![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
38 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
exocrine glands deliver by...
|
ducts that lead to the body exterior
|
|
|
endocrine glands deliver by...
|
secreting hormones directly into body fluids (without ducts)
-secrete hormones that regulate metabolic processes |
|
|
2 major hormone mechanisms
|
direct gene activation (makes receptor-chaparone complex, then binds to DNA)
second messenger system |
|
|
permissiveness
|
the situation where one hormone cannot exert its full effects without another hormone being present
|
|
|
synergism
|
the situation where more than one hormone produce the same effect at the target cell, and the combined presence of both amplifies the effect.
(e.g. glucagon and epinephrine cause the liver to release glucose) |
|
|
3 types of endocrine gland stimuli
|
humoral
neural hormonal |
|
|
prostaglandins
|
biologically active lipids that are released by nearly all cell membranes.
Multiple targets and effects, including raising blood pressure, causing uterine contractions, enhancing blood clotting, functions in pain and inflammation |
|
|
the two categories of eicosanoids (biologically active lipids)
|
1. leukotrines - signalling chemicals that mediate inflammation and some allergic reactions
2. prostaglandins |
|
|
4 tropic hormones of anterior pituitary
|
TSH
ACTH FSH LH |
|
|
features of GH
stim by... inhibited by... effects include... |
Secretion stimulated by GHRH
Secretion inhibited by GHIH (somatostatin) Affects epiphyseal plates in bones, muscle cells Lack in children pituitary dwarf Excess in children pituitary giant Excess in adults acromegaly |
|
|
features of TSH
|
Stimulated by TRH
Stimulates thyroid gland Inhibited by negative feedback from thyroid hormones acting on hypothalamus and pituitary |
|
|
features of ACTH
|
Stimulated by CRH
Inhibited by negative feedback from adrenal cortex hormones function: stimulates release of glucocorticoids (chiefly cortisol), mineralocorticoids (chiefly aldosterone), and gonadocorticoids (chiefly androgens) |
|
|
the 3 gonadotropins
|
Follicle-stimulating hormone FSH
Luteinizing hormone LH Interstitial Cell-stimulating hormone ICSH |
|
|
features of FSH
|
In females – stimulates growth and development of egg-containing follicles in ovaries
In males – Stimulates the first production of sperm in testes at puberty |
|
|
features of LH (in females)
|
With FSH causes maturation of egg
Triggers ovulation Promotes synthesis and release of ovarian hormones |
|
|
features of ICSH (in males)
|
Chemically same as LH
In males Promotes secretion of androgens (testosterone) |
|
|
features of prolactin (PRL)
|
Release stimulated by prolactin-releasing hormone from hypothalamus
Inhibited by prolactin-inhibiting factor (dopamine) Responsible for milk production after birth Rises and falls with estrogen levels Little effect on males |
|
|
posterior pituitary features
|
Hormones formed in hypothalamus, stored in posterior pituitary
Two chemically similar hormones Oxytocin Antidiuretic hormone |
|
|
features of oxytocin
|
Release stimulated by nerve impulses from stretching uterus and cervix as birth nears and by suckling of infant
Causes uterine contractions that result in birth Causes milk “let-down” Positive feedback mechanism In non-sexual relationship, promotes affectionate behavior = “cuddling hormone” |
|
|
features of ADH
|
Prevents wide swings in water balance
Osmoreceptors in hypothalamus monitor solute concentrations Highly concentrated solutes release Alcohol inhibits ADH secretion Diuretic drugs antagonize ADH effects High levels of ADH vasoconstriction Deficiency = diabetes insipidus Stimulates kidney tubules to reabsorb water from forming urine and returns it to blood Controlled by negative feedback |
|
|
features of thyroid gland hormones
|
Thyroxine T4
Triiodothyronine T3 Produced by follicle cells, stored in follicles Increase metabolic rate and heat production Help maintain blood pressure Regulate tissue growth and development parafollicular cells produce calcitonin |
|
|
thyroid abnormalities
|
Hypothyroid
cretinism myxedema Hyperthyroid (exophthalmic goiter) Autoimmune disease |
|
|
features of calcitonin
|
Produced by parafollicular cells
Helps regulate calcium levels in blood Inhibits osteoclast activity Stimulates calcium incorporation into bone Mainly important in childhood |
|
|
features of PTH (and parathyroid gland)
|
On posterior surface of thyroid gland
Produce parathyroid hormone PTH Most important hormone controlling blood calcium Stimulates osteoclasts to demineralize bone and increase calcium in blood Enhances retention of calcium by kidneys, absorption of calcium from gut, activates vitamin D |
|
|
hormones of adrenal cortex
|
Mineralocorticoids (chiefly aldosterone)
Glucocorticoids (cheifly cortisol) Gonadocorticoids (chiefly androgens, which convert to testosterone or estrogen after release) |
|
|
hormones of adrenal medulla
|
Epinephrine (adrenaline)
Norepinephrine (noradrenaline) |
|
|
features of glucocorticoids
|
Major one is cortisol
Effects include Gluconeogenesis Enhances vasoconstriction by epinephrine Lowers inflammation |
|
|
features of glucocorticoid anbnormalities
|
Excess Cushing’s Disease
Persistent hyperglycemia Muscle and bone loss Water and salt retention Buffalo hump Inflammation inhibited Depressed immune system Lack Addison’s Disease |
|
|
features of mineralocorticoids
|
Main one is aldosterone
Promotes renal Na+ absorption and K+ excretion Part of renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system Increases blood pressure Opposed by atrial natriuretic peptide |
|
|
features of gonoadocorticoids
|
Most are androgens
Contribute to onset of puberty Responsible for sex drive in women May be converted to estrogens after menopause |
|
|
features of adrenal medulla
|
Modified sympathetic neurons
Fight or flight (or fright!) reaction Effect lasts much longer Epinephrine (adrenaline) Norepinephrine (noradrenaline) |
|
|
short term vs. long term stress response
|
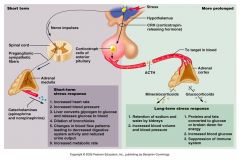
|
|
|
blood insulin/glucagon homeostasis
|
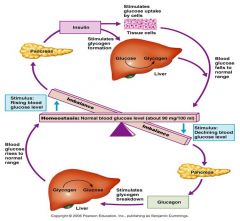
|
|
|
organ responses to insulin deficiency
|
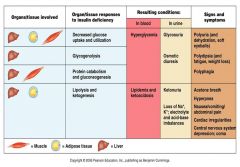
|
|
|
types of diabetes
|
Type I – Juvenile onset
Autoimmune No insulin produced Long-term vascular and neural problems Type II – Adult onset Inadequate insulin receptors Obese individuals |
|
|
hyperinsulinism features
|
Excess insulin production
Low blood sugar May be caused by tumor or insulin overdose |
|
|
thymus releases...
+ features |
Thymosins, thymopoietins - unknown trigger.
Most act locally as paracrines; involved in T lymphocyte development and in immune responses |
|
|
gluconeogenesis
|
the process of forming new glucose from non-carbohydrate molecules.
Occurs in the liver in response to low blood sugar (once glucose reserves have been depleted), and uses glycerol and amino acids for the conversion. |

