![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
23 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Dimensions of Strategic Actions for Complimenting Basic Competitive Strategy |
1. Offensive and defensive competitive actions 2. Competitive dynamics and the timing of 3. Breadth of a company’s activities.
Which all leads into: 1) Offensive Strategic Moves 2) Defensive Strategic Moves 3) Horizontal Integration (Related / Unrelated) 4) Vertical Integration (backward or forward) 5) Outsourcing of value chain activities AND 6) Strategic Alliances
*can pursue one selectively or a mix of them |
|
|
Strategic Offensive Principles |
– Focus on relentlessly building competitive
– Apply resources where rivals are least able
– Employ the element of surprise as opposed
– Display a strong bias for swift, decisive, and |
|
|
OFFENSIVE STRATEGY OPTIONS Within Existing Market Space: |
• Offer an equally good or better value product
• Leapfrog competitors by being first to
• Pursue continuous product innovation to
• Adopt and improve on the good ideas of
• Use hit-and-run or guerrilla warfare tactics
• Launch a preemptive strike to secure an |
|
|
Strategic Defensive Principles: |
– Focus on lowering the risk of being attacked
– Focus on weakening the impact of any
– Influence challengers to aim their attacks at |
|
|
DEFENSIVE STRATEGY OPTIONS |
• Adopt alternative technologies as a hedge
• Introduce new features and models to
• Maintain economy-pricing to thwart lower
• Discourage buyers from trying competitors’
• Make early announcements about new
• Challenge quality and safety of
• Grant discounts or better terms to
*get bid for selling your product only ex. only your beer sold in arenas |
|
|
Decision to Pursue Offensive /Defensive |
• Dependent upon position along strategy
• Subject to Considerations of Market Readiness: 1. Does market takeoff depend on the
2. Is new infrastructure required before
3. Will buyers need to learn new skills or
4. Are there influential competitors in a |
|
|
Decision about Timing of Offensive or Defensive Pursuit is subject to Considerations: |
• Pioneering Cost / Benefit versus Imitative
• Ability to establish high switching costs via
• Ability to establish rights protection/
• Ability to gain lead down learning curve
• Ability to establish benchmark quality / |
|
|
Scope Breadth of Operations: |
Is the range of activities which the firm performs internally, the breadth of its product and service offerings, the extent of its geographic market presence, and its mix of businesses. |
|
|
Horizontal vs Vertical Scope |
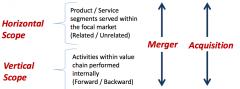
|
|
|
Horizontal Integration - Potential Benefits: |
– Improved operational efficiencies
– Heightened product differentiation
– Introduction into new product categories
– Reduced market rivalry
– Increased bargaining power over suppliers
– Enhanced its flexibility and dynamic
– Expanded geographic coverage |
|
|
Vertical Integration (Backward) - Potential Benefits: |
– Improved operational efficiencies
– Reduced dependence on suppliers of crucial components
– Enhanced control of inputs (quantity, quality,
– Lessened vulnerability to price increases
– Enhanced protection of proprietary |
|
|
Vertical Integration (Forward) - Potential Benefits: |
– Improved operational efficiencies
– Enhanced control of end user experience
– Diminished bargaining powers of buyers |
|
|
Outsourcing – Potential Benefits: |
– Activity performed better by outside
– Improved organizational flexibility and speed to market
– Reduced exposure to changes in market
– Rapid access to specialized expertise/services
– Enhanced ability to focus on core business/ competitive advantage enhancing services |
|
|
Strategic Alliances |
Is a formal agreement between two or more separate companies in which they agree to work cooperatively toward some common objective. |
|
|
Strategic Alliance – Potential Benefits: |
– Facilitates business objective / flexibility
– Enhances capabilities / resources
– Enhances bargaining powers over suppliers
– Enables entrance into new markets
– Requires minimal investment relative to |
|
|
Joint Ventures |
Is a type of strategic alliance in which the partners set up an independent corporate entity that they own and control jointly, sharing in its revenues and expenses. |
|
|
The best offensives use a company's...? |
Most powerful resources and capabilities to attach rivals in the areas where they are weakest. |
|
|
What is a blue-ocean stategy |
It offers growth in revenues and profits by discovering or inventing new industry segments that create altogether new demand. |
|
|
Are good defensive strategies a way to create a competitive advantage? |
Rarely, but they can help protect a competitive advantage. |
|
|
How can being a first-mover be a disadvantage? |
- When pioneering is costly and allows for follower to copy with lower cost
- When products of innovator are somewhat primitive and do not live up to buyers expectations; follower can win buyers by having better products
- When rapid market evolution (due to fast-paced changes in either technology or buyer needs) give second-movers the opening to leapfrog with more attractive next-version products
- When market uncertainties make it difficult to ascertain what will eventually succeed, allowing late movers to wait until these needs are clarified. |
|
|
What does the scope of the firm refer to? |
Refers to the range of activities which the firm performs internally, the breadth of its products and service offerings, the extent of its geographic market presence, and its mix of business |
|
|
What does a company need to guard against when outsourcing activities? |
A company must guard against outsourcing activities that hollow out the resources and capabilities that it needs to be a master of its of destiny. |
|
|
The best alliances are highly selective, why? |
They should enable a firm to build on its strengths and to learn by focusing on particular value chain activities and on obtaining a specific competitive benefit. |

