![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
28 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the most common type of stroke?
|
Ischemic
|
|
|
What is small vessel disease most often attributed to?
|
Hypertension
|
|
|
What is a stroke?
|
Sudden neurological dysfunction due to a vascular cause
|
|
|
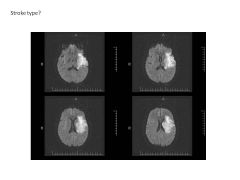
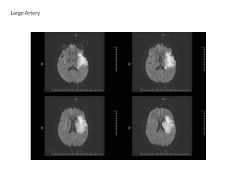
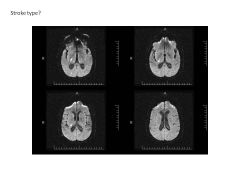
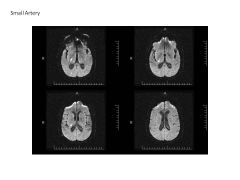
Describe the four subtypes of occlusive strokes (include origin/cause).
|
Cardioembolic (strokes of cardiac origin; includes atrial fibrillation, valvular heart dz)
Small vessel dz (strokes due to occlusion of vessels; often due to HTN, DM) Large Vessel Dz (occlusion of vessels 1-4mm; carotid, MCA; due to high chol) Rare and UNK (stroke due to arterial dissection--tear--blood coagulation abnormality) Each accounts for about 25% of ischemic stroke. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
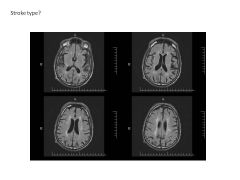
|
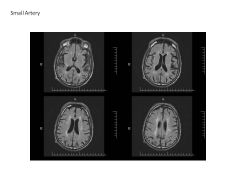
FLAIR Image showing strokes over lifetime
|
|
|
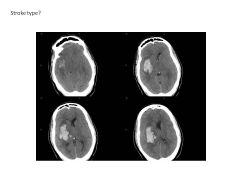
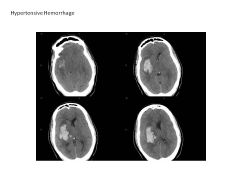
About what percent of strokes are hemorrhagic? Cause?
Describe the two subtypes (include causes, location). Which is more prevalent? |
10% of all strokes are hemorrhagic (much more lethal than ischemic stroke)
Due to vessel rupture (40% mortality) 1) Lobar hemorrhage (75%): HTN, deep structures (putamen, basal ganglia) Amyloid angiopathy (superficial, older) Arteriovenous malformation (superficial, younger) 2) Subarachnoid Hemorrhage (about 25%): aneurysm, arteriovenous malformation |
|
|
|
|
|
Signs of a Left Middle Cerebral Artery stroke?
|
Aphasia
Right Hemiparesis (weakness): face/arm more than leg Deviation of eyes to LEFT Right hemianesthesia (sensory loss) Right hemianopia (right visual field loss) |
|
|
|
|
|
Signs of a Right Middle Cerebral Artery stroke?
|
Neglect
Left hemiparesis (weakness): face/arm more than leg Deviation of eyes to RIGHT Left hemianesthesia (sensory loss) Left hemianopis (loss of left visual field) |
|
|
Broca's vs Wernicke's Aphasia
|
Broca: no expression, writing, repetition or naming; COMPREHENSION and READING INTACT
Wernicke's: No comprehension, reading, writing, repetition, naming; EXPRESSION INTACT (word salad) |
|
|
Signs of Global Aphasia
|
No expression, comprehension, reading, writing, repetition, naming
|
|
|
Transcortical Motor vs Transcortical Sensory Aphasia
|
Trans Motor (Broca's with reptetition intact): no expression, writing, naming; Comprehension, Reading, Repetition intact
Trans Sensory (Wernicke's with repetition intact): No comprehension, reading, writing, naming; Expression and repetition intact |
|
|
Signs of Conduct Aphasia
|
Can't repeat but expression, comprehension, reading, writing, and naming intact
|
|
|
Signs of Alexia-Agraphia Aphasia
|
Can't read; expression, comprehension, writing, repetition, naming intact
|
|
|
Signs of a Lacunar Stroke
|
One sided weakness without aphasia or neglect
Brainstem lacunes may have crossed findings |
|
|
Signs of Weber Lacunar Stroke
|
3rd Nerve Palsy
Contralateral hemiparesis (midbrain) |
|
|
Signs of Benedikt Lacunar Stroke
|
3rd Nerve Palsy
Contralateral dysmetria (pons) |
|
|
Signs of Millard-Gubler Lacunar Stroke
|
CN 6 + 7 palsy (facial weakness)
Contralateral hemiparesis (pons) |
|
|
If patient has a one-sided ptosis but is able to converge eyes, what is diagnosis?
|
Internuclear ophthalmoplegia (not a 3rd nerve palsy because can converge eyes)
|
|
|
______ strokes are NOT associated with aphasia
|
Lacunar
|
|
|
In a patient with atrial fibrillation and stroke, what is the treatment of choice for secondary stroke prevention?
|
Warfarin
|
|
|
A patient with left MCA stroke had 75% stenosis on the left internal carotid. What is the best treatment to prevent a stroke over the next 2 years?
|
Carotid endarterectomy
|
|
|
What is the timeframe for tPA wadministration? ASA?
|
tPA within 4.5 hours
ASA within 48 hours |
|
|
Describe the ABCDE treatment plan for stroke.
|
Antiplatelets (ASA, Aggrenox, Plavix)
Anticoag (Warfarin) Blood Pressure Control (less than 140/90) Carotid Artery Repair (if more than 70% narrowing) Cholesterol Lowering Cessation of Smoking Diet Exercise |
|
|
What are MCA strokes typically associated with (that differentiate them from other strokes)?
|
Aphasia and Neglect
|

