surgery on a cow and it ends up with a surgical site infection with S. aureus, it is YOUR FAULT!! |
True!
|
|
|
T or F:
Unlike most S. aureus, the S. aureus found in cats is coagulase positive. |
False! Nearly all S. aureus is coagulase positive (including that of cat skin). Yeah dumb question, I know....
|
|
|
Describe tendon structure histologically:
|
type 1 collagen arranged in parallel bundles
|
|
|
What are the two types of tendons? What are examples of each?
|
Vascular (triceps, deep gluteal tendons)
Avascular (tendon sheath; eg: digital flexors, biceps tendons) |
|
|
What are the 3 types of tendon dysfunctions and how are they often diagnosed?
|
Tendinosynovitis
Tendonitis Tenosynovitis (dx: w/ultrasound) |
|
|
What are the 3 phases of tendon healing? What is the approximate timeline for each?
|
Inflammatory (0-4d)
Repair (4-30d) Remodeling (20-365d) |
|
|
What is critical to regaining and maintaining collagen strength in tendon healing?
|
MOVEMENT
|
|
|
Which of the following is true:
a) injured flexor tendons should be mobilized in extension b) injured extensor tendons should be immobilized in extension c) large animals tolerate a gap in tendon healing better than small animals d) the myotendinous junction is one of the most challenging sites of surgical repair. |
b) injured extensor tendons should be immobilized in extension
d) the myotendinous junction is one of the most challenging sites of surgical repair. |
|
|
What are the 4 factors influencing tendon healing?
|
Cause
Location of injury Gap (or no gap) Mobilization vs. immobilization |
|
|
An immobilized tendon is _____% weaker after just 6 weeks of immobilization.
|
50%
|
|
|
Describe a 3-loop pulley for tendon repair.
|
Near-far; middle-middle; far-near
120 degrees apposition to next |
|
|
What suture pattern is used to repair flat tendons?
|
Locking loop
|
|
|
inflammation of the ligament is called...
|
Desmitis
|

