![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
23 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the internal arcuate fibers? |
1. Axons fo gracile and cuneate nuclei crossing to the opposite side 2. Form sensory decussation in the middle part of the medulla |
|
|
How do the internal arcuate fibers ascend? |
1. In OPEN medulla as medial lemniscus |
|
|
How do the fibers of the pyramidal tract descend? |
1. In lower part, most fibers decussate to form motor decussation and continue downwards in lateral column as crossed pyramidal tract 2. Rest of fibers descend on same side as direct pyramidal tract in anterior column |
|
|
What structures surround the fourth ventricle? |
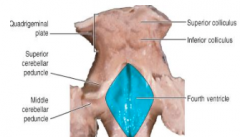
1. Superolateral= superior cerebellar peduncles 2. Inferolateral= inferior cerebellar peduncles |
|
|
What structures form the roof and floor of the medulla? |
1. Roof=Superior and inferior medullary vellum 2. Floor=back of pons and back of upper medulla (separated by transverse medullary stria) |
|
|
What are the medullary velae? |
1. Superior/inferior form roof of 4th ventricle 2. Superior stretches between superior cerebellar peduncles 3. Inferior stretches between inferior cerebellar peduncles |
|
|
What pierces the superior medullary velum? |
1. Trochlear nerve |
|
|
What are the stria modulars? |
1. Axons of arcuate nuclei 2. Run to cerebellum via inferior cerebellar peduncles |
|
|
What is the median longitudinal sulcus? |
1. Divides floor of 4th ventricle into right and left halves--- 4 quadrants |
|
|
What is found in the upper quadrant of the medullary floor? |
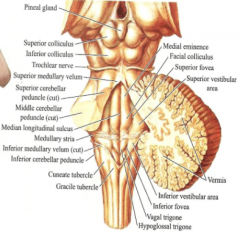
1. Superior fovea--divisions are: 2. Medial eminence 3. Facial colliculus 4. Superior vestibular area |
|
|
What forms the medial eminence? |
1. Fibers of abducent nerve |
|
|
What forms the facial colliculus? |
1. Nucleus of abducent nerve encircled by fibers of facial nerve |
|
|
What does the superior vestibular area overlie? |
1. Vestibular nucleus |
|
|
What is found in the lower quadrant? |
1. Inferior fovea---- divisions: 2. Hypoglossal trigone 3. Vagal trigone 4. Inferior vestibular area |
|
|
What does the hypoglossal trigone overlie? |
1. Hypoglossal nucleus
|
|
|
What does the vagal trigone overlie? |
1. Dorsal motor nucleus of agus |
|
|
What doe the inferior vestibular area overlie? |
1. Inferior vestibular nucleus |
|
|
Where is the choroid plexus located? |
1. Lower part of roof of 4th ventricle |
|
|
What is the arterial supply of the choroid plexus? |
1. Posterior inferior cerebellar artery |
|
|
What are the recesses of the 4th ventricle? |
1. Dorsal 2. 2 lateral--- extend into flocculus of cerebellum |
|
|
What are the apertures of the 4th ventricle and where do they lie? |
1. Media aperture: lower part of roof 2. 2 lateral apertures of Luschka: end of each lateral recess |
|
|
What is the arterial supply of the ventral part of the medulla? |
1. Vertebral and basilar arteries |
|
|
What is the arterial supply lateral and dorsal parts of the medulla? |
1. Posterior inferior cerebellar artery |

