![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
56 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Define a NREM arousal.
|
An abrupt change in EEG frequency that lasts for 3 seconds or more. Must be preceded by 10 seconds of sleep.
|
|
|
Define a REM arousal.
|
An abrupt change in EEG frequency that lasts for 3 seconds or more. Must be preceded by 10 seconds of sleep. REM arousal require an increase in chin tone.
|
|
|
How is the mea sleep latency calculated in a MSLT?
|
Add up all of the sleep latencies for all of the naps and then divide by the number of naps.
(N1+N2+N3+N4+N5)/5 |
|
|
How frequent are the naps scheduled during the MSLT?
|
First nap is 1.5-3 hours after wake time, then every 2 hours after that.
|
|
|
What does MSLT refer to?
|
Multiple Sleep Latency Test
|
|
|
How many naps are usually preformed during the MSLT?
|
4-5 naps throughtout the day; naps occur every 2 hours.
|
|
|
After sleep onset occurs, when is the nap terminated.
|
15 minutes from the first epoch of sleep.
|
|
|
If there is no sleep noted during the nap, when is the nap terminated?
|
20 minutes from "Lights Out".
|
|
|
What is the purpose of a MSLT?
|
to assess and diagnose diseases of excessive somnolence and to evaluate daytime sleepiness.
|
|
|
How long before a nap should the subject stop smoking?
|
30 minutes.
|
|
|
What epoch size is best for recording the MSLT?
|
30 seconds
|
|
|
A mean sleep latency of less than 5 minutes during the MSLT indicates what?
|
Pathological sleepiness
|
|
|
A normal mean sleep latency is how many minutes?
|
10-20 minutes
|
|
|
How many naps must have REM periods to arrive at a diagnoses of narcolepsy?
|
2
|
|
|
What is the the anrcoleptic tetrad?
|
Excessive Daytime Sleepiness
Hypnogognic Hallucinations Sleep Parlysis Cataplexy |
|
|
What montage is generally used for recording the MSLT?
|
4 EEG - C3,C4,O1,O2
2 EOG Chin EMG EKG |
|
|
Sleep latency is defined as;
|
The amount of time elapsed from "Lights Out" to the 1st epoch of sleep.
|
|
|
Reflux is identified in the distal esophagus by a drop in the pH to below what?
|
4.0
|
|
|
A patient is susceptible to shock when
|
ALL the equipment is not connected to a common ground.
|
|
|
What are the effects of chronic alcoholism on sleep?
|
Reduction of delta sleep and REM sleep.
|
|
|
Sleep distrubance that lasts one to several nights in an isolated period; most often caused by actue stress or travel across multiple time zones.
|
Transient Insomnia
|
|
|
Poikilothermia
|
1.Of or relating to an organism having a body temperature that varies with the temperature of its surroundings; cold-blooded; occurs during REM
|
|
|
60 Hz interference
|
an artifact; caused by impedences greater that 10,000 ohms which allows for greater potential of electrode imbalance, and the artifact in the signal.
|
|
|
What is the minimum paper speed recommended to allow clear visual resolution of alpha and sleep spindles?
|
10 mm/sec.
|
|
|
Stage 1?
|
Low voltage mixed frequency EEG wtih a prominence of 2-7 cps activity, slow eye movements.
|
|
|
Stage 1
|

|
|
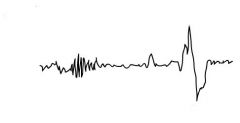
Identify these waveforms
|
K-Complex and Sleep Spindle
|
|
|
What is the gold standard for diagnosing OSA?
|
A PSG [reformed at a Sleep Lab.
|
|
|
List the four skull landmarks used in the 10-20 system of electrode pacement?
|
Nasion
Inion Right Preauricular Left Preaucicular |
|
|
The sleep test used to assess and diagnose disorders of excessive somnolence and to evaluate daytime sleepiness?
|
MSLT
|
|
|
In order to assess the occurence of REM sleep during a MSLT, the test should continue how long after sleep onset?
|
15 minutes
|
|
|
NREM sleep in an infant is also known as?
|
Quiet sleep
|
|
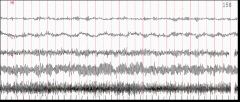
Identify?
|
Alpha Waves
|
|
|
REM percntage of sleep for a neonate at term?
|
50%
|
|
|
Thermregulatory responses such as sweating and panting are noted in NREM or REM sleep?
|
NREM. They are absent in REM sleep because of Poikilothermia.
|
|
|
REM density
|
A function that expresses the frequency of eye movements per unit time during REM sleep.
|
|
|
RDI or Respiratory Distrubance Index
|
is the number of apneas, includes apneas and hypopneas, and may also include other respiratory disturbances such as snoring arousals, hypoventilation episodes, desaturation events, etc. They are often identical, but depending upon what is scored, the RDI may be larger than the AHI.
ERA's |
|
|
___________apneas and hypopneas per hour of sleep.
|
AHI or Apnea-Hypopnea Index
|
|
|
Hypercapnia
|
More than the normal level of carbon dioxide in the blood.
|
|
|
Does family history increase risk of OSA?
|
Yes, risk increases with the number of affected family members and is fourfold greater if three relatives are affected
|
|
|
During a cataplexy attack, does the person stay conscious?
|
Yes.
If the eyelids are open or are opened, the person can even recall visual events that occurred during the attack. |
|
|
How are nightmares differentiated from night terrors?
|
Nightmares occur during REM sleep, while night terrors occur during Stage 4 non-REM sleep.
|
|
|
How many stages of sleep are there?
|
5
1. Stage 1 2. Stage 2 3. Stage 3 4. Stage 4 5. REM |
|
|
In healthy adults, what is the percentage of sleep one would have in each stage?
|
Stage 1 2-5%
Stage 2 45- 5% Stage 3 13-22% REM 20-25% |
|
|
What are anatomic abnormalities that predispose to OSA?
|
1) nasal obstruction
2) adenotonsillar hypertrophy 3) macroglossia 4) micrognathia 5) retrognathia |
|
|
What are hypnagogic hallucinations?
|
They are episodes of auditory, visual, or tactile hallucinations that occur during sleep paralysis as the individual is falling asleep.
|
|
|
What are hypnapompic hallucinations?
|
They are episodes of auditory, visual, or tactile hallucinations that occur during paralysis as the individual is awakening.
|
|
|
What are some factors that are responsible for or related to insomnia?
|
Nightmares
Sleep apnea Restless-leg syndrome Myoclonus Drug-inducing insomnia Insomnia due to brain damage |
|
|
How can one prevent cataplexic attacks
|
By maintaining tight control of ones' emotions.
|
|
|
How effective is UPPP for curing OSA?
|
40-50%: Sher et al. showed 41% response rate
|
|
|
How effective is UPPP for curing snoring?
|
90%
|
|
|
What are the cardiovascular consquences of OSA?
|
Systemic Hypertension Cardiac Arrhythmia Pulmonary Hypertension Polycythemia
Cor Pulmonale |
|
|
What is the definition of apnea?
|
cessation of airflow for 10 or more seconds
|
|
|
What is upper airway resistance syndrome?
|
UARS refers to increased ventilatory effort due to upper airway narrowing, leading to sleep fragmentation, arousals, and daytime somnolence but without apnea, hypopnea, or O2 desats.
|
|
|
What RDI value indicates sleep apnea?
|
greater than or equal to 5
|
|
|
What waves are observed during Stage 1 non-REM sleep?
|
Theta waves (medium amplitude, 4-7 waves/sec).
Stage 1 is usually brief and is a transition between wakefulness and Stage 2. |

