![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
47 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What vertebral level is associated with the thoracic inlet? What anterior structure is associated with it?
|
-T1
-jugular notch |
|
|
The diaphragm runs from what to what vertebral level?
|
T8-T12
|
|
|
The plane between the superior and inferior mediastinum is marked by what structure anteriorly? What vertebral level posteriorly?
|
-sternal angle
-T4-5 |
|
|
The outermost level of the superior mediastinum contains what structures (2)
|
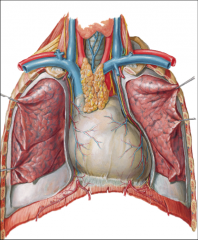
-thymus
-SVC |
|
|
The next inner level of the superior mediastinum has what 5 structures
|
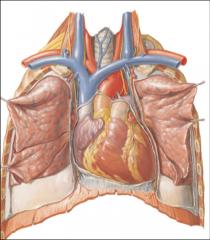
-brachiocephalic veins
-arch of aorta -vagus nerves -phrenic nerves -left recurrent laryngeal nerve |
|
|
The deepest level of the superior mediastinum contains (10) structures...
|
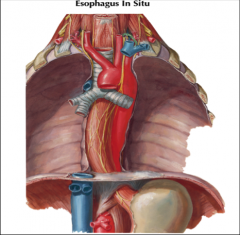
-trachea
-arch of the aorta -brachiocephalic trunk -left common carotid artery -left subclavian artery -esophagus -thoracic duct -sympathetic trunks and lymphatics -left recurrent laryngeal nerve -right recurrent laryngeal nerve |
|
|
The Azygos vein is on the ________ side of the thorax; the hemiazygos vein is on the _________ side of the thorax; the aorta is on the _______ side of the thorax.
|
-right
-left -left |
|
|
All splanchnic nerves are ____________ except the pelvic splanchnics.
|
sympathetic
|
|
|
The thoracic aorta becomes the abdominal aorta at what vertebral level
|
T12
|
|
|
The thoracic aorta descends in the posterior mediastinum from level _____ to _____.
|
T5-12
|
|
|
The space in the diaphragm through which the aorta passes is called what?
|
aortic hiatus
|
|
|
The 2 visceral branches of the thoracic aorta
|
bronchial and esophageal arteries
|
|
|
The 4 parietal branches of the thoracic aorta
|
-pericardial arteries
-posterior intercostal arteries -superior phrenic arteries -subcostal arteries |
|
|
The azygos vein is always on the _____ side; it forms an arch and drains into the ______.
|
Right; SVC
|
|
|
The azygos gets tributaries from where?
|
posterior intercostal veins 5-11
|
|
|
The right superior intercostal vein gets tributaries from where? Where does it drain to?
|
-posterior intercostal veins 2-4
-drains to arch of azygos |
|
|
The first posterior intercostal vein drains into where?
|
Subclavian or axillary veins
|
|
|
The hemiazygos and accessory azygos veins are always on what side?
|
left
|
|
|
The hemiazygos vein gets tributaries from where? Drains to where?
|
-posterior intercostal veins 8-11
-drains to azygos |
|
|
The accessory hemiazygos vein gets tributaries from where? Drains to where?
|
-posterior intercostal veins 5-7
-drains to azygos |
|
|
The left superior intercostal vein gets tributaries from where? Drains to where?
|
-posterior intercostal veins 2-4
-left brachiocephalic vein |
|
|
The first left posterior intercostal vein drains into where?
|
Subclavian or axillary veins
|
|
|
Lymphatic drainage of the visceral pericardium
|
-posterior mediastinal lymph nodes
|
|
|
Lymphatic drainage of the esophagus
|
-posterior mediastinal lymph nodes
|
|
|
Pathway of lymphatic drainage from the heart
|
posterior mediastinal lymph nodes --> carinal/superior and inferior tracheobronchial lymph nodes --> paratracheal lymph nodes --> thoracic duct
|
|
|
Lymphatic drainage of the parietal pericardium
|
-phrenic and intercostal lymph nodes
|
|
|
The thoracic duct empties where?
|
Left venous angle (junction of left internal jugular and subclavian veins)
|
|
|
Confluence of right and left lumbar lymphatic trunks and intestinal trunk; only present in 20-25% of people
|
cisterna chyli
|
|
|
Trachea is __________ to the esophagus
|
anterior
|
|
|
Trachea lies only in the ___________ mediastinum
|
superior
(esophagus is in both superior and posterior mediastinum) |
|
|
The upper part of the esophagus has __________ muscle and is innervated by what?
|
skeletal; recurrent laryngeal nerve
|
|
|
Damage to the recurrent laryngeal nerve can cause what?
|
hoarseness and dysphagia
|
|
|
Lower part of the esophagus has _______ muscles and is innervated by what?
|
smooth; esophageal plexus
|
|
|
The esophagus has narrowings at what 4 areas?
|
T4 - at level of arch of the aorta
T5 - main bronchus level T8-9 by thoracic aorta T 10 by crus of diaphragm |
|
|
What provides sensory innervation to the pericardium? the mediastinal pleura?
|
The phrenic nerve
|
|
|
The phrenic nerve has branches from what cranial nerves? What fibers does it contain?
|
-C3, 4, 5
-somatic efferent and afferent fibers |
|
|
Which phrenic nerve is longer? Where does it pass through the diaphragm?
|
Right; with the IVC at T8
|
|
|
The phrenic nerve runs (anterior/posterior) to the root of the lung. What vessels is it associated with?
|
-anterior
-pericardiacophrenic vessels |
|
|
What pleural/epicardial layers is the phrenic nerve located between?
|
-between the fibrous parietal pericardium and the (mediastinal) parietal pleura
|
|
|
Supplies sympathetic innervation of the abdominal viscera
|
thoracic splanchnic nerves
|
|
|
The thoracic sympathetic trunks run paravertebral and contain ganglia ___-____
|
9-12
|
|
|
They have (gray/white/gray and white) rami communicantes
|
gray and white
|
|
|
Post-ganglionic fibers from the thoracic sympathetic trunks form what 3 plexuses
|
-esophageal
-cardiac -pulmonary |
|
|
Which ganglia form the greater splanchnic nerve? The lesser? The least?
|
-5-9 greater
-10-11 lesser -12 least |
|
|
The recurrent laryngeal nerve is a branch of what?
|
-Vagus nerve
|
|
|
What level of the diaphragm does the vagus nerve pass through? What runs with it? What do the vagus nerves become once they pass through?
|
-T10
-Esophagus -Left - becomes anterior vagal trunk; Right - becomes posterior vagal trunk (LARP) |
|
|
Severe pulmonary hypertension can damage what nerve (lies posterior to it)?
|
-Recurrent laryngeal nerve
|

