![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
40 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Richard Lazarus |
- Interested in experimental evaluation - Effects of motivation on people - Book Psychological Stress and Coping - Psych Stress is proportional to stress potency |
|
|
Magna Arnold |
Coined the appraisals |
|
|
Magna Arnolds Appraisals |
1. Primary Appraisal: Capacity to produce strong coping effects 2. Secondary Appraisal: Coping with the stress 3. Re appraisal: Change in a coping response because of a stimulus e.g. when there is a cage full of tigers at the zoo, and the cage has been left open |
|
|
Coping Efficacy comes from 2 locations |
1. Environment 2. Personal |
|
|
Pain tolerance depends on ... |
Source, coping efficacy, and amount of harm of appraisal evaluation |
|
|
TA study on environment: Results (The one done with 3 different conditions) |
Stress potency: Didn't really matter what group people were in for environmental and coping efficacy, all that mattered was that they felt they were able to cope with it. |
|
|
Formal and Non Formal Theory |
Split into 2 instruments 1. Non formal: (Un aided verbal reasoning) - Vast majority of work is done this way - Surveys etc. 2. Formal: (aided verbal reasoning) - Computer language - Symbolic logic - Mathematics |
|
|
Stress arousal |
Activation of stress |
|
|
Coping propensity |
To engage in counter stress activity (formal and non formal theory) - Not coping and low propensity = mood disorders and depression |
|
|
Excessive Coping |
Engaging in counter stress activity when there is no environmental impact |
|
|
Absensive coping |
Not engaging in counter stress acitivity when there would be an impact |
|
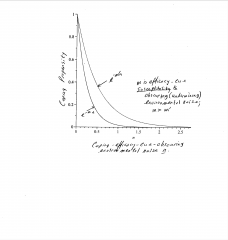
Formal Graph |
*One curve signifies more coping propensity and resistance to environmental noise than the other Top curve = Increased coping prosperity M = Vulnerability of the coping producing cue to environment noise (as M goes up greater vulnerability) N= Environmental Noise (When N is high there is a coping breakdown) E= The natural logarithm (2.72) * can predict momentary change * allows for the creation of relevant summaries of coping activity * can get quantitative predictions * can imply clinical assessment |
|
|
Formal Theory |
Specifies its own measures, research designs and tests |
|
|
Model Testing |
Tests precise quantities E.g. Goodness of Fit Tests: To do with quantities that are extensive and expansive |
|
|
Explanatory incites |
Inspection of structure 1. Aesthetic appeal: A property that is desired 2. Self-diagnostic: Selective influence, manipulations directed towards the environment should influence the decision. 3. Liberating Qualities: Does not require you to have empirical support every step of the way 4. Realist vs. Instrumental: Empirical data vs. A thought without concrete data |
|
|
3 Types of Theoretical Modelling |
1. Normative Model: Optimal way about making judgement or predictions about something 2. Descriptive Model: Inferences choices and judgement B. Similarity Heuristic Model: (falls under descriptive) E.g. Tell me if the person who wrote this essay is in computer science or arts and humanities Prob of computer science writing this essay X Prob of someone in arts writing the essay 3. Abnormal Descriptive: Deals with extremities |
|
|
Hans Selye |
- Wrote a book called Stress of Life General Adaptation Syndrome: Concept of a combination of events (multiplicity syndrome) - Emphasis was on mental or physical danger |
|
|
Pollard and Ice HPA |
Hypothalamic Pituitary Adrenal (release of cortisol into the system) Allistasis: Psychological disorder Allistatic: Chronic physical disorder 1. Alarm 2. Period of resistance |
|
|
Jenkins, Holmes, Rahe |
Life Events Scale: Had to do with the probability of developing an illness - They investigated major life incidents Jenkins Activity Survey: Developed a new way of measuring things, they were not interested in major life events, but rather a persons response to them. Developed into 2 types of people Type A: People who reacted to situations with active involvement Type B: People who responded with passivity, took things in stride |
|
|
Lazarus and Folkman (2 scales) |
Daily Hassles Scale: used for examining a broadspectrum of everyday stresses, and provided initial evidence regarding itsreliability, validity, and ability to predict psychological symptoms Ways of Coping Scale: Engaging in relaxation exercises religious exercises, and social support |
|
|
Mandler |
Rather than a typed definition, stress and coping should be approached through implicit shared understanding and implementing different ideas. Textbook title approach: Working model: |
|
|
3 Realms of Stress Activation |
Psychophysiological: Involve automatic reactions that can be detected (e.g. sweat reaction) Behavioural: Observes how much stress interferes with performance Subjective: Has to do with rating scales, that can measure unique individual differences - Common analogue scale: Ranges from 0 to stress extreme |
|
|
Coping |
Ways of coping - Seek support - Even 1 allie evidence has shown can make a huge difference - Systematic coping - Electromyography: Sensitive to processing information. Chine muscles are observed during cognitions (digastricus and obiculoris) |
|
|
Diagnostic Interview Scale |
Requires an interview/ structured interview, aims is to separate objective and subjective stressors. |
|
|
Quasi |
Sum of the number of goals that an individual has. N= the number of goals being implemented - Stress proportional to: summation of goal importance X Intensity of deprivation * As either goes up, stress goes up |
|
|
Response Directed "Emotion" Focused Coping |
- Getting your own reaction under control - Have different response then you want, and trying to counteract with that response - Synthesizing energy - More complex level should improve cognitive efficiency |
|
|
Stimulus directed coping |
- Problem focused, instrumental, decisional control - Directed towards social evaluation |
|
|
Problem focused coping |
- Placing oneself in a multi faced stressful situation to minimize the probability of an unfavourable event - Recuperation, this can be done through a variety of mechanisms, distraction, social support and relaxation exercises. |
|
|
Palliative |
- Making experience less aversive, until coping is complete - Engage in comfort and cognitions |
|
|
Comprised Vigilance |
- Focus on psychological subjective - Focus on physiological level of activation when in danger |
|
|
Neurotic paradox |
- Disadvantage of response directed coping - Long term events - Punishing aspect, because of aversive aspect is so remote to the positive reinforcement - Anxiety disorders, OCD - Multiple set of manipulations to take into account |
|
|
Kinds of stimulus directed coping |
Instrumental control: Individual acts directly to stress activation e.g. assault Decisional control: Position oneself in a stressing situation to minimize the likelihood of an aversive event Restorative: After a stressing event has happened, one wants to put things back in order e.g. natural disaster |
|
|
Kinds of response directed coping |
Palliative coping: Reducing adverseness, recuperation. Creating a buffer between subjective experience and subjective optimal level |
|
|
Endler (Multi dimensional scale) |
4 Dimensions - Physical danger of threat - Ego Threat - Unexpected/Unfamiliar situation - Daily routine |
|
|
Charles (2 scales) |
State anxiety: What is immediate state that a person is feeling? Trait Anxiety Scale: Characteristics of individual, how they typically react to stress |
|
|
Pre-pulse interval |
The interval between stimulus 1 and stimulus 2 that helps a person brace themselves from engaging in a buffering activity |
|
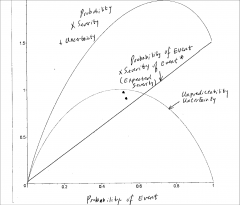
|
- 0 probability means fully predicable, people will be cautious and relaxation will not happen - As probability goes up the more likely that the stress activation will increase w/ the likelihood of that event - The 2 lines are a sum of linear components, individuals will differ in terms of what event had more of an impact on them - Stress activation increases with event probability, but it varies |
|
|
Shannon- Weonder Information Theory |
Relates to binary logarithms, used to separate predictability from probability - Foundation for current hardware and software - A Mathematical Theory: All related to horizontal line of probability. As probability becomes separate, predictability is increased but are they are more equal to each other, uncertainty is maximized |
|
|
3 Kinds of Log in Science |
Common log: Whatever you have to do to 10, in order to get a certain value of X Natural log: Whatever you have to do to 2.72, in order to get a certain value of X Binary Log: Whatever you have to do to 2, in order to get a certain value of X |
|
|
Maximax |
Maximize likelihood of an outcome |

