![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
10 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Elements
|
A pure substance that is made entirely from one atom
Eg: |
|
|
Compounds
|
Are pure substances made up entirely from two or more elements that are chemically combined
|
|
|
Law of Conservation of Energy
|
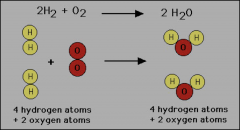
Mass cannot be created nor destroyed in ordinary chemical of physical changes
|
|
|
Law of definite proportion
|
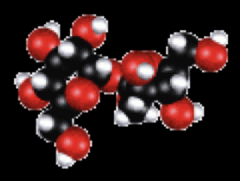
A chemical compound always contains the same elements in exactly the same proportion by weight or mass
Eg: C12H22O11 |
|
|
Law of multiple proportions
|

When two elements combine to form two or more compounds, the mass of one element combined with the given mass of the other is in the ratio of whole numbers
|
|
|
Dalton's theory 1
|
All matter is composed of extremely small particles called atoms, atoms cannot be created, subdivided or destroyed
|
|
|
Dalton's theory 2
|
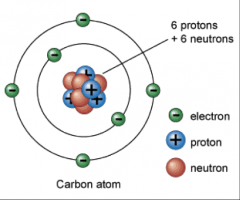
Atoms of a given element are identical in their physical and chemical properties
|
|
|
Dalton's theory 3
|
Atoms of different elements differ in their physical and chemical properties
Eg: Nitrogen has 7 and Oxygen has 6 |
|
|
Dalton's theory 4
|
Atoms of different elements combine in simple, whole-number ratios to form compounds
|
|
|
Dalton's theory 5
|
In chemical reactions, atoms are combined, separated or rearranged, but never created, destroyed or changed
|

