![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
16 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
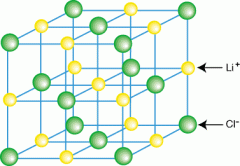
Explain an ionic lattice |
Ionic compounds have a structure described as an ionic lattice. It is a 3D network of positive and negative ions held together by ionic bonds (electrostatic forces) between the oppositely charged ions. |
|
|
Properties of ionic bonds
|
Crystalline solids, high melting and boiling points, conducts electricity only when molten or dissolved in water, most dissolve in water, don't dissolve in organic substances.
|
|
|
Properties of simple covalent substances
|
Low melting and boiling points, don't conduct electricity because there are no charged electrons, mostly insoluble or have low solubility in water.
|
|
|
What are the weak forces of attraction between molecules called? |
'Van der Waal's forces of attraction'.
|
|
|
Properties of giant covalent structures |
No charged ions, all atoms bonded to each other by strong covalent bonds, very high melting and boiling points, don't conduct electricity even when molten (except graphite), usually insoluble in water. |
|
|
What are allotropes?
|
Elements that can exist in two or more different physical form are said to exhibit allotropy, eg. diamond and graphite are allotropes |
|
|
Explain the structure of diamond |
Each carbon atom forms 4 covalent bonds in a very rigid structure. |
|
|
Properties of diamond |
Very hard solid because breaking diamond requires breaking many strong bonds, high melting and boiling points because lots of energy needed to break such strong bonds, insoluble in water, doesn't conduct electricity beacause there are no delocalised electrons. |
|
|
Explain the structure of graphite |
Each carbon atom only forms 3 covalent bonds leaving electrons to wander freely. |
|
|
Properties of graphite |
Soft slippery solid because the 3 bonds form layers which sre free to slide over each other, feels greasy and can be used to write with on paper, high melting and boiling points because of the 3 strong bonds, insoluble in water, conducts electricity because some delocalised electrons are not used in bonds and are free to wander and carry charge. |
|
|
Properties of metallic bonds
|
Malleable and ductile as the layers can slide over each other without disrupting the bond, high melting and boiling points, good conductor of electricity even when molten because of free electrons that can carry charge about (when a potential difference if applied, they will move together allowing the current to flow).
|
|
|
Define alloy |
A mixture of 2 or more elements, at least one of which is a metal, it has metallic properties. |
|
|
Uses of aluminium |
Overhead electrical wiring (good conductor of electricity) and alloys for aircrafts (strong and hard). |
|
|
Uses of copper |
Electrical wiring (good conductor of electricity) plumbing, brass and coinage (doesn't rust) |
|
|
Uses of iron |
Bridges and structures (strong and hard) |
|
|
Uses of magnesium |
Flares (burns with a bright white light) and alloys for aircrafts (strong and hard) |

