![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
707 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Drug of choice for trigeminal neuralgia? |
Carbamazapine
|
|
|
A patient has increased ICP, what drug can you give? |
Mannitol |
|
|
Diuretic most often causing hypokalemia? |
Loop Diuretic |
|
|
Ototoxicity is caused by which diuretic class? |
Loop Diuretic |
|
|
What side effect caused by Mannitol would be a contraindication in patients with CHF presenting with increased ICP from a head trauma? |
Pulmonary Edema |
|
|
Inheritance of Huntington's Dz? |
AD |
|
|
Earlier onset of Huntington's Dz (age 20) is most likely from Autosomal Dominant inheritance from mom or dad? |
Dad -------------------------------------------------- This is paternal anticipation and the CAG repeat sequence is far less stable in spermatogenesis than oogenesis which leads to earlier onset of Huntington's |
|
|
This Autosomal Dominant syndrome presents with Vascular lesions to the retina and CNS. It also causes renal carcinoma/failure and pheochromocytoma. |
von-Hippel Lindau |
|
|
What type of brain tumor is most prevalant in Von-Hippel Lindau? |
Hemangioblastoma (SUB-tentorial) --------------------------------- Autosomal Dominant Vascular lesions of Retina and CNS Increased risk of Renal Cell Carcinoma and failure Increased risk of pheochromocytoma |
|
|
A woman with anoxeria is admitted to te hospital and TPN is started. What metabolic derrangement must you be careful of? |
HYPOphosphatemia -------------------------------------------- Basal metabolic rate is depressed, but increases once re-feeding occurs. There is not enough Phosphate available for the higher demand for ATP. This can cause multiple organ system problems (confusion, Arrythmias, MSK) |
|
|
A woman with anoxeria is admitted to te hospital and TPN is started. What must you be careful of? |
Re-feeding Syndrome --> Hypophosphatemia |
|
|
Patient is hit in the head with a bat. Experiences a brief loss of consciousness. Regains consciousness and is lucid. Has headache and slowly begins to have an altered mental status. |
Epidural Hematoma |
|
|
Vasculature damaged in Epidural Hematoma? |
Middle Meningeal a. |
|
|
Vasculature damaged in Subdural Hematoma? |
bridging veins |
|
|
Most common locations for berry aneurysms in patients with Sub-arachnoid hemmorhage? |
Anterior Communicating Artery **(M/C)** and Posterior Communicating Artery |
|
|
Convex deformit on CT scan with a skull fracture |
Epidural Hematoma |
|
|
Patient presents after head trauma: CT shows a concave, crescent- shaped hyperdensity |
Subdural Hematoma |
|
|
What is the systolic BP goal for a patient with a hematoma/brain bleed? |
< 160 mm Hg |
|
|
A 40-year-old man is brought to the hospital by his wife after he came into the house salivating and complaining of diarrhea and nausea. He was out all day on his farm working with the corn crops. On physical examination, he is wheezing, and his pupils are constricted but reactive to light. Which of the following is the best next step in managing this patient? A. Administer naloxone B. Give diphenhydramine C. Immediately give pralidoxime D. Provide activated charcoa E. Remove all of the patient's clothing |
E. Remove all of the patient's clothing ----------------------------------------------------------- Then, pralidoxime (and atropine if needed) |
|
|
Treatment of choice for acute MS? |
IV Methylprednisolone -------------------------------------- Prednisone taper is given after high dose IV Methylprednisolone |
|
|
In Bipolar I: Patients have mania for at least _______ |
1 week ------------------------ Causes significant impairment |
|
|
In Bipolar II: Patients have HYPOmania for at least _______ |
4 days -------------------------------- No significant impairment |
|
|
If lithium cannot be used to treat Bipolar disorder, what is the next first-line treatment? |
Valproic Acid (Valproate) |
|
|
Why is Buproprion contraindicated in Anorexia? |
Risk of Seizure |
|
|
Pharmacotherapy for Bulemia nervosa? |
SSRI (fluoxetine, duoexetine,paroxetine, citalopram, sertaline) |
|
|
What class of Psych drugs: imipramine, amitriptyline, desiparmine, nortriptyline |
TCA's |
|
|
What class of Psych drugs: fluoxetine,paroxetine, citalopram, sertaline |
SSRIs |
|
|
What class of Psych drugs: venlafaxine, duloxetine |
SNRIs |
|
|
What class of Psych drugs: phenelzine, isocarboxazid, tranylcypromine, selegiline |
MAO Inibitors |
|
|
What atypical antipsychotic commonly caused weight gain and dyslipidemia? |
Olanzapine |
|
|
Which psych drugs cause Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome? |
High-potency antipsychotics (haloperidol, droperidol, fluphenazine, thiothixene) |
|
|
Patient starts an antipsychotic medication and within a few DAYS begins to have: Fever Muscle Rigidity "lead pipe" decreased consciousness increased BP Tachycardia |
Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome |
|
|
Normal bereavment lasts for no more than _____ months |
6 months |
|
|
High voltage "triphasic spikes" on EEG in a patient with acute progressive dementia and myoclonus |
Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease |
|
|
History of stroke within ___ months is an absolute contraindication to thrombolytic therapy in a patient with suspected stroke |
3 months
------------------------------------------------------- Other contraindications: * -Surgery w/in 14 days* -Intracranial Hemorrhage * -Severe uncontrolled HTN * -AVMs * - Intracranial tumor |
|
|
Thrombolytic therapy must be given within ____ hours of suspected stroke |
3 hours ------------------
**Recombinant thrombolytics must be given within 4.5 hours** |
|
|
A patient presents with HYPOnatremia, low serum osmolarity and highly concentrated urine. What is the Dx? |
SIADH ------------------------------------------ Anti-diuretic Hormone |
|
|
First-line treatment for a patient with status epilepitcus? |
Lorazepam |
|
|
What studies confirm amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)? |
Nerve conduction and electromyography (will show wide-spread muscular denervation and motor block) |
|
|
Patient presents with both UMN and LMN symptoms. Electromyography shows wide-spread muscular denervation and motor block. What is the diagnosis? |
ALS |
|
|
Schizophreniform disorder is diagnosed when a patient has symptoms of schizophrenia for less than ___ months |
6 months
------------------------ More than 6 mo = Schizophrenia |
|
|
A patient is diagnosed with a social phobia (fear of embarassment in social situations, dreads going into public)
What is the first line pharmacological Tx? |
SSRI/SNRI
--------------------------------------- Beta-blockers and Benzo's are useful for performance situations (public speaking) |
|
|
Bilateral trigeminal neuralgia in a young female patient? |
Multiple Sclerosis |
|
|
Two drugs you can use to treat NMS? |
Dantrolene Bromocriptine |
|
|
Torticollis due to SCM contracture is defined as:
Myoclonus Dystonia Akathesia |
Dystonia |
|
|
_________ is the painless loss of vision from emboli and is a warning sign of impending stroke. |
Amaurosis fugax
-------------------------------------
Emboli commonly come from the bifurcation of the carotid a. Do a duplex carotid U/S |
|
|
In patient's with suspected Acetomeniphen overdose, a serum acetomeniphen level should be obtained ______ hours after ingestion to determine the next step in treatment |
4 hours (you can use activated charcoal during these 4 hours)
--------------------------------------------- N-acetylcistine is the antidote |
|
|
Always suspect _____________ when a pt w/ Parkinson-like symptoms experiences postural hypotension, impotence or incontinenc |
Multiple System Atrophy (Shy-Drager Syndrome)
----------------------------------------------------------------- Characterized by: 1-Parkinsonism 2-Autonomic dysfunction (Postural hypotension, abnormal sweating, bowel or bladder control problems, abnormal salivation or lacrimation, Impotence or gastroparesis) 3-Widespread neurological signs
Tx: Intravascular Volume Expansion (incr. BP/Volume, high salt diet) |
|
|
Elderly patient presents with gradual onset of: 1) Confusion 2) Ataxia 3) Urinary Incontinence |
Hydrocephalus
------------------------------------------------ "Wet, Wild and Whacky" |
|
|
Shizophrenia:
Fluphenazine & Haloperidol (both are typical antipsychotics & long acting and injectable) are the tx of choice in pts who suffer relapses due to ____________________. |
Non-compliance
------------------------------------------ These are given as 2 injections/month |
|
|
Shizophrenia is characterized by (high/low) Dopamine
and (high/low) Glutamate |
High Dopamine
Low Glutamate |
|
|
Schizophrenic patients who are catatonic (extreme rigidity) should be given ____________ |
Benzodiazepines
(Lorazepam) |
|
|
A patient is brought to the ED after losing consciousness while standing in line. A bystander says he witnessed the fall and the patient was making jerking movements. What is the next best step |
non-Contrast CT (if clear) ---> MRI or CT w/contrast
(You have to rule out hemorrhage, even in the case of syncope or seizure) |
|
|
______________ is a focal weakness in part of the body after a seizure |
Todd's Paralysis |
|
|
What is the Tx of choice for seizure? |
Benzo's
(lorazepam -> diazepam -> midazolam) -------------------------------------------------- If benzo's don't work use phenytoin [phenytoin can also be used for prophylaxis] |
|
|
Sudden onset, PAINLESS & mostly unilateral photophobia and floaters, the most classic description is "a curtain coming down over my eyes" |
Retinal Detachment
Tx: laser and cryotherapy |
|
|
Most commonly by HSV & VZV (rare) in HIV pts. Associated with pain keratitis, uveitis and peripheral pale lesions |
Acute Retinitis
------------------------------------------------
If CMV is the cause, it's painless, there is no keratitis or conjunctivitis |
|
|
HIV patient's right eye presents as yellowish-white patches of retinal opacification and retinal hemorrhages & is painless
Their CD4 count is < 50. |
CMV retinitis
Tx: Ganciclovir, Foscarnet |
|
|
Most common cause of retinitis in HIV patients? |
HSV |
|
|
Treatment for cluster headaches? |
100 % pure O2 |
|
|
Best treament for a patient with a social phobia? |
CBT, add an SSRI if necessary |
|
|
Best treatment for a patient with a fear of flying? |
CBT, add an SSRI if necessary |
|
|
67 yr old post-op patient is complainng of increasing abdominal pain with bloody diarrhea the day after an Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm repair graft. The graft was taken from the inferior mesenteric artery. His LLQ is painful to palpation, his temperature is 101 F, his respirations are 22, BP is 110/65. Femoral pulses are intact bilaterally.
What is causing this? |
Sigmoid Colon Ischemia
-------------------------------------------- (1-7% incidence in Abdominal Aorta Surgeries)
The inferior mesenteric artery supplies the Sigmoid Colon and can fail after it is used for a graft. |
|
|
Pt. presents with a painful, watery, red eye that has been persistent for 2 days. Slit lamp examination reveals vesicles and dendritic ulcers of the cornea.
Most likely diagnosis? |
Herpes Keratitis |
|
|
Contact lens wearers are at increased risk for what corneal issue? |
Bacterial Keratitis
-------------------------- Central ulcer with an adjacent stromal abscess |
|
|
An elderly patient complains of fever, malaise, and a burning itchy sensation in his left periorbital area. Examination reveals a vesicular rash in the distribution of the cutaneous branch of the V1 devision of the Trigeminal nerve.
The left eye has conjunctivitis and corneal ulcers. What is going on? |
Herpes zoster ophthalmicus |
|
|
A construction worker present to the ER after sanding wood all day. His left eye is extremely painful and he states that light makes it worse.
What is the most likely diagnosis? |
Corneal Abrasion
------------------------------------ Intense pain with photophobia |
|
|
Are patients presenting with DKA hyper/or/hypo kalemic? |
(Paradoxical) HYPERkalemia
-------------------------------------------- Intracellular potassium crosses into the serum in exhange for hydrogen ions and hyperosmalrity (K is actually lost, but it is all extracellular in the serum!!!)
Insulin usually drives the K back into the cell! (but there is no insulin action in patients with DM 1 in DKA)
Must hydrate, give insulin and K+ because insulin will drive what little K+ is left back into the cells and the patient will become Hypokalemic... |
|
|
A patient is crushed under a log. What metabolic complication can be expected? |
Hyperkalemia
----------------------------------- Damaged cells spill K+ into the serum |
|
|
A previously healthy 2 month old infant presents with bilateral ptosis, sluggish pupillary response to light, poor suck reflex, poor gag reflex and a descending paralysis of all 4 limbs.
Baby has not ingested any foods, and especially not honey. Mom likes to take baby on walks around their newly constucted neighborhood. |
Clostridium botulinum
------------------------------------------------------------ (Floppy Baby)
Toxin blocks ACh release at presynaptic neuromuscular junctions
Spores can be ingested from dust: IV Human-derived botulism immune globulin
Spores can also be ingested from honey: IV Equine-derived botulism immune globulin
**DDX: Guillan Barre has ascending paralysis** |
|
|
A child presents with symmetric proximal muscle weakness and hyporeflexia. Weakness is greater in the lower extremities. Pupils are unaffected.
|
Werding Hoffman disease (Spinal Muscular Atrophy)
|
|
|
Difference between food-borne and infantile botulism? |
Foodborne: Ingestion of toxin, prodrome of nausea/Vomiting and abdominal pain
Infantile: Inhalation of spores from soil dust (m/c in California, Utah, and Pennsylvania) |
|
|
What is a pharmacologic treatment proven to help patients with hoarding disorder that are alseo receiving cognitive-behavioral therapy? |
SSRI's |
|
|
What's a good reason to withhold diagnosis information from a patient? |
Patient is depressed and at risk of suicide |
|
|
Crescendo-decrescendo murumur systolic ejection murmur that in the right 2nd intercostal space that radiates to the carotid arteries. |
Aortic Stenosis
-------------------------------------------- May hear pulsus parvus et tardus -(weak/small (parvus), and late (tardus) relative to its usually expected character)
weak S2, and S4 may also be present
|
|
|
A pregnant woman presents for prenatal care. She is estimated to be at 28 weeks gestation.
She has moved to your state and states that she has been negative for HIV, Chlamydia, gonorrhea and urine cultures were negative.
Her blood type is A negative and she is Rh (D) negative.
What should be done at this time? |
Rh (D) antibody test
---------------------------------------------------------- Rhesus Isoimmunization
This results in formation of Anti-Rh antibodies in the mother's after the 1st pregnancy and they cross over to baby's circulation and cause hemolysis of baby blood. In severe cases it causes Hydrops Fetalis. In mild cases it causes, jaundice, w/i the first 24hr after birth. Any incident that causes bleeding can cause this (amniocentesis, CV Sampling, abortion, ectopic pregnancy, labor and delivery.)
The best tx is to prevent mother's immune system to be in contact with fetus blood cells, the best thing is AntiD-gammaglobin (Rho-GAM) which prevents contact by decreasing availablity of fetal RBC in maternal circulation. In case mother was not sensitized (antibody titers <1:6) RhoGAM is still indicated. It should be given to ALL Rh-negative women at 28 weeks and w/i 72 hours AFTER DELIVERY (NOT BEFORE!!) any procedure of incident (ie. abortion) and delivery |
|
|
When do you give AntiD-gammaglobin (Rho-GAM) to a Rh (-) mother with an Rh (+) fetus? |
Small dose at 28 weeks
72 hours AFTER DELIVERY (NOT BEFORE!!) any procedure of incident (ie. abortion)
|
|
|
Most common indication for hysterectomy? |
Uterine fibroids |
|
|
Woman presents with dysmenorrhea, heavy menses and an enlarged uterus. What is the cause? |
Utine fibroids
--------------------------------------------
These are estrogren dependent tumors! - increase in size with OCP's - increase in size during pregnancy - decrease/regress after menopause |
|
|
A patient is involved in a highspeed MVA where his car hit a concrete barrier. Chest X-ray shows a widened mediastinum, left hemothorax, deviation of the mediastinum to the right.
What is the diagnosis? |
Aortic Injury |
|
|
Patient is in an MVA and presents to the emergency department with Hypotension, distended neck veins, muffled heart sounds |
Cardiac Tamponade
------------------------------------- Need a pericardiocentesis to drain blood surrounding the heart!
Beck's Triad: Hypotension, distended neck veins, muffled heart sounds |
|
|
Patient is involved in an MVA:
Presents with abdominal pain that travels to the right shoulder, vomiting and difficulty breathing.
X-rays show abdominal viscera above the diaphram |
Ruptured Diaphragm |
|
|
A woman presents with with mood swings, irritability, bloating and headaches and breast tenderness. These occur monthly and often she has to take a day or two off of work.
She is not sure if her symptoms coincide with menstruation.
What is the next best step in order to diagnose PMS? |
A menstrual diary can confirm that these symptoms arise 1-2 weeks before menstruation
----------------------------------------------------
Premenstrual Dysmorphic D/o is a severe varient of PMS and presents with prominent irritability and anger symptoms |
|
|
Gold standard for diagnosing endometriosis? |
Laparoscopy |
|
|
Woman presents with pelvic and back pain that is worse during her premenstrual period, sex and defecation. |
Endometriosis
--------------------------------------------
Laparoscopy is the gold standard for Dx |
|
|
Most common sequalae of Endometriosis? |
Decreased fertility/Infertility
--------------------------------------------- Up to 30% of females with infertility are found to have endometriosis |
|
|
An HIV-positive patient presents with altered mental status. He is lethargic, disoriented and has loss of recent memory.
CD4 count is 40/microL
Brain MRI shoes a weakly ring enhancing mass in the periventricular region.
PCR of CSF shows EBV DNA.
What is the most Likely Dx? |
Primary CNS Lymphoma
------------------------------------
Presence of EBV in CSF is specific in this condition.
MRI shows a weakly ring enhancing mass in the periventricular region |
|
|
HIV positive patient presents with an altered mental status.
Brain MRI shows multiple, ring enhancing spherical lesions in the basal ganglia. |
Toxoplasmosis
-----------------------------------------------
Note: A positive Toxoplasma serology is common in normal subjects and therefore is not specific in toxoplasmosis |
|
|
An HIV positive patient presents with an altered mental status.
MRI shows cortical and subcortical atrophy and secondary ventricular enlargement |
AIDS dementia |
|
|
False Negatives will ___________ when the cut-off level of a diagnostic test is raised. |
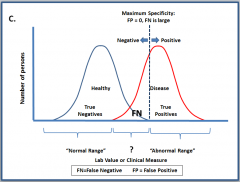
False Negatives Increase!!
|
|
|
During a study, subjects change their behavior because they know they are being observed.
What is this called? |
Hawthorne Effect |
|
|
Screening tests have (high/low) sensitivity |
Screening tests have high sensitivity
-------------------------------------------------
as a result, screening tests have LOW specificifty |
|
|
Which of the following has not been proven to increase survival in patients with CHF?
-ACE Inhibitors -ARBs -Beta-blockers - Digoxin -Aspirin -Spironolactone |
Digoxin has not been proven to improve survival in patients with CHF
---------------------------------------- Digoxin is a cardiac glycoside that helps improve the contractility of the heart. It helps resolves dyspnea and fatigue. It has been shown to decrease hospitalization time with no benefit in mortality.
[Digoxin and Loop diuretics only treat symptoms of CHF but do not improve survival] |
|
|
Which of the following has not been proven to increase survival in patients with CHF?
-ACE Inhibitors -ARBs -Beta-blockers - Loop Diuretics -Aspirin -Spironolactone |
Loop Diuretics have not been proven to improve survival in patients with CHF
-------------------------------------------------- Used for symptomatic relief. The only class of diuretics proven to increase survival in pts with CHF are are aldosterone antagonists (spironolactone, eplerenone)
[Digoxin and Loop diuretics only treat symptoms of CHF but do not improve survival]
|
|
|
A 60 year old male patient presents with fever, back pain, and focal spinal tenderness. He had a UTI 2 weeks ago. His urinary symptoms have resolved. His labs show increased WBCs, ESR and C-reactive protein.
He has a history of BPH, and the digital rectal exam shows an enlarged, non-painful prostate with no nodules or irregularities.
Spinal x-ray shows no abnormalities.
What is the next best step? |
MRI of spine
------------------------------------------- You're looking for osteomyelitis. Likely cause is from a Staph aureus UTI in this case.
If MRI shows osteomyelitis, the next step is a CT-guided bone biopsy |
|
|
A mother presents with her 2 year old child who is having vomiting, and aggitation. While in the ER, the patient develops lethargy and stupor.
Mom says that the child had a cold which she treated with aspirin.
Most likely diagnosis? |
Reye Syndrome
----------------------------------------- Characteristic lab findings are hyperammonemia, normal or slighly increased bilirubin and Alk Phos, increased prothrombin time, hypoglycemia, moderate to severe elevations in AST and ALT, and increased LDH
treatment is supportive |
|
|
An immigrant mother brings her 3 year old son into the ED for stridor and acute onset of high fever. The patient appears toxic and is leaning forward and drooling.
The child has had no immunizations since immigrating to the U.S.
You suspect epiglottits caused by which organism? |
H. influenzae Type B
----------------------------------------------- All children in the US are vaccinated for HiB. |
|
|
A mother brings her 3 year old son into the ED for stridor and acute onset of high fever. The patient appears toxic and is leaning forward and drooling.
Diagnosis?
|
Epiglottitis
---------------------------------------------------------- Next step is endotracheal intubation with prep for a tracheostomy (tubing these kids is difficult) |
|
|
a 65 year old man complains of difficulty hearing in high-noise environments such as restaurants. He has no history of exposure to loud noises.
Most likely diagnosis? |
Presbycusis
------------------------------------ Bilateral sensorineural hearing loss often seen in the 6th decade. High-frequency hearing loss occurs. Patint shave difficulty hearing in noisy, crowded environments |
|
|
Overdose:
Patient has tachycardia, aggressive behavior, ataxia, mild hypertension and multi-directional nystagmus |
PCP overdose |
|
|
Overdose:
Tachycardia, hypertension, dilated pupils (mydriasis), sense of euphoria, increased arousal. |
Cocaine Overdose |
|
|
Overdose:
Tachycardia, hypertension, dry mouth, conjunctival injection, increased appetite |
Marijuana Overdose |
|
|
An expectant mother experiences a stillbirth. Baby is small in size, has multiple fractures and limb deformities, and blue sclerae |
Osteogenesis Imperfecta Type II
-------------------------------------------------- * Autosomal Dominant* Defects in gene coding for type I collagen * Commonly results in fetal or perinatal death
|
|
|
Use of which drug during pregnancy is associated with craniofacial abnormalities, fingernail hypoplasia, growth deficiency, developmental delay, cardiac defects and facial clefts? |
Phenytoin |
|
|
2 year old is brought to the ED due to cough and a "whistling sound" while breathing.
Two days ago, he developed a hoarse cry and a harsh "barky" cough and rhinorrhea.
Lateral x-rays show a mildly narrowed subglottic region.
Diagnosis? |
Croup
---------------------------------------------- * M/C cause is parainfluenza virus |
|
|
Most common cause of croup? |
parainfluenza virus |
|
|
What 2 heart murmurs get louder during Valsalva and standing? |
Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
Mitral Valve Prolapse
Right Sided heart murmurs also increase during LATE VALSALVA
(↓ Venous Return) (↓ LV Volume)
-------------------------------------------- All other murmurs ↓ during Valsalva and Standing |
|
|
What heart murmurs get louder during squatting or hand gripping? |
Aortic Regurgitation
Mitral Regurgitation
VSD
(↑ Venous return, ↑ Afterload by kinking femoral arteries, ↑ reverse flow) |
|
|
What happens to the murmurs heard in HCM and MVP when a patient squats? |
Murmurs decrease in HCM and MVP when a patient squats.
|
|
|
A patient has Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy. What effect will hand gripping have on the murmur? |
Murmur will get softer
|
|
|
A patient has a short diastolic cardiac murmur at the cardiac apex that goes away with squatting. A non-ejection click is present. |
MVP
------------------------------------
Murmur may also present with a non-ejection click or mid-to-late systolic murumur
|
|
|
Loud holosystolic murmur with maximal intensityover the 3rd or 4th left intercostal space. The intensity of the murmur increases with squatting |
Ventricular Septal Defect |
|
|
Most common cardiac deformity caused by Rheumatic Heart Dz? |
Mitral Stenosis |
|
|
A young obese woman is being treated for acne using isotrnitoin cream. She complains of headaches, blurred vision and a whooshing sound in her ears that has gotten worse over the past 2 weeks. Exam shoes papilledema.
CT imaging is normal. An LP is performed and no abnormalities are noted other than an opening pressure of 260mm/Hg.
Diagnosis |
Pseudotumor-cerebri (Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension)
---------------------------------------------
Drugs that cause IIH: * Growth Hormone* Tetracyclines (minocycline, doxycycline) * Excess Vitamin A and derivatives (isotenitoin, all -trans-retionic acid) |
|
|
A positive Trendelenburg sign shows drooping of the contralateral hemipelvis below its normal horizontal level. It is caused by weakness off the _____________ muscles which are innervated by the _______ nerve |
It is caused by weakness off the gluteus medius and minimus muscles which are innervated by the Superior gluteal nerve |
|
|
A newborn infant fails to feed for the first time 3 hours after birth. The infant has choking, drooling, and coughing.
An attempt is made to place an enteric tube but X-ray shows it stops in the proximal esophagus.
What is the most likely diagnosis |
Esophageal Atresia with tracheoesophageal fistula. |
|
|
A patient with obstructive sleep apnea has a Hemocrit of 65%.
What causes polycythemia in patients with obstructive sleep apnea? |
↑ erythropoeitin production |
|
|
A tanned patient presents with palve, velvety hypopigmented macules that do not tan, and do appear scaly but do scale with scraping.
What is the diagnosis? |
Tinia Versicolar
------------------------------------------------------ Malassezia furfur
Scrapings viewed on KOH staining can show large, blunt hyphae and thick walled budding spored (spaghetti and meatballs)
Tx: selenium sulfide cream or ketoconazole shampoo
**EXTREMELY HIGH-YIELD** |
|
|
A patient presents with oval, fawn-colored lesions that measure 2cm in diameter and occur in a christmas tree pattern on his back.
Diagnosis? |
Pityriasis rosea
-------------------------------------- The initial lesion is a herald patch and generalized eruption occurs in 2 weeks |
|
|
Most common presenting symptom of Pancost tumor? |
Shoulder Pain (most common)
also can see Horner's Syndrome |
|
|
What is the most common extraarticular manifestation of Ankylosing Spondylitis? |
Anterior Uveitis
------------------------------- Bilateral SI joints, HLA-B27 (+) |
|
|
Glutamic acid decarboxylase antibodies are seen in 70% of patients diagnosed with _________ |
Type I Diabetes |
|
|
A patient of Northern European descent presents with hemolytic anemia, jaundice and splenomegaly. His urine is cola-colored.
Bloodwork shows a decreased hemoglobin, but a normal MCV with a decreased Reticulocyte count.
He is also having acute symptoms of cholecystitis and ultrasound reveals pigment gallstones.
Diagnosis? |
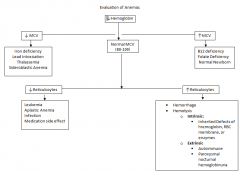
Hereditary Spherocytosis
--------------------------------------------- Inherited deficiency of ankrin and spectrin
Mis-shaped RBCs get trapped in the spleen
Short lifesplan of these RBCs causes rapid turnover and excess bilirubin that overloads the system --> cola-colored urine d/t hyperbilirubinemia
Patients can develop an acute cholecystitits with pigmented gallstones, Tx is a cholecystectomy
Other treatments are folate as chronic hemolysis consumes folate and ultimately a splectomy
|
|
|
When treating an episode of depression, the antidepressant should be continued for ________ following the patient's response. |
6 months |
|
|
A 45 yo female presents with excessive hair growth over her face and body. Her hirsutism rapidly developed over 6 months. She has not menstruated in 3 months.
She has hairgrowth on her face, she is masculine in appearance with a large clitoris. She has significant temporal balding.
What test should be ordered? |
Serum testosterone and DHEAS
------------------------------------------
Rapid progression of her symptoms indicate a likely ovarian or adrenal tumor.
Elevated testosterone with with a normal DHEAS indicates an ovarian source
Normal testosterone with with elevated DHEAS indicates an adrenal source |
|
|
What type of cancer most commonly causes hypercalcemia by producing PTHrp (Parathyroid Hormone related peptide)?
|
Breast CA |
|
|
How do tumor cells cause bone resorption that results in hypercalcemia? |
Secrete factors that activate osteoclasts |
|
|
Best imaging modality to use for suspected confirming Diaphragmatic rupture or avulsion? |
CT of chest |
|
|
The most beneficial therapy to reduce progression of Diabetic Nephropathy in presence of renal insufficiency is to ___________________ |
Control Blood Pressure
(ACEi or ARBs) |
|
|
Biggest risk for thryoid cancer? |
Previous neck radiation therapy |
|
|
Hashimoto Thyroiditis can lead to increased risk of what cancer? |
Thyroid Lymphoma |
|
|
_______________________ is the most common pediatric renal malignancy. It presents in a toddler with a firm, smooth, unliateral abdominal mass that does not cross the midline and hematuria |
Wilm's Tumor
--------------------------------------------- Versus: A neuroblastoma is the most common cancer in the first year of life. It presents as an abdominal mass that does cross the midline and presents with sympathetic symptoms. |
|
|
Toddler with a firm, smooth, unliateral abdominal mass that does not cross the midline and hematuria |
Wilm's Tumor
---------------------------------------- Most common pediatric renal malignancy
Can be assosciated with:
WAGR syndrome = Wilms tumor + Aniridia + GU anomalies + Mental retadation
Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome = Wilms tumor + organomegaly, macroglossia, & neonatal hypoglycemia (excess insulin)
|
|
|
10 month old with an abdominal mass that crosses the midline, fever, weight loss, hepatomegaly and HTN |
Neuroblastoma
--------------------------------------- Most common malignancy in the 1st year of life
dx is made by measuring urinary cathecholamine products |
|
|
Most serious side effectfor PTU and Methimazole for Hyperthyroidism? |
Agranulocytosis |
|
|
Hyperthyroidism:
Methimazole vs. PTU
Which is safe in the 1st trimester of pregnancy? |
PTU |
|
|
Imaging study of choice for a pregnant lady with nephrolithiasis? |
Ultrasound
----------------------------------------------- Don't zap the baby with radiation using a CT scan! |
|
|
Test of choice to diagnose a kidney stone? |
CT w/o contrast |
|
|
Which type of mutation leads to a more serious form of disease:
Nonsense mutation or Missense mutation |
Nonsense mutations |
|
|
A man loses his job and silently packs up his office. When he gets home, his children are excited to see him and want to play. He begins yelling and swearing at them.
What type of defense mechanism is he displaying? |
Displacement |
|
|
A man being treated for acute diverticulitis is back in the ER two days after discharge complaining of worse symptoms. A CT scan of his abdomen shoes a peritoneal abscess with more than 3 cm of fluid collection next to the sigmoid colon.
What is the next best step? |
CT guided drainage
----------------------------------------------
If that doesn't work, next step is surgical debridement |
|
|
The _________ bursa is located anteriomedially over the tibial plateau just below the joint line of the knee. |
Anserine bursa |
|
|
Asymptomatic lesion is noted on a chest x-ray of a patient who grew up in either the Mississippi or Ohio River valleys or Central America. |
Histoplasmosis |
|
|
Chorionic Villus sampling offers the advantage of an early diagnosis. It can be done between ____ and _____ weeks of gestation. |
10 to 12 weeks
-------------------------------------------- BEST for detecting fetal chromosomal abnormalities in the first trimester
Gestation Age of fetus is the most significant risk factor for fetal limb injury. CVS before 10 weeks is associated with greater risk |
|
|
What test is the best for confirming fetal chromosomal abnormalites during the 1st trimester? |
Chorionic Villus Sampling |
|
|
Post-term pregnancies (>42 weeks) are assosciated with a greater risk for:
Oligohydramnios? or Polyhydramnios? |
Oligohydramnios
------------------------------------------------ Mothers must be moniored twice weekly |
|
|
Treatment for impetigo? |
Topical mupirocin
or
Oral erythromycin |
|
|
Pelvic ultrasound shows streak ovaries and an infantile uterus in a 15 year old girl with amenorrhea. |
Turner Syndrome (45 XO) |
|
|
Patient presents with primary amenorrhea, delayed puberty, short stature, broad-shaped chest and a bicuspid aortic valve |
Turner Syndrome (45 XO)
------------------------------------------------------------ U/S may show streak ovaries |
|
|
Common cardiac valve defect seen in Turner Syndrome (45 XO)? |
bicuspid aortic valve
-----------------------------------
also commonly have: -coarctation of aorta -Horseshoe kidney |
|
|
Bug that causes osteomyelitis in patients with Sickle cell? |
Salmonella |
|
|
Children with sickle cell anemia should be on prophylactic _________ until 5 years of age |
Penicillin
|
|
|
Pharmacological treatment for primary biliary cirrhosis? |
Ursodeoxycholic acid
------------------------------------------------- PBC is a chronic liver disease characterized by autoimmune destruction of intrahepatic bile ducts and cholestasis
- Middle aged women
-Pruritus is first symptom and can be extreme appearing mostly at night
-xanthomatous lesions on the eyelid, skin or tendons
-Jaundice, steotorrhea, portal hypertension, and osteopenia may develop |
|
|
A diabetic patient is 3 days post-op and complains of intense pain at the incision site. Exam shows decreased sensitivity around the edges of the wound, cloudy grey discharge and crepitus of the skin.
What is the next best step? |
Surgical exploration of the wound
-------------------------------------------- This is a necrotizing skin infection and surgery is essential |
|
|
What is the heterophile antibody test used to diagnose? |
Infectious Mononucleosis
----------------------------------------- This is also known as the Mono-spot test! |
|
|
A child is brought to you for hyper-phagia and temper tantrums when his parents try and stop him from eating. He is short in stature and is in the 99th percentile for weight. He has almond-shaped eyes, a narrow forehead and a down-turned mouth.
His mother says her pregnancy was uncomplicated and that he did have poor suck and feeding problems during infancy.
What is the Dx? |
Prader-Willi Syndrome
----------------------------------------------- This is due to a maternal uniparental disomy. * inherited both copies of chromosome 15 from mom* there was a deletion of the paternal copy of chromosome 15
One of the most common complications of PWS is Sleep Apnea (70%), followed by DM 2 (20%) |
|
|
A child is brought to your office for her short stature and evaluation of a suspected intellectual disability. SHe frequently smiles and laughs for no apparent reason, and constantly flaps her hands. Her past medical history is significant for ataxia and seizures. |
Angelman Syndrome
----------------------------------------------------
This is due to a paternal uniparental disomy. * inherited both copies of chromosome 15 from dad* there was a deletion of the maternal copy of chromosome 15 |
|
|
Test of choice to Dx Amyloidosis?
|
Abdominal Fat Pad Biopsy |
|
|
WHich has longer morning stiffness?
RA or Osteoarthritis? |
Rheumatoid Arthritis
-------------------------------------------- Morning stiffness in patients with RA lasts longer than 30-60 minutes |
|
|
Best test to find lytic bone lesions associated with Multiple Myeloma? |
Skeletal Survey (X-ray) |
|
|
Where would you see:
Bone pain (m/c presentation)
Increased ESR (typically over 100)
Bence Jones Proteins in urine (free monoclonal or light chains)
M-spike on immunoelectrophoresis |
Multiple Myeloma
--------------------------------------------
Complications include: Renal failure, Hypercalcemia, hyperviscosity syndrome.
Complete work-up includes: CBC with differential and morphology, serum electrolytes, kidney and liver screening, skeletal survey, serum plasma electrophoresis & urinary plasma electrophoresis (SPEP & UPEP!!) are the NEXT steps and BM biopsy (definitive) which shows over production of plasma cells (>10%)!.
|
|
|
How would you find the mean in this data set?
20, 22, 21, 22, 18 |
Add them all up, and divide by 5
20.6 |
|
|
How would you find the median in this data set?
20, 22, 21, 22, 18 |
You find the number in the data set that separates the low from the high. So you have to put the numbers in ascending order:
18, 20, 21, 22, 22 |
|
|
How would you find the mode in this data set?
20, 22, 21, 22, 18 |
It's the number that occurs the most!
22 |
|
|
Most common cause of conjunctivitis in a newborn? |
Chemical Conjunctivitis from silver nitrate drops! |
|
|
Both Hereditary spherocytosis and Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia have spherocytes on peripheral blood smear.
Which one has a (+) Coomb's test? |
AIHA
--------------------------- Will have a negative family history |
|
|
Both Hereditary spherocytosis and Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia have spherocytes on peripheral blood smear.
Which one has a (-) Coomb's test? |
Hereditary Spherocytosis
-------------------------------------- (+) family history! It is Autosomal Dominant! |
|
|
In what hemolytic disease would you see Heinz Bodies? |
G6PD-deficiency |
|
|
Rheumatic heart disease most commonly affects which heart valve? |
Mitral valve ---> Mitral Stenosis
------------------------------------------ Can cause A-fib due to left atrium dilation |
|
|
A patient is experiencing an acute dystonic reaction ( like torticollus) after he was administered haloperidol for an acute psychotic episode.
What drug can be given to reverse the dystonia? |
Anticholinergic (benztropine)
Antihistamine (Diphenhydramine) |
|
|
Most common nephrotic syndrome in children? |
Minimal Change Dz |
|
|
What empiric therapy is started for any child with suspected Minimal Change Disease? |
Steroid therapy (Prednisone) |
|
|
Treatment of choice for Minimal change Disease? |
Steroids! (prednisone)
-------------------------------------------- Do not do a renal biopsy! |
|
|
A patient is diagnosed with meningococcal meningitis.
What drugs should you use for prophylaxis in close contacts of the patient? |
Rifampin
or
Ciprofloxacin |
|
|
A 22 year old runner presents with amenorrhea for 6 months. She has been training for olympic trials in that time.
She has a BMI of 20, and a negative pregnancy test. Prolactin levels are normal. FSH and LH levels are low.
The patient has the greatest risk of developing what disorder?
|
Decreased bone mineral density
--------------------------------------------------------- HPO axis is suppressed due to low BMI, low leptin
and
elevated Grehlin, neuropeptide Y, GABA, beta-endorphin, corticotropin |
|
|
What disease causes upper and lower motor neuron symptoms without loss of sensation?
Common symptoms are muscle twitching, weakness and cramping |
ALS |
|
|
10 hour old infant has a scalp swelling limited to one cranial bone. There is no discoloration or pulsation. |
Cephalohematoma
-------------------------------------------- -Subperiosteal hemorrhage, does not cross suture lines
Most cases do not require treatment and will resolve in 2-3 months |
|
|
10 hour old infant has a diffuse, ecchymotic scalp swelling that extends across the midline and suture lines |
caput succedaneum
------------------------------------------------------ Extends across suture lines. Is ecchymotic in appearance |
|
|
Tamoxifen increases the risk for what cancer? |
Endometrial Cancer |
|
|
Ramoxifen is a selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM)
It has mixed agonist/antagonist effects of estrogen receptors. In breast and vaginal tissue, it is an antagonist. In bone tissue, it is an agonist.
It is a first-line treatment for osteoporosis and decreases breast cancer risk.
It is contraindicated in patients with a history of _________________ |
DVT/Thromboembolism |
|
|
A 34 year old female presents with amenorrhea for 3 months. She is experiencing hot flashes, atrophic vaginitis, breast atrophy and some irritability.
You suspect premature ovarian failure.
A markedly increased _________ level in a patient under 40 who is experienced > 3 months of amenorhhea confirms diagnosis of premature ovarian failure. |
A markedly increased FSH level in a patient under 40 who is experienced > 3 months of amenorhhea confirms diagnosis of premature ovarian failure.
------------------------------------------------------------------ Studies will show ↓ estrogen, ↑↑FSH, ↑LH |
|
|
In children, over 90% of medulloblastomas develop in the ______________ |
Cerebellar vermis
---------------------------------------------------- Second most common posterior fossa tumor (behind cerebellar astrocytoma)
Children develop posterior vermis syndrome (unbalanced gait, trunk dystaxia, horizontal nystagmus, papilledema) |
|
|
What is the fluid of choice for initial fluid rescusitation in patients with severe hypovolemic hypernatremia? |
Normal Saline (0.9%)
or
Lactated Ringers
-------------------------------------------- These are isotonic solutions
Hypotonic solutions --> Contraindicated * Quickly exit the intravascular system* Lower sodium too rapidly * can cause cerebral edema
I |
|
|
_____________ antibodies are seen in over 90% of patients with primary biliary cirrhosis, a chronic liver disease characterized by autoimmune destruction of intrahepatic bile ducts and cholestasis |
Antimitochondrial antibodies
----------------------------------- Severe pruritis is the most common initial symptom and often seen at night. |
|
|
Furosemide is the drug of choice if a patient having an MI develops ___________________ |
Flash pulmonary edema
-------------------------------------------- Metoprolol is contraindicated in this setting of acute CHF! Even if the patient is having an MI.
Furosemide rapidly relieves pulmonary edema by decreasing cardiac preload, thereby decreasing pulmonary capillary pressure |
|
|
A Mexican man presents with RUQ pain for the past 12 days. The pain migrates to his right shoulder. Deep inspirations make it worse. He provides a history of bloody diarrhea 6 months ago after travel to Mexico to visit family.
He has RUQ tenderness but no jaundice. An U/S reveals a single, thin-walled cyst in the right lobe of his liver.
Most likely diagnosis? |
Entamoeba Histolytica liver abscess
-------------------------------------------------------- -Primary infection is through colon which produces bloody diarrhea
-Amebic liver abscesses are generally single and located in the right lobe of the liver.
-Diagnosis can be confirmed b trophozoites in the stool, serology and liver imaging
Treat with Metronidazole |
|
|
What electrolyte abnormality may occur after treating a patient with severe asthma with high-dose beta-2-agonists (Albuterol)? |
HYPOkalemia
---------------------------------- Albuterol drives K+ into cells |
|
|
Statins _______ the number of hepatic LDL receptors |
increase |
|
|
Statins decrease _____________ synthesis, which is involved in muscle cell energy production and possibly contributes to statin-induced myopathy |
coenzyme Q-10 |
|
|
Patient with a history of chronic duodenalulcer presents with upper right quadrant pain.
Endoscopy shows prominent gastric folds and a duodenal ulcer, and an upper jejunal ulceration (damage beyond duodenal bulb)
what is the most likely Dx? |
Zollinger-Ellison syndrome (Gastrinoma)
-------------------------------------------- All patients need a fastin serum gastrin level - a level >1000pg/mL is diagnostic
If gastrin test is non-diagnostic, a secretin stimulation test should be done |
|
|
What is the most common cause of infertility in women less than 30 with normal menstruation? |
PID |
|
|
WTF? Congenital syndrome:
Syncopal episode w/o following disorientation.
There is a hearing impairent, normal PE, and family hx of sudden cardiac death
What is the Diagnosis? |
Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome
(Congenital Long QT Syndrome, Autosomal recessive)
------------------------------------------------------------------ Treatment is with 𝞫 -blocker (Propanolol) and pacemaker to prevent cardiac arrest
Avoid electrolyte derrangements, medications that block K+ channels (Torsades), and vigorous physical activity
------------------------------------------------------------------- Romano-Ward Syndrome is the Autosomal Dominant version |
|
|
Cardiac ausculation reveals mid-diastolic rumble with opening snap best heard at the apex |
Mitral Stenosis |
|
|
Which virus causes Molluscum contagiousum? |
Poxvirus |
|
|
Which virus causes Kaposi Sarcoma? |
Human Herpes virus 8 |
|
|
A patient presents with Charcot's Triad of fever, severe jaundice and right upper quadrant pain.
|
Acute Ascending Cholangitis
---------------------------------------------------------- It’s an infection of the COMMON BILE DUCT (NOT THE CYSTIC DUCT!!!!), generaly 2ndary to OBSTRUCTION OF CBD with a stone leading to DILATATION OF CBD**** (seen on imaging).
Broad spectrum antibiotics (cover gram – rods & anaerobes!!) should be started immediately, however, its very important to decompress the billiary duct and provide their drainage (USING ERCP!!).
Most common pathogens involved are E.coli & Klebsiella (gram – rods; NOT enterococci…which are gram + |
|
|
A woman presents with 3 months of worseing pain in her right knee. No medications have helped
On examination the knee is swollen and tender with decreased range of motion.
X-ray shows an expansible and eccentrically placed lytic area in the epiphysis of the distal femur.
Serum chemistries and CBC are completely normal.
Diagnosis? |
Giant Cell Bone Tumor
------------------------------------ -Pain, swelling, decreased range of motion in joint
usually in the epiphyses of bone – “soap bubble” apearance
-Surgery is 1st line Tx |
|
|
Knee pain due to over-use injury caused by repetitive strain.
Typically seen in children and adolescents who have recently undergone a growth spurt.
Xray shows avulsion of the apophysis of the tibeal tubercle.
|
Osgood Schlatter |
|
|
External cephalic version is indicated if breech presentation is persistent at _________ weeks gestation. |
37 weeks
------------------------------------------- If external cephalic version fails, plan for a C-section....
Most breech presentations resolve spontaneously by 37 weeks. No attempts to convert are needed before then |
|
|
On an EKG, you see the PR interval gradually lengthening until a beat is dropped |
Mobitz I (Wenchebach)
---------------------------------- Impaired AV Node conduction |
|
|
Hypercalcemia is the most common paraneoplastic syndrome assosciated with ________ type cancers |
Squamous Cell Cancers (eg, Squamous Cell Lung CA)
--------------------------------------------------- PTHrP is released by the malignancy and stimulates PTH receptors
↑Calcium, ↓Phosphate, Normal or ↓ PTH
|
|
|
What is the earliest manifestation of vaso-occlusive syndrome in patients with Sickle-cell? |
Dactylitis
-------------------------------------------------
Usually presents between ages 6 mo and 2 years with acute onset pain and swelling of hands and feet |
|
|
Pathology involves a point mutation which results in the substitution of valine for glutamic acid on the surface of the Hb S molecule on the 6th codon of the beta-globulin chain |
Sickle Cell |
|
|
HY
_______ are benign suprasellar tumors which present with signs of hypopituitarism, headaches and bitemporal blindness |
Craniopharyngioma
----------------------------------------------- Seen in sella tursica
characterized with cystic structure with calcification. |
|
|
Do these Meds cause HYPER or HYPO K+?
-Propanolol -Lisinopril -Losartan -Triamterene - Digoxin - Aspirin |
Hyperkalemia
---------------------------------------------- Non-selective 𝞫-antagonists (Timolol, Propanolol) - interfere with 𝞫-2 mediated intracellular K+ uptake
ACE-I's - Inibit angiotensin II formation which ↓ aldosterone production
ARB's -Block AT1 receptor which ↓ aldosterone production
K+ Sparing Diuretics (spironlolactone, triamterene) -Block epithelial Na channel (ENaC) or aldosterone receptor
Cardiac Glycosides (Digoxin) -Inhibit Na+/K+-ATPase pump
NSAIDs - ↓ prostaglandin synthesis --> ↓ renin + aldosterone
|
|
|
What is the treatment of choice for Slipped capital femoral epiphysis (SCFE)? |
Surgical Pinning to prevent further slippage and avascular necrosis |
|
|
An obese, 11 year old male presents with right knee, groin and hip pain.
Physical exam reveals a normal knee. Hip exam reveals a loss of ABduction and internal rotation of the hip as well as external rotation of thigh when the hip is being flexed. |
Slipped capital femoral epiphysis (SCFE)
---------------------------------------------------- Surgical pinning is indicated
Frog-leg lateral hip xray is imaging modality of choice |
|
|
What is the most commonly identified risk factor for placental abruption? |
Hypertension!
----------------------------------------- Risk factors are: 1-HT and preecclampsia, 2-Placental abruption in previous pregnancy, 3-trauma, 4-short umbilical cord, 6-COCAINE abuse
Placental abruption is the most common cause of DIC in pregnant women |
|
|
Treatment of choice for asymptomatic Chlamydia? |
Azithromycin (single dose) or Doxycycline (7 days)
|
|
|
Treatment for Gonorrhea? |
cetriaxone |
|
|
Most significant risk factor for stroke? |
HTN |
|
|
Mutation of type I collagen |
Osteogenesis Imperfecta |
|
|
Mutation of fibrillin-I gene? |
Marfan Syndrome |
|
|
Patient presents with blue sclera and recurrent fractures |
Osteogenesis imperfecta |
|
|
A 3 month old patient presents with jaundice and acholic (pale ) stools |
Biliary Atresia |
|
|
GI manifestation seen with neonates with Down Syndrome |
Duodenal Atresia/Stenosis
--------------------------------------------- Duodenal Atresia is the m/c anomaly associated with Down Syndrome, in xray you see a double bubble sign (dialated stomach & duodenum).
Prenatal U/S shows polyhydramnios due to an inability to swallow and remove amniotic fluid |
|
|
M/C cause of death in neonates or children with Down Syndrome? |
Heart Failure
------------------------------------------ Due to endocardial cushion defects (ASD/VSD) |
|
|
What would you see on a Quad Screen to diagnose Down Syndrome? |
LOW AFP & unconj Estriol; High BHCG & inhibin |
|
|
Cardiac problem assosciated with Turner Syndrome? |
Coarctation of Aorta
-------------------------------------------- May see high BP in arms, low BP in legs
Rib notching on chest x-ray |
|
|
__________ is characterized by osteonecrosis of the femoral head. It presents in boys ages 4-10 with insidious onset hip or knee pain with an atalgic gait. |
Legg-Calve-Perthes Disease
-----------------------------------------------------
|
|
|
In what disease do you see Howell-Jolly bodies? |
Sickle Cell Anemia
Also seen in Autosplenectomy
----------------------------------------------------- On peripheral smear you will see Sickle Cells, Howell-Jolly Bodies and Polychtomasia(from reticulocytosis) |
|
|
Most common drugs to cause Stevens Johnson Syndrome? |
NSAIDs Sulfa Drugs Phenytoin |
|
|
A patient is treated with TMP-SMX after being diagnosed with a UTI. After 3 days of medicine, he presents with the sudden onset of fever and a mucocutaneous rash involving the mouth, throat, trunk arms and feet. He appears toxic and complains the sores in his mouth and throat are extremely painful
The lesions are erythematous and blistered and have a target-appearance.
|
Stevens-Johnson Syndrome
-------------------------------------------------
NSAIDs Sulfa Drugs Phenytoin |
|
|
A patient presents with an acute exacerbation of COPD. She is tachycardic and tachypnic. She is in moderate distress. Pulse Oximetry shows 84% on 2L O2 by nasal canula.
She is given additional oxygen, a nebulizer treatment, intravenous levofloxacin and methylprednisolone. She still remains dyspneic and bedridden.
Chest X-ray shows emphysema but no pulmonary edema, consolidation, pleural effusion, or pneumothorax.
Arterial blood gas shows a pH of 7.2, PCO2 of 60 mm Hg, and PO2 of 52 mm Hg.
What is the next best step? |
Non-invasive positive pressure ventilation (NPPV)
---------------------------------------- . *****Non Invasive Positive Pressure Ventilation is the best option for pts with COPD exacerbation. It should be tried before intubation and mechanical ventilation in COPD pts with CO2 retention. ****** |
|
|
_________________ is an autoimmune disorder involving muscles and the skin. Skin eruption is dusty red in color. Edema around the eye and the heliotrope rash of the eyelid are more specific.
Proximal muscle weakness & Gottron’s papules (skin over the back of knuckles show non-scaly violaceous erythematous eruption) = “dark papules over the dorsum of hands” - Labs show an elevated creatinine kinase, since it’s an inflammatory reaction in muscles. |
Dermatomyositis
--------------------------------------------
Over 10% of patients will develop an internal malignancy. Most common is ovarian cancer
Age-appropriate cancer screening is essential. Especially in women. |
|
|
_____________ is characterized by shoulder pain, which is absent at rest but present at overhead activity.
Range of movement is limited by pain. Neer sign (pain on passive pronation of the arm and forward flexion at shoulder) is present. |
Subacromial Bursitis |
|
|
Patient presents with heat intolerance, weight loss, and increased appetite.
There is some painless swelling in the front of her neck.
Labs show: decreased TSH increased Total T4 increased Free T4
A radioactive iodine uptake scan shows very low uptake of radioiodine.
Most Likely Diagnosis? |
Painless (Lymphocytic) Thyroiditis
----------------------------------------------- **may follow pregnancy** |
|
|
This form of nephrotic syndrome is more common in African Americans and Hispanics
It is associated with obesity, HIV and heroin use |
Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis
------------------------------------------------- M/C form of nephrotic syndrome in adults |
|
|
Positive predictive value _________ with an increase in prevalance of a disease |
increases
----------------------------------- The more common the disease, the more likely a patient that tests positive has the disease |
|
|
Negative predictive value __________ with a decrease in prevalance of a disease. |
increases ------------------------------------ The more rare the disease in a population, the more likely patients that patients who test negative for a disease actually do not have the disease |
|
|
What is the best surgical option for a patient with a appendiceal rupture with a contained abscess? |
Wait 6-8 weeks and return for an appendectomy on an elective basis ("interval appendectomy")
|
|
|
HY
Best treatment option for a single metastatic brain lesion? |
Surgical resection ↓ Followed by whole-brain radiation
|
|
|
HY
Best treatment options for a patient with multiple brain metastases? |
Pallative whole-brain radiation |
|
|
Drug of choice in a patient with OCD? |
SSRI
or
Clomipramine |
|
|
A patient falls from his roof and lands on his back. He sustaines a burst fracture of the T4 vertebra. He has a total paralysis of both legs (paraplegia). He also has loss of pain and temperature in both of his legs, although proprioception is spared.
Dx? |
Anterior Cord Syndrome
(best visualized with MRI)
--------------------------------------------------------------- DDX: Central Cord Synd: Burning pain and paralysis in upper extremities with relative sparing of lower extremities. Seen in elderly due to hyperextension of the neck injury.
3-Brown Sequard synd: Ipsilateral motor (at the level of lesion), ipsilateral UMN sx below the level of lesion, ipsilateral proprioception/touch/vibration loss below level of lesion and contralateral loss of pain below the level of lesion. |
|
|
What is the preferred sceening test for HIV?
What is the preferred confirmatory test for HIV? |
Screen: HIV ELISA (99.9% sensitivity)
Confirmatory: Western Blot (99% specificity ) |
|
|
A patient with increased homocysteine levels develops a DVT.
What can you give her to decrease homocysteine levels? |
Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine) |
|
|
A 10 year old girl is brought in for a follow-up visit. She has been previously diagnosed with viesicourethral reflux, and has had multiple UTIs in the past.
Intravenous pyelography (IVP) reveals bilateral focal parenchymal scarring and blunted calyces.
Most Likely DX? |
Chronic pyelonephritis |
|
|
What drug should you never give to a patient with suspected closed-angle glaucoma? |
Atropine (a pupil dilator)
--------------------------------------------- Reduce pressure with: Mannitol (1st-line) Acetozolamide Timolol Pilocarpine |
|
|
A child presents with fever, dysphagia, drooling, inability to extend the neck, muffled voice.
Lateral x-ray shows a widened paravertebral space |
Retropharyngeal Abscess
--------------------------------------------------
|
|
|
Osteoporosis predominantly involves the (DIP or PIP) joints |
DIP joints |
|
|
What hand joints are classically affected by Rheumatoid Arthritis? |
PIP MCP |
|
|
Preferred antibiotic therapy for mastitis? |
Dicloxacillin or Cephalexin (Covers methicillin-sensitive Staph a.)
--------------------------------------------------- Women with risk factors for MRSA (recent antibiotic therapy, residence in prison, HIV infection) should be treated with clindamycin, TMP-SMX or vancomycin |
|
|
A patient is started on warfarin due atrial fibrillation.
She returns two days later with skin necrosis.
What is going on? |
Warfarin blocks Protein C & S, and initially causes a hypercoagulable state which can lead to Warfarin Induced Skin Necrosis
------------------------------------------------------------------
UWorld states that protein C deficiency is the cause. It's half-life is only 9 hours, so it becomes deficient quick and can lead to hypercoagubility! |
|
|
This condition is seen in premature/low-birth-weight infants. Pt presents with pallor, cyanosis, hypotension, seizures, focal neurologic signs, bulging or tense fontanels |
Intraventricular Hemorrhage of Newborn
--------------------------------------------------------- -transfontanel US is mandatory for all infants with risk factors.
-Drug given to mom before birth to reduce the risk: corticosteroids (betamethasone/dexamethasone) |
|
|
HY
What class of drugs can slow diabetic nephropathy? |
ACE-I's
---------------------------------
|
|
|
A woman who was recently diagnosed with hypothyroidism consults her physician about her dose of levothyroxine.
She wants to get pregnant and wonders how her pregnancy will affect her levothyroxine dosage. |
She will need an increased dose of levothyroxine |
|
|
A patient presents with a 4-5 Hz resting hand tremor that goes away with intentional movement.
On examination his arms are rigid |
Parkinson's
-------------------------------------------------- The resting hand tremor with muscle rigidity is often one of the earliest signs! |
|
|
You suspect a child has swallowed a coin and it is lodged in the esophagus.
What diagnostic modality is the next best step? |
Flexible endoscopy
--------------------------------------------------------- Can directly visualize foreign body and manipulate it. Can also visualize gastric mucosa and inspect for damage |
|
|
Procedure of choice for foreign body aspiration? |
Rigid bronchoscopy |
|
|
You suspect a child has swallowed a coin. How long can you observe the child before attempting flexible endoscopy? |
24 hours
----------------------------------------------- Objects that are smooth and nontoxic may pass through on their own. Wait 24 hours and check an x-ray.
Batteries, magnets and sharp objects need to be removed immediately with flexible endoscopy |
|
|
Complication of iron poisoning :
2 days: ________________ 2-8 weeks ______________________ |
2 days: Hepatic necrosis
2-8 weeks: Pyloric stenosis from gastric scarring |
|
|
A 3 year old boy presents with acute N/V/D and abdominal pain. GI bleeding (hememesis) and anion-gap metabolic acidosis develop. Hypotensive shock is noted after arrival to the ED. Abdominal X-ray shows radioopaque objects in the stomach.
What is going on? |
Iron Poisoning
-------------------------------------------------
Stabilize and treat with deferoxamine |
|
|
Treatment for iron poisoning? |
Stabilize, and then deferoxamine |
|
|
HY
In patients with suspected hyperthyroidism, _______________ is used for symptomatic relief until the underlying cause is identified and treated. |
Propanolol |
|
|
When does post-operative atelelectasis typically become most severe? |
2nd postoperative night
-----------------------------------------
- can last up to 5 days
-As compensation for hypoxemia, patients hyperventilate and develop respiratory alkalosis and ↓PCO2
-Acute post-op Pulmonary embolism can also present this way. |
|
|
Before surgery, it is recommended that patients stop smoking at least _________ weeks before surgery |
8 weeks
------------------------------------------------------------- -Not always the case. Must have them stop smoking immediately to ↓ post-op pulmonary problems |
|
|
What should be done to prevent post-op atelectasis? |
Breathing excercises/Inscentive spirometry
--------------------------------------------------- Other strategies:
-Epidural analgesia instead of IV opiods - CPAP - Smoking cessation 8 weeks before surgery |
|
|
Is pain better or worse in a patient with endometriosis during her menses? |
Pain is worse during menses |
|
|
17 year old girl has primary amennorhea, bilateral inguinal masses (or labial), and breast development without pubic or axillary hair.
On exam she has a blind vaginal pouch and no uterus/fallopian tubes/or ovaries are visualized by U/S.
Karyotyping reveals 46 XY
What is the diagnosis? |
Androgen insensitivity syndrome (X-linked recessive)
-------------------------------------------------------- -Mutation of the androgen receptor (AR) gene making peripheral tissues unresponsive to androgens
-Patients are phenotypically female (despite being 46 XY) and breast development occurs from testosterone conversion to estrogen. However, there is no axillary or pubic hair. There is a blind vaginal pouch and NO uterus/ovaries/fallopian tubes
-Testes are located in either the inguinal canal or within the labia majora --> surgical removal after the completion of puberty is reccommended to protect against testicular cancer
-Wait until after puberty for patient to finish breast development and grow to adult height |
|
|
What is the treatment of choice for Mucormycosis? |
Surgical debridement and amphotericin B
-------------------------------------------------- - Commonly seen in biabetic patients with DKA.
-Caused by Rhizopus fungi |
|
|
What is the most common cause of Mucormycosis in patients with DM Type 1 and DKA? |
Rhizopus |
|
|
Whicdh atypical antipsychotic is most likely to cause extrapyramidal side effects? |
Risperidone
------------------------------------------------ Remember to treat with an antimuscarinic like beztropine
- Also remember that atypical antipsychotics can cause ↑ prolactin |
|
|
A child is diagnosed with pinworms (Enterobius vermicularis).
What is the drug of choice? |
Albendazole or Mebendazole
---------------------------------------------
2nd line- Pyrantel pamoate
Can't use albendazole or mebenazole in pregnant patients! |
|
|
A patient experiences hyperactive reflexes after an abdominal surgery with many transfusions for a liver laceration.
What is the electrolyte abnormality? |
HYPOcalcemia
------------------------------------- Hypocalcemia can occur during or right after SURGERY, especially if transfusion is involved.
First manifestation is increased DTR. -muscle cramps, possibly convulsions
|
|
|
Formula to calculate anion gap? |
Anion Gap =Na - Cl - HCO3
(Normal = 8-12) |
|
|
HY
What is the most common cause of abnormal hemostasis in patients with Chronic Renal Failure? |
Platelet dysfunction -Uremic toxins such as guanidinosuccinic acid have been implicated in pathogenesis
Desmopressin (DDAVP) is the treament of choice * ↑ release of Von-Willebrand factor and factor VIII from endothelial storage sites----------------------------------------------------------------------- Will see normal PT, PTT and platelet count.
There will be an ↑Bleeding time (BT) |
|
|
A patient with a history of IV drug use has a holosystolic murmur that increases in intensity with inspiration.
What is the murmur? |
Tricuspid regurgitation |
|
|
A patient with a history of IV drug use presents with fatigue and fever.
Ausculation reveals a holosystolic murmur that increases in intensity with inspiration.
What empiric antibiotic should be started?
|
Vancomycin
------------------------------------------------------------- Here you should suspect right-sided bacterial endocarditis due to history of IV drug use and presence of tricuspid regurgitation
- Staph aureus is most common organism
|
|
|
Most common murmur seen in patients with IV drug use? |
Tricuspid Regurgitation |
|
|
What should be ordered first in all patients who undergoe a central-venous catheterization? |
Chest X-ray to confirm placement |
|
|
Drug of choice for syphilis? |
Penicillin |
|
|
𝞫 blocker overdose causes AV Block, bradycardia, hypotension, wheezing and potential cardiogenic shock.
Atropine and IV fluids are first-line treatments. If they do not completely reverse cardiac symptoms, what is the next therapy of choice?
|
Glucagon |
|
|
This disease can cause megacolon, megaesophagus and cardiac dysfunction |
Chagas Disease (Trypanosoma Cruzi) |
|
|
What class of drugs can limit ventricular remodeling after a myocardial infarction? |
ACE-I's
-------------------------------------------------------------
ACE-I's should be initiated within 24 hours of MI in all patients witout a contraindication |
|
|
Small bowel biopsy shows villous atrophy in a patient who has been having frequent, foul-smelling, bulky stools and weightloss for the past 6 months. He has fatigue and occasional joint pain.
Most Likely Diagnosis? |
Celiac Disease
------------------------------------------------------- (+) IgA anti-tissue transglutaminase (+) IgA anti-endomysial antibodies
However, man patients with biopsy-confirmed celiac disease will have negative results on IgA antibody testing due to an associated IgA deficiency (must measure total IgA) |
|
|
What is a key feature of the CSF analysis of Guillan-Barre syndrome? |
Elevated pressure
Elevated protein
Low WBCs
-------------------------------------------------------
This is called albuminocytologic dissociation |
|
|
What causes an anaphylactic reaction to a blood transfusion?
------------------------------------------------------- Immediate reaction Shock, angiodema/uticaria and resp. distress |
recipient anti-IgA antibodies |
|
|
What is the cause of febrile nonhemolytic blood transfusion reaction?
------------------------------------------------------------ (Most common transfusion reaction) -1-6 hrs after transfusion - Causes fever/chills |
Build-up of inflammatory cytokines during blood storage |
|
|
Most common cause of chronic iron deficiency anemia? |
Chronic Blood Loss |
|
|
A patient presents one week after an acute upper respiratory infection with shortness of breath, weakness and an increased, "water bottle" silhouette on chest x-ray.
EKG shows low voltage in all leads and there is a non-palpable point of maximal impulse. |
pericardial effusion |
|
|
A child displays poor communication and reduced verbal expression at school 1 month after beginning kindergarten but behaves normally at home. |
Select Mutism
-------------------------------------------
- at least 1 month duration - consistently fails to speak in specific situations - no attributable lack of knowledge or ↓ hearing |
|
|
A patient presents with GI complaints for one week followed by muscle pain, swelling and weakness.
Examination shows presence of of subungul splinter hemorrhages , conjunctival and retinal hemorrhages, periorbital edema and eosinophilia.
|
Trichinosis
--------------------------------------------------------------- - Roundworm infection from eating undercooked pork
- Phase 1: abdominal pain, N/V/D
-Phase 2: Larva migrate and induce a hypersensitivity rxn, "splinter hemorrhages", conjunctival and retinal hemorrhages, periorbital edema and chemosis
-Phase 3: Larvae enter skeletal muscle and cause muscle pain, tenderness, swelling and weakness. |
|
|
Most common antibiotic class to cause photosensitivity? |
Tetracyclines |
|
|
Rare condition characterized by precoscious puberty, cafe au lait spots and mutliple bone defects |
McCune Albright Syndrome
-------------------------------------------------- 3 P's: -precoscious puberty - pigmentation - polyostotic fibrous dysplasia |
|
|
In patients with influenza, neuraminidase inhibitors (oseltamivir and zanamivir) must be started within ______ hours to be effective |
48 hours |
|
|
Most common thyroid cancer? |
Papillary Carcinoma
------------------------------------------------------- -Fine Needle Biopsy shows psammoma bodies
- Large cells with ground glass cytoplasm, and pale nuclei with inclusion bodies and central grooving |
|
|
Which thyroid cancer is encapsulated? |
Follicular Thyroid Carcinoma
------------------------------------------------------------------
Demonstration of invasion of the capsule and blood vessels is necessary to differentiate follicular cancer from follicular adenomas!
-Follicular thyroid cancers like to invade blood vessels and metastasize to distal organs |
|
|
Most common electrolyte abnormalities observed with Cushing Syndrome? |
HYPOkalemia and HYPERnatremia
------------------------------------------------------- -There is corticosteroid excess
- Corticosteroids will bind to aldosterone receptors in the kidney and cause potassium wasting |
|
|
Most common risk factor for plancental abruption? |
Maternal HTN |
|
|
An incidental renal cyst is noticed on an abdominal CT.
What features of the cyst would require more studies for further evaluation? |
-Thick, irregular wall - Multilocular with multiple septae - Contrast enhancement on CT/MRI
------------------------------------------------------ These types of cysts are associated with malignant transformation.
Unlike simple renal cysts, these may cause symptoms such as hematuria, pain or hypertension |
|
|
First line treatment for PMS/PMDD? |
SSRIs |
|
|
______ should be included as secondary prevention following unstable angina/NSTEMI for at least 12 months.
It hsould also be prescribed for 30 days (bare metal stents) to 1 year (drug eluting stents) following percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), as it has been shown to help prevent subacute stent thrombosis
|
Clopedigrel
------------------------------------------------------- Belongs to a class of drugs known as Thienopyridines which includes ticlopidine.
Has an anti-platelet effect and acts by blocking ADP |
|
|
Hydroxychloroquine is used for patients with SLE that have significant skin and joint involvement.
What is its most serious side effect? |
Retinopathy
---------------------------------------------------- Need eye exams q 6 months! |
|
|
How does squatting affect the murmur heard in a child with Tetrology of Fallot? |
The murmur will increase
------------------------------------------------------ Squatting (↑ afterload and ↑PVR) decreases the right to left ventricular shunting associated with the VSD and will improve cyanosis! |
|
|
Digoxin toxicity is more common in patients with what electrolyte deficiency? |
HYPOkalemia
--------------------------------------------------- Digoxin competes with K+ for the Na/K pump |
|
|
What is the first step in a workup of acromegaly? |
Measure serum IGF-1 first
Then, Oral glucose supression if IGF-1 is ↑ (GH will decrease)
-------------------------------------------------
Even though they most likely have a pituitary tumor, you should do IGF-1 first --> Glucose supression --> MRI |
|
|
Hemochromatosis can lead to what type of cancer? |
Hepatocellular Carcinoma |
|
|
First line treatment for hypertrophic cardiomyopathy? |
Beta-blockers or Diltiazem |
|
|
Several small, teardrop shaped lesions on the vulva. Application of trichloroactic acid results in complete resolution of lesions |
Genital warts (condyloma accuminata) |
|
|
A patient is found on the floor and unresponsive after several hours.
He has an elevated K+, elevated CPK, and history of cocaine abuse.
What are we worried about as a result of his cocaine abuse? |
Rhabdomyolysis --> immobilization + cocaine
--------------------------------------------------------------------
↑CPK d/t rhabdo can lead to acute renal failure
|
|
|
What is the best way to prevent HIV/AIDs tranmission between a mother and fetus? |
HAART triple antiviral therapy throughout pregnancy
---------------------------------------------------------- 3-drug HAART: - 2 nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors PLUS -Non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor OR protease inhibitor
NRTIs with good placental transfer are Zidovudine and tenofovir
Zidovudine should be administered to the neonate for up to or more than 6 weeks |
|
|
What should you monitor in patients taking 2nd-generation antipsychotics --> Olanzapine or Clozapine? |
Fasting glucose and lipid panels
(d/t ↑weight gain and dyslipidemia and hyperglycemia)
------------------------------------------------------- Clozapine is also associated with agranulocytosis |
|
|
What is the first line treatment for noninflammatory (comedonal) acne? |
Topical Retinoids
---------------------------------------------------- Inflammatory Acne --> topical retinoids AND benzoyl peroxide
Moderate to Severe Inflammatory Acne - ADD topical antibiotics (doxycycline)
Severe or Recalcitrant Acne - Oral antibiotics and isotrenitoin |
|
|
First step in work-up of achalasia? |
Barium swallow
----------------------------------------------- However, if you suspect and obstruction from a tumor, you could start with an endoscopy. But generally, you would do barium swallow first |
|
|
An athlete suffers a clavicular fracture. A loud bruit is heard underneath the clavicle.
Next step? |
Angiography
-------------------------------------------------------
Need to rule out damage to subclavian artery and brachial plexus |
|
|
HY
_____________ and tacrolimus have the same mechanism of action (calcineurin-inhibitors) that inhibit the transcription of interleukin-2 and several other cytokines.
The major side effects include nephrotoxicity, hyperkalemia, hypertension, gum hypertrophy, hirsutism and tremor.
Tacrolimus has similar toxicities, but lacks hirsutism and gum hypertrophy. |
Cyclosporin
--------------------------------------------------------- Immunosuppresant side effects: azathioprine--> dose related diarrhea, leukopenia, hepatotoxicity
mycophenolate --> bone marrow suppression |
|
|
What is the best way to prevent bacterial UTI in a patient with chronic neurogenic bladder? |
Intermittant catheterization -----------------------------------------------------
Although each passage of the catheter has risk of bacterial induction, indwelling catheters have a higher risk of infection due to bacterial biofilm that can develop along the catheter wall |
|
|
Prophylactic treament for patients with non-bleeding, small esophageal varices? |
non-selective 𝞫-blockers (Propanolol or nadolol)
----------------------------------------------------------------- Mechanism involves decreased andrenergic tone in mesenteric arterioles that causes unopposed alpha-vasocontriction and decreased portal vein flow |
|
|
Multiple duodenal ulcers with the presence of a jejunal ulcer |
Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome
------------------------------------------------------
Characterized by multiple severe drug resistant ulcerations in the GI track. The mcc of ZES is a gastrin-producing pancreatic tumor.
As a result of uncontrolled gastrin production, parietal cell hyperplasia occurs and stomach acid production is significantly increased. Multiple Duodenal ulcer are typical, and a Jejunal ulcer is almost pathognomonic for this condition.
Dx = secretin test (if a pt has a gastrinoma, an IV Bolus of secretin should cause a huge rise in gastrin).
Steatorrhea may develop because increased production of stomach acid inactivates pancreatic enzymes. Tx of choice is K-H ATPase inhibitor Omeprazole, indefenitely until surgery. If meds fails we have to go to a total Gastrectomy.
*Is Associated with MEN-I…so if someone presents with a gastrinoma…also look for these other tumors = Hyperparathyroidism and Pituitary tumors causing varius symptoms such as acromegaly, etc (+Pancreatic carcinoma/gastrinoma)
- To Dx a gastrinoma – can use an octreotide scan to localize the tumor! |
|
|
Method of choice for diagnosing lactose intolerance? |
Hydrogen breath test
-------------------------------------------------- (+) test is characterized by a rise in exhaled hydrogen after administration of lactose, which indicates bacterial lactose metabolism |
|
|
Most common cause of UTI-acquired infectious endocarditis? |
Enterococcus faecalis |
|
|
Common rash seen on extensor surfaces in patients with Celiac Disease? |
Dermatitis herpetiformis
-------------------------------------------------- Treat with dapsone |
|
|
Surgery for stress incontinence? |
urethroplexy
------------------------------------------------ Kegel Excercises should be done first!
Urethral hypermobility = >30 degrees angle with cotton swab test and increased intrabdominal P |
|
|
Most common shoulder injury after a tonic-clonic seizure? |
Posterior shoulder dislocation
------------------------------------------------- patient holds arm ADducted and internally rotated |
|
|
What maneuver will worsen the murmur heard in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy? |
Valsalva
--------------------------------------------------- Valsalva --> ↓ preload --> ↓ size of ventricular cavity --> worsens outflow obstruction
Most murmurs will decrease when there is decreased venous return (↓preload) since there is less flow through the heart |
|
|
HY
In infant presents with cyanosis while feeding that resolves when he is crying |
Choanal atresia |
|
|
The common presentation of cryoglobulinemia includes palpable purpura, glomerulonephritis, arthralgias, hepatosplenomegaly, peripheral neuropathy and hypocomplementemia.
Most of these patients also have an infection with what virus? |
Hepatitis C |
|
|
Seizure medication assosciated with acute pancreatitis? |
Valproic Acid
-------------------------------------------------------------- Other Drugs associated with acute pancreatitis: 1. Diuretics (furosemide, thiazides)2. IBD drugs (sulfasalazine, 5-ASA) 3. Immunosupressive agents (azathioprine) 4. HIV- medications (didanosine, pentamide) 5. Antibiotics (metronidazole, tetracycline) |
|
_________ is diagnosed by the presence of crooked, branching, beaded, Gram (+) and partially Acid-fast filaments on microscopy.
|
Nocardia
---------------------------------------------------------- Tx: TMP-SMX
Can present with pulmonary, CNS or cutaneous manifestations.
-Patients with deficient cell-mediated immunity (HIV, lymphoma, transplant patients) are at increased risk |
|
|
Best treatment for hypercalcemia with symptoms? |
Bisphosphonates (zolendroic acid) + Normal saline + Calcitonin
-------------------------------------------------------- Bisphosphonates are used long term in patients with malignancy causing hypercalcemia |
|
|
Carotid endarterectomy is recommended for patients with "symptomatic" carotid stenosis of more than ______% |
more than 70% |
|
|
HIV patient with a CD4 count <180 has severe, watery diarrhea, abdominal cramps and an inability to eat.
Acid fast stain of stool specimen shows 4-6mm oocysts.
Diagnosis? |
Cryptosporidium parvum
---------------------------------------------------- Causes diarrhea in immunocompromised patients |
|
|
Pleural effusion:
Exudative effusion is caused by ______________ |
increased capillary permeability
---------------------------------------------------------------- Increased permeability allows LDH to leak from capillaries
Transudative effusion: increased hydrostatic P or decreased oncotic P |
|
|
Pleural effusion:
Transudative effusion is caused by ___________ |
increased hydrostatic pressure (CHF) or decreased oncotic pressure (liver failure)
----------------------------------------------------------------
Exudative effusion: increased capillary permeability (Infection, neoplasm, Autoimmune Dz) |
|
|
Transudative pleural effusion in CHF is caused by _________________ |
increased hydrostatic pressure |
|
|
Transudative pleural effusion seen in liver failure is caused by _________________________ |
decreased oncotic pressure |
|
|
Where is the most frequent origin of the ectopic foci that cause atrial fibrillation? |
pulmonary veins |
|
|
Most common cause of atrial flutter stems from a re-entry circuit located where? |
tricuspid annulus --> cavotricuspid isthmus |
|
|
Sinus Tachycardia stems from increased sympathetic/decreased vagal influences on the _____ node |
SA node |
|
|
Treatment for patients with immune thrombocytopenia?
---------------------------------------------------------------------
Most common in patients 2-5 yrs old.
Follows a viral infection
Asymptomatic petechiae and echymosis most common
Can cause mucosal bleeding (GI, epitaxis, hematuria)
Labs show Thrombocytopenia < 100,000 and megakaryocytes on peripheral smear with no other abnormal findings |
Skin manifestations only: observation
Bleeding: IVIg or Glucocorticoids
------------------------------------------------------------------
When this occurs in adults, you can observe if the platelet count is <30,000
If platelet count < 30,000 or there is bleeding: -IVIg or Glucocorticoids |
|
|
Most common malignant cancer of the liver? |
METASTASIS from another source
|
|
|
Hyperventilation causes what acid-base disorder? |
Respiratory Alkylosis
---------------------------------------------------- Seen in hyperventilation with pneumonia, altitude sickness and salicylate poisoning |
|
|
This skin condition of infancy presents with pruritis and skin lesions typically distributed symmetrically over the scalp, chest and extensor surfaces of the extremeties.
The diaper area is typically spared |
Atopic Dermatitis
------------------------------------------------- Treatment improves the skin barrier through the use of mild cleansers and thick bland emollients + topical antiinflammatory ointments |
|
|
A patient presents with an acute abdomen and you suspect a perforated viscus. He is on warfarin for a-fib.
He requires an emergent laparotomy. Since he is on warfarin, reversal of anticoagulation must be rapidly achieved by infusion of ___________ |
Fresh Frozen Plasma
--------------------------------------------------------------- FFP normalizes prothrombin time (PT) and resores vitamin K clotting factors |
|
|
HY
The risk of sepsis by encapsulated bacteria (Pneumococcal, Haemophilus, Menningococcal) but especially Strep pneumo is present up to ____ years after splenectomy |
30 years
--------------------------------------------------- Asplenic patients need :
Anti pneumococcal + meningococcal +Haemophilus vaccinations several weeks befroe surgery
Daily penicillin prophylaxis for 3-5 years following splenectomy
|
|
|
What special precautions do patients undergoing splenectomy need in order to gaurd against encapsulated bacterial sepsis? |
Anti pneumococcal + meningococcal +Haemophilus vaccinations several weeks befroe surgery
Daily penicillin prophylaxis for 3-5 years following splenectomy |
|
|
Watery diarrhea after eating raw or undercooked seafood? |
Vibrio parahaemolyticus |
|
|
A patient from Greece has a microcytic anemia that is non-responsive to iron therapy. |
𝞫-Thalassemia
-------------------------------------------------- There is reduced hemoglobin synthesis due to point mutations on the 𝞫-hemoglobin genes
𝞫-Thalassemia minor: defect in one gene -will see a modest anemia
𝞫-Thalassemia Major: defect in both genes -will see severe anemia and likely transfusion dependence at an early age |
|
|
Metformin is contraindicated in patients with which 2 diseases? |
Renal failure
Liver failure
---------------------------------------------------
Increased risk of lactic acidosis
In conditions with an increased BUN, lactic acidosis will only cause more problems |
|
|
A patient presents with an insenasate (no sensation), hypopigmented lesion on his forearm. He has muscle weakness and wasting of his upper arm and shoulder.
Skin biopsy shows acid-fast bacilli. |
Mycobacterium leprae (Leprosy)
--------------------------------------------------------------------
|
|
|
Fetal monitor shows recurrent variable decelerations. What is the next best step? |
1. Administer O2
2. Place Mom in lateral decubitus position |
|
|
20 year old female presents with copius malodorous vaginal that is Greyish-green color, thin and frothy.
She also has vaginal pruritis, dysurea and dyspareunia. Petechial pathes on the cervix show "strawbery cervix".
Dx by microscopic obervation of flagellar, pear-shaped organism in wet mount preparation |
Trichomonas vaginalis
----------------------------------------------------------------- treat BOTH partners with metronidazole |
|
|
Fluphenazine is a "typical" psychotic medication used to inject schizophrenic patients every 2-3 weeks due to poor compliance.
What is a special climate situation a patient taking fluphenazine should try to avoid? |
Cold climates ---> HYOTHERMIA
----------------------------------------------------------------- Fluphenazine disrupts the shivering mechanism |
|
|
Most common bug to cause pneumonia in nursing home residents? |
Strep pneumonia
--------------------------------------------------- Also m/c cause of community pneumonia |
|
|
Immunocompromised patient presents with fever, cough, dyspnea and hemoptysis.
Chest CT shows pulmonary nodules with a halo sign. |
Aspergillosis
------------------------------------------------------- X-ray may show cavitary lesion
Chest CT shows pulmonary nodules with a halo sign or lesions with an air crescent
|
|
|
What 2 drugs can be used to decrease the frequency of exacerbations in patients with relapsing-remitting Multiple Sclerosis? |
Beta-interferon
Glatiramer
---------------------------------------------------------- "Beta take interferon, you'll be glat you did" |
|
|
fetal monitor tracings |
|
|
|
A schizophrenic patient is meeting with her psychiatrist. During conversation she seems to have disorganized thought and speech.
Her responses are irrelevant, but detailed. Her answers drift away from the subject but eventually return. Her answers deviate from the topic of conversation but remain vaguely related and there is an eventual return to the original subject.
What is she demonstrating? |
Circumstantiality (comes back to original topic eventually)
-------------------------------------------------------------
"Flight of ideas"-loosely associated thoughts that move from topic to topic.
Tangentiality- thought process in which there is abrupt, permanent deviation from current topic. New thought process is minimally relevant and never returns to origninal subject
Loose Assosciations - best described as a lack of logical connection between thoughts or ideas. It is a more severe form of tangentiality where one statement follows another but there is no clear assosciation between sentences.
Preservation - repetition of words or ideas during a conversation
|
|
|
Aminoglycosides are used for serious gram-negative infections.
What side effect do you have to be aware of before treating a patient? |
Nephrotoxicity
----------------------------------------------------------------
-Amikacin was used as an example
Tobramycin, Gentamycin, Neomycin, Streptomycin |
|
|
Radiation exposure during the first _____ days of conception can cause fetal death and resorption |
14 days
|
|
|
What should you do for household contacts of a patient recently diagnosed with Pertussis? |
Macrolide prophylaxis for ALL household members DESPITE vaccination status
---------------------------------------------------------------
Age < 1 month: Azithromycin x 5 days
Age > 1 month: Azithromycin x 5 days or Clarithromycin x 7 days or Erythromycin x 14 days |
|
|
A homeless man presents with tingling lips, and muscle pain. He is an alcoholic and has been drinking a lot lately.
His serum calcium and phosphorous are both low.
What could be causing his hypocalcemia? |
Malabsorption
--------------------------------------------------- He is predisposed to malabsorption d/t pancreatitis. Vitamin D malabsorption causes hypocalcemia and hypophosphatemia because active 1,25-dihydro cholecalciferol usually would raise levels of both calcium and phosphorous. |
|
|
Acid-base disturbance seen in Aspirin overdose? |
Respiratory Alkalosis with Metabolic acidosis
-------------------------------------------------------------------
Respiratory alkalosis is due to increased respiratory drive (hyperventilation)
Metabolic acidosis is caused by increased production and decreased renal elimination of organic acids (lactic acid, ketoacidosis) |
|
|
Leukemia:
(+) Tartate-resistant acid stain (TRAP)
(+) CD11c |
Hairy Cell Leukemia
------------------------------------------------
B-lymphocytic derived chronic leukemia.
-TARTRATE-RESISTANT ACID PHOSPHATASE (TRAP) STAIN is Dx.
****Picture looks like hairy projections of large cells (lymphocytes)***
Bone marrow may become fibrotic so BM aspirate are frequently unsuccessful (Dry Tap).
Tx DOC are = Nucleoside analogs. It’s toxic to BM, & causes neurological and kidney damage. |
|
|
(+) Reed Sternberg cells (Owl's Eye cells) are diagnostic for __________________ |
Hodgkin's Lymphoma |
|
|
What test is commonly used to compare the means of two groups of subjects? |
t-test |
|
|
What test is commonly used to compare the means of three or more groups of subjects? |
ANOVA (Analysis of Varience) |
|
|
A 15 year old boy comes to his physician with a new onset of facial muscle weakness, dysphagia, upper extremity muscle wasting, and an inability to release hand with handshake (myotonia). |
Myotonic Muscular Dystrophy (Steinert Disease) -Autosomal Dominant
----------------------------------------------------------- 2nd mcc of muscular dystrophy, after Duchenne. Autosomal Dominant, wheras Duchenne and Becker are X-linked recessive
-A trinucleotide expansion disease: * CTG trinucleotide repeat in DMPK gene on chromosome 19
ALL muscle in body atrophy, lip looks like a V. Its .
It’s defined as delayed mucle relaxation, characteristic is not being able to release the hand after hand shake.
- Cardiac manifestations = cardiomyopathy & arrhythmias
- Occular manifestations = cataracts
- Also presents with gonadal atrophy and balding |
|
|
Inheritance for Duchenne and Becker Muscular Dystrophies? |
X-linked recessive |
|
|
A physician is assessing a patient for brain death and reveals that the patient still has intact DTRs despite no signs of brainstem function.
What is going on? |
DTRs reveal an intact spinal cord
The spinal cord may still be intact, but the patient is brain dead.... |
|
|
Most common cause of non-sexually transmitted epididymitis? |
E. Coli
------------------------------------------------------------- Most frequent in older men |
|
|
Most common cause of sexually-transmitted epididymitis? |
Chlamydia or Gonnorrhea infection
------------------------------------------------------------------- More frequent in younger males |
|
|
Most common cause of viral "pinky eye" conjunctivitis? |
Adenovirus
------------------------------------------------------------ Commonly seen in children (and care-takers) in daycare or school settings in late summer/early fall.
Tx: Warm/Cool compresses +/- Antihistamine or decongestant drops
DO NOT use Steroid Eye drops for Viral eye infections |
|
|
A child with known TOF is having a "tet" spell. What position should he be placed in to increase systemic vascular resistance to reduce the degree of right-to-left shunting, and increase pulmonary bloodflow, and resolve symptoms and cyanosis. |
Knees-to-Chest position
---------------------------------------------------------- Tetralogy of Fallot: "Tet" spells are hypoxic episodes characterized by rapid breathing. Rapid breathing increases pulmonary vascular resistance which causes a shunting of unoxygenated blood from the right ventricle across the VSD and into the aorta. This causes cyanosis
Immediate tx is Oxygen and put the child in a Knee-Chest position, followed by fluids, morphine, propranolol
Squatting and Knee-to-chest positions increase systemic vascular resistance to reduce the degree of right-to-left shunting, and increase pulmonary bloodflow, and resolve symptoms and cyanosis. |
|
|
What is the drug of choice to treat Lyme disease in Pregnant women, breast-feeding women, or children <8 years old? |
Amoxicillin
--------------------------------------------------------- Doxycycline is a tetracyline antibiotic that can cause tooth discoloration and decreased bone growth in children and fetuses |
|
|
A patient with chronic alcoholism and cirrohsis presents with fever and acute abdominal pain. Abdominal exam shows shifting dullness and diffuse tenderness to palpation.
You suspect peritonitis. What is the next best step for diagnosis? |
Paracentesis
---------------------------------------------------------------- (+) Ascites fluid culture for most commonly E. Coli or Klebsiella AND PMN level greater than 250 make the diagnosis |
|
|
A 32 year old woman presents with intermittent blood staining on her bra from her left breast. She has not felt any bumps or masses
Physical examination reveals no breast mass, lymphadenopathy or skin changes.
U/S of the breast is within normal limits |
Intraductal Papilloma
-------------------------------------------------------- Benign breast disease
Most are situated beneath the aereola and difficult to palpate
Often no larger than 2mm so U/S won't pick it up |
|
|
Diagnostic test for Heparin-induced Thrombocytopenia? |
Serotonin Release Assay
|
|
|
Treatment for Heparin-induced Thrombocytopenia? |
1) STOP ALL HEPARIN DRUGS
2) Start a direct thrombin inhibitor (argatroban) or fondaparinux (synthetic pentasaccharide)
---------------------------------------------------------------- Warfarin is usually started after treatment with a non-heparin anticoagulant and platelet count recovery > 150,000 u/L |
|
|
34 year old African American man presents with cough, intermittant chest pain, and fatigue for 2 months duration.
He denies alcohol, tobacco or drug use. He has not traveled out of the country and has not been incarcerated.
Auscultation reveals patchy crackles. Chest X-ray shows several lung nodules and mediastinal adenopathy.
A biopsy of lung nodules shows non-caseating granulomas |
Sarcoidosis
----------------------------------------------------------- Systemic steriods are the DOC for Sarcoidosis. They are indicated in pt’s with disabling systems (visual disturbances, cough, shortness of breath) and organ dysfunction.
Pt has bilateral Hillar lymphadenopathy (organ derangement). Steroids suppress activated T-induced cell process at disease site. Asymptomatic pts need no tx.
****Cxr shows granular Hilar opacity in lungs bilaterally (midiastinum adenopathy). Once midiastinum adenopathy is seen on CXR, the next step is to perform mediastinal bronchoscopy and obtain tissue for biopsy.
Ca++ & ACE are increased (macrophages in the granuloma’s convert Vit D to calcium, irrespective of PTH or Ca levels in the blood!) and
Steriods are tx of choice for SYMPTOMATIC pts.****Pt with no symptoms but dyspnea that has gotten worse and joint pain with cxr showing hilar adenopahty and non-caseating granuloma.****
Skin manifestation of rash is found in 30% of pts, to Dx Scintigraphy, to Confirm biopsy and non-caseating granulomas.
-Triad of: bilateral hilar lymphadenopathy, polyarthralgia, & erythema nodosum (esp knees)
|
|
|
Therapy of choice in patients with acute bleeding and Chronic Liver Failure? |
Fresh Frozen Plasma
------------------------------------------------------------------
Contains Vit K dependent factors: II, VII, IX, X that the liver cannot synthesize due to failure. |
|
|
A patient with a history of Hepatitis C and chronic liver failure presents with fatigue and shortness of breath.
Exam reveals decreased breath sounds at the right lung base, significant abdominal distension, 2+ peripheral edema. Periumbilical venout distension is appreciated.
Chest X-ray shows a moderate to severe right pleural effusion and a small left pleaural effusion. Thoracentesis reveals a transudative exudate.
What is the best way to manage his hepatic hydrothorax? |
Initial treatment is diuretics and salt restriction
If perfusion persists, then a Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt (TIPS) should be placed |
|
|
Which renal-pulmonary syndrome is treated with emergency plasmaphoresis? |
Goodpasture's
---------------------------------------------------------
Plasmapharesis is requires to remove the anti-glomerular basement membrane antibodies (anti-GBM) in order to minimize kidney damage! |
|
|
Treatment for Wegener's Disease? |
Cyclophosphamide and Steroids
(c-ANCA --> Cyclophosphami
------------------------------------------------------------ Hematuria+Hemoptysis+Sinusitis.
Underlying pathology involves Necrotizing vasculitis with granuloma formation.
Postive c-ANCA (aka antiproteinase 3 Ab).
Typical Xray shows nodular cavities.
****Demonstration of Anti Neutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibodies confirm dx |
|
|
What steps should you take to prevent contrast nephropathy in a patient with increased risk (Diabetes, Renal insufficiency)? |
1) Adequate IV hydration with either normal saline or sodium bicarbonate
2) Acetylcysteine (Vasodilation + antioxidant)
--------------------------------------------------------------------
Contrast Nephropathy presents as a Creatinine spike within 24 hours of contrast administration, with a return to normal renal function 5-7 days later
Diabetics already have a high baseline Creatinine and are at an increased risk |
|
|
What is asymmetric intrauterine growth restriction in a fetus?
|
Asymmetric interuterine growth restriction is the result of a later exposure to a maternal factor that does not allow for fetal growth.
It is characterized by normal or near normal head size, and a reduced abdominal circumfrence.
Maternal Factors: hypertension, smoking, hypoxia, vascular disease, preeclampsia |
|
|
What is symmetric intrauterine growth restriction in a fetus? |
In symmetric growth restriction, the insult to the fetus occurs before 28wks gestation, and growth of the head and body are similarly lagging behind in dates
It is caused by fetal factors such as chromosomal abnormalities, congenital infections (TORCH) and congenital anomolies |
|
|
Pt presents with massive hemoptosis, weight loss, hematuria and proteinuria.
Blood tests show Anti-GBM antibodies |
Goodpastures |
|
|
Acid-base disorder you would expect to see in an infant with pyloric stenosis? |
Hypochloremic Metabolic Alkalosis |
|
|
Study used to confirm pyloric stenosis in an infant? |
Abdominal Ultrasound |
|
|
A 33 year old morbidly obese female presents with amenorrhea for 9 months. She had her last child 2 years ago and had a tubal ligation afterwards. Her menses were normal until about 18 months ago and then started to skip every other month.
She did not breastfeed, and was not on any medicines. Initial bloodwork, serum TSH, prolactin, FSH and LH were all within normal limits.
What is causing her amenorrhea? |
Anovulation secondary to morbid obesity
------------------------------------------------------------------- Normal FSH and LH levels show that the ovaries are still producing estrogen.
However, progesterone is not being produced normally at post ovulation levels. No progesterone withdrawl means no menses |
|
|
A 2 week old neonate is brought to the office for poor feeding and persistent vomiting. He is irritable and jaundiced. His liver and spleen are enlarged. Bilateral cataracts are evident.
What is the condition? What enzyme is deficient? |
Galactosemia
Galactose-1-phosphate uridyl transferase (GPUT)
----------------------------------------------------------- Symptoms include failure to thrive, bilateral cataracts, jaundice and hypoglycemia.
Early dx and tx by removing galactose from diet are mandatory. Must be put on SOY milk
It’s a metabolic disorder caused by Galactose-1-Phosphate Uridyltransferace def. That leads to increased levels of Galactose-1-P. Infants are at an increased risk for E. Coli neonatal sepsis
DDX: Galactokinase Deficiency ---> bilateral cateracts but are otherwise asymptomatic!
|
|
|
An infant is brought to the office for a well visit. His mother reports no concerns. He is eating, gaining weight and producing an appropriate amount of wet and dirty diapers.
Physical exam is normal except for bilateral cataracts noted on ophthalmic exam.
What enzyme is deficient? |
Galactokinase |
|
|
A patient is found to have needle shaped crystals in his urine. They were not present on U/S or abdominal X-ray.
What test can be used to visualize these crystals? |
Uric Acid Stones
CT Abdomen
Intravenous pyelogram |
|
|
This form of emergency contraception is 99% effective if used within 120 hrs. |
Copper IUD
--------------------------------------------------------------- Causes an inflammatory response that is toxic to sperm and egg. Can be taken up to 5 days (120hrs) after unprotected intercourse. |
|
|
What test can be used to differentiate between fetal and maternal blood if there is a suspected rupture of an umbilical vessel? |
Apt Test |
|
|
DOC for a cat bite? (Or dog bite) |
Amoxicillin/Clavulanate (Augmentin)
------------------------------------------------------------- Cat/Dog Bite: Pasturella Multicoda Gram (-) Coccobacillus |
|
|
DOC for a cat scratch? |
Azithromycin
-------------------------------------------------------------- Bartonella henslae Gram (-) bacillus
Can develop vesicular erythema at scratch site and tender lymphadenopathy 3-14 days after scratch |
|
|
What is the treatment of choice for central retinal artery occlusion? |
Gentle Massage of the globe and highflow O2
---------------------------------------------------------------------- Massage helps to dislodge the emboli and the highflow O2 (CO2 : 5% / O2 95%) is thought to cause opthalmic vessel vasodilation |
|
|
Painless loss of vision in one eye. Fundoscopic examination shows a pale retina (maybe cherry red spots) |
Central Retinal Artery Occlusion |
|
|
Treatment for Torsades De Pointes? |
Magnesium Sulfate |
|
|
Treatment for hyperkalemia with tall, peaked T-wave? |
Calcium Gluconate |
|
|
Presence of Philadelphia Chromosome (t[9;22]) |
CML
------------------------------------------------------------- May also see BCR-ABL fusion gene May also see Low leukocyte alkaline phosphatase |
|
|
Presence of Auer Rods |
AML |
|
|
Absence of measurable erythropoetin in urine |
Polycythemia Vera |
|
|
Low leukocyte alkaline phosphatase is classic for which leukemia? |
CML |
|
|
Atypical antipsychotic most likely to cause extra-pyramidal symptoms? |
Risperidone |
|
|
Most common pituitary tumor? |
Prolactinoma |
|
|
Arises from Rathke's cleft formed during pituitary development |
Craniopharyngioma |
|
|
A patient has overdosed on TCAs. She is hypotensive and obtunded.
EKG shows QRS elongation.
What drug should you give? |
Sodium Bicarbonate
------------------------------------------------------------- Improves hypotension Narrows QRS Decreases risk of Ventricular Arrythmia |
|
|
A patient complains of hip and groin pain for 2 weeks. Medical history is significant for SLE diagnosed 7 years ago.
She is currently taking prednisone, hydroxychloroquine and lansoprazole
Exam shows no local tenderness or decreased ROM. Hip X-ray is normal.
What is the next best step? |
MRI of the hip to rule out avascular necrosis
----------------------------------------------------------------- The well known causes of non-traumatic avascular (aseptic) necrosis are chronic corticosteriod therapy, alcoholism and hemoglobinopathies.
Pt presents with progressive hip pain w/o restriction of motion and normal Xray.
MRI is the gold standard. |
|
|
Thyroid cancer with worst prognosis? |
Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer |
|
|
Thyroid cancer that arises from parafollicular C-cells? |
Medullary Thyroid Cancer ------------------------------------------------- Seen in MEN 2a and MEN 2b |
|
|
Most common thyroid malignancy? |
Papillary Thyroid cancer |
|
|
Most common cause of otitis externa? |
Pseudomonas |
|
|
A patient has hypoglycemia, high insulin levels, and low C-peptide.
Diagnosis? |
Exogenous Insulin Use |
|
|
A patient has hypoglycemia, high insulin, and high C-peptide levels
Diagnosis? |
Insulinoma (Beta-cell Tumor)
------------------------------------------------------------------- Insulin pruduced by the body has C-peptide cleaved off of it. As a result, C-peptide levels increase as the body makes and uses more insulin.
Exogenous insulin DOES NOT have a c-peptide to be cleaved. C-peptide will be low with exogenous insulin use |
|
|
Klumpke's Palsy affects which nerves? |
C8 and T1
----------------------------------------------------------------- "Claw" hand and forearm supination
-Horner's Syndrome due to sympathetic damage to C8 and T1
|
|
|
What is Ludwig's Angina? |
Potentially life-threatening cellulitis or connective tissue infection, of the floor of the mouth, usually occurring in adults with concomitant dental infections.
An infection of submandibular and sublingual glands and source of infection is most often the 2nd or 3rd mandibular molar.
Pt presents with inflamed mouth, drooling and fever and dysphagia. Infection can spread to pharynx or tongue and cause death by asphyxiation
Tx is IV penicillin with anaerobic coverage. |
|
|
What is occuring in patients with Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria? |
The cell membrane anchor protein GP1 is abnormal. This prevents the binding of cell surface molecules such as CD55 and CD59, which normally help to inhibit destruction on RBCs.
RBCs without CD55 and CD59 are attacked by complement, which leads to hemolytic anemia that occurs in paroxysms.
Since RBC is more suseptable to hemolysis in acidic environment and serum is more acidic at night, lysis occurs at night and morning urine shows red urine
|
|
|
Best test for Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria? |
Flow cytometry
--------------------------------------------------------- Will show ↓ CD55 + CD59 on RBC surface (leads to hemolysis by complement during sleep)
Other tests not as heavily favored: - Sugar Water Test
-Acidified Hemolysis test (HAM test; checks whether red blood cells become more fragile when they are placed in mild acid), |
|
|
Asbestos exposure increases the risk of what cancer? |
Bronchogenic Carcinoma
(NOT MESOTHELIOMA)
-------------------------------------------------------- -risk is increased 59 fold with smoking |
|
|
Lung biopsy shoes (+) ferrungious bodies that stain with Prussian Blue |
Asbestos Fibers
--------------------------------------------------------------------- -Get coated with protein and iron --> (+) Prussian Blue |
|
|
Where do more than 90% of acutePulmonary embolisms come from? |
PROXIMAL Deep Veins of the Lower Extremity
(Popliteal, Iliac, Femoral veins)
----------------------------------------------------------- -these are above the knee |
|
|
Pulmonary Embolisms that arise from the renal veins are most likely to be seen in patients with _____________ syndrome |
Nephrotic Syndrome |
|
|
Patient presents with:
-Pelvic fracture
-Blood in the urethral meatus
-Inability to urinate and suprapubic pain
-Scrotal pain and swelling
- High-riding prostate |
Posterior Urethral injury
(Prosatic and Membranous urethra)
------------------------------------------------------------------- Commonly associated with pelvic fractures
|
|
|
Patient presents with:
- Straddle Injury
- Painful perineal hematoma
- Inability to urinate
-Blood in urethral meatus
- Normal prostate |
Anterior Urethral Injury
|
|
|
LH vs. FSH in PCOS |
↑ LH
↓ FSH
-------------------------------------------------------------------
Excess LH stimulates ↑ androgen production by ovarian theca cells resulting in hirsutism, male estucheon, acne and androgenic alopecia.
Anovulation is caused by LH/FSH imbalance and insulin resistance! |
|
|
Common nerve problem following removal of a parotid gland tumor? |
Facial Nerve (CN VII) palsy --> facial droop
--------------------------------------------------------------------- The 2 lobes of the parotid gland are separated by the facial nerve. |
|
|
A patient presents with flushing and feelings of warmth, valvular heart disease and diarrhea.
Abdominal exam shows hepatosplenomegaly.
Urine analysis shows ↑5-HIAA |
Carcinoid Syndrome
----------------------------------------------------------------- Seen when a carcinoid tumor metastasizes to liver
Carcinoid tumors secrete serotonin. 5-HIAA, is a serotonin metabolite.
|
|
|
A mother brings a 2 week old child in for "noisy breathing". It is loudest when the child is lying supine or crying
It dimishes when the child is prone.
Laryngoscopy shows collapse of supraglottic structures with inspiration and an omega-shaped eppiglotis
What is the diagnosis? |
Laryngomalacia
---------------------------------------------------------- -Very common condition of infancy, in which the soft, immature cartilage of the upper larynx collapses inward during inhalation. Increased laxity of supraglottic structures
-Worse when supine or crying, better when prone
- Begins in neonatal period, peaks at 4-8 months, resolves by 8-12 months
-Reassurance is indicated for most cases. Never feed baby while lying down
-Severe cases may need a Supraglottoplasty (poor weight gain, apnea, cyanosis) |
|
|
Treatmeant for an infant born with Transposition of the great vessels? |
Prostaglandin E --> Maintains patency of ductus arteriosis |
|
|
Patients with Wolf-Parkinson-White syndrome who develop atrial fibrillation should be treated with cardioversion or antiarrythmics like __________ |
Procainamide
-----------------------------------------------------------------
AV nodal blockers used in A-fib include: Beta-blockers, CCBs, digoxin and adenosine
These are CONTRAINDICATED IN WPW because they cause increased conductance through accessory pathway |
|
|
HY Where is the most common site of ulnar nerve entrapment? |
Elbow (Where ulnar nerve lies at epicondylar groove)
------------------------------------------------------------------ Decreased sensation of 4th and 5th digits
Weak Handgrip from weakened interosseous hand muscles |
|
Most common cause of bright red, firm, friable nodules in an HIV patient? |
Bacillary Angiomatosis
-------------------------------------------------------- caused by Bartonella, gram (-) bacillus
Tx: Erythromycin |
|
|
Nodular and papilar cutaneous lesions of the external auditory meatus in a patient with HIV |
Pneumocystis jirovecci (extrapulmonary)
------------------------------------------------------ Tx: TMP-SMX |
|
|
You suspect a patient has SLE. You confirm with (+) anti-DS antibodies.
What test should you order next? |
Renal biopsy |
|
|
Antihistone antibodies suggest __________? |
Drug induced lupus |
|
|
24 year old male has severe hypertension (180/110), headaches, epistaxis, and evidence of LVH on EKG. |
Suspect Coarctation of Aorta
------------------------------------------------------------------ -Check BP in upper and lower extremities * if BP higher in arms --> get an ECHO to diagnose |
|
|
Nephrotic syndrome (proteinuria, hypoabluminemia and edema) is a well known complication of Hodgkin's Disease.
It is usually caused by _______________ |
Minimal Change Disease |
|
|
After stabilizing a patient who has ingested caustic acid, what is the next best step? |
Endoscopy
-----------------------------------------------------------------
Needs to be done within 24 hrs.
Remember to remove clothes as well |
|
|
A patient with a past history of IV drug use and endocarditis presents with Right arm weakness, a drooping right lower face, and a (+) extensor plantar reflex on the right side.
What caused his symptoms? |
Septic Emboli from infected heart valve |
|
|
A woman presents for a PPD test reading. She has 12mm induration.
She has never had Tuburculosis. Never traveled outside the U.S., is not a healthcare worker, and has never been incarcerated.
Next Step? |
No intervention necessary
-------------------------------------------------------------------- Healthy Individuals with no h/o TB are not treated unless induration is >15mm
Healthcare workers, prison workers/prisoners, Diabetes, Children under 4, Recent immigrants leukemia patients require no treatment unless induration is > 10mm
HIV (+), recent TB contacts, Organ transplant recipients and patients with Nodular or Fibrotic chest x-ray findings do not require treatment unless induration >5mm |
|
|
Blood tests show:
↑ Mean corpuscular Hemoglobin Concentration
↑ Osmotic fragility on acified glycerol lysis test
Abnormal eosin-5-maleimide binding test |
Hereditary Spherocytosis (Autosomal-Dominant)
--------------------------------------------------------------------
Will also see (+) Spherocytes and (-)Coombs
Jaundice, Splenomegaly, Hemolytic Anemia |
|
|
Why has TB infection increased 10% since 1985? |
HIV Epidemic |
|
|
In hereditary spherocytosis, what gene is mutated? |
Ankryn gene --> leads to decreased spectrin |
|
|
Heart defect that occurs with a massive PE? |
Right Ventricular Dilation
--------------------------------------------------- Can also see: -new onset Right Bundle Branch Block -Right Axis Deviation
|
|
|
New onset Left Bundle Branch Block in a patient presenting with dyspnea, sweating and chest pain indicates ______________ |
Acute MI |
|
|
First-line drug for fibromyalgia? |
TCAs (Amitriptyline)
---------------------------------------------------------- Pregabalin, duloxetine and milnacipran can be used in patients not responding to TCAs
-Good Sleep hygiene and Aerobic excercise should be initiated first |
|
|
A 27 year old male presents with increased fastigue and weightloss
Chest X ray shows a mediastinal mass.
Bloodwork reveals and ↑ Beta-HCG and ↑ Alpha Feto protein. |
Nonseminomatous germ cell tumor |
|
|
Most common cause of elevated Alk Phos in an asymptomatic patient? |
Paget's Disease of Bone (osteitis deformans) |
|
|
Tumors to which area of the brain cause ipsilateral ataxia, nystagmus, intention tremors and loss of coordination. |
Cerebellar Tumors
-------------------------------------------------------------- With Ataxia, patient falls TOWARD the side of the lesion. |
|
|
What is pulsus paradoxus? |
Fall in systemic BP >10mmHg during inspiration
Commonly seen in cardiac tamponade |
|
|
This systolic murmur increases with standing |
HOCM |
|
|
How does the colon look in a patient with IBS? |
Completely Normal! |
|
|
Crypt Abscesses are seen in _______ |
Ulcerative Colitis |
|
|
How does the A-a gradient look in a patient with a Pulmonary Embolism? |
↑ A-a gradient in all instances of HYPOXIA |
|
|
25 year old patient comes in with a deep wound from a rusty piece of tin.
Last tetanus shot was 12 years ago.
Do you give Tetanus toxoid, tetanus immunoglobulin, or both? |
Tetanus toxiod
|
|
|
Painless, monocular vesion loss. Fundoscopic exam shows optic disc swelling, retinal hemorrhage, dilated veins and cotton wool spots |
Central Retinal Vein Occlusion
--------------------------------------------------------------------- DDX: Centreal Retinal Artery Occlusion -Sudden, painless loss of vision in one eye -Fundoscope shows pallor of optic disc, cherry red fovea, and "boxcar segmentation" of blood in retinal veins |
|
|
When do you use diagnostic peritoneal lavage in a suspected peritoneal hemorrhage? |
Used when a FAST exam is unequivocal or poor quality in a hemodynamically unstable patient
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
If the FAST U/S finds blood in the abdomen, next step is emergency laparotomy. DPL is not needed... |
|
|
CT shows acute pacreatitis in a patient with NO heavy alcohol consumption. What is the next best step? |
RUQ Ultrasound
----------------------------------------------------------------------- Acute pancreatitis is most commonly caused by heavy alcohol intake and gallstones. In the absence of heavy alcohol, a RUQ ultrasound is needed to look for gallstones since CT is poor at visualizing them |
|
|
Most useful intervention for patients with peripheral artery disease and claudication? |
EXCERCISE
------------------------------------------------------------------ Aspirin can be added to limit risk of MI, stroke, and cardiovascular mortality. Aspirin has no effect on the claudication. |
|
|
Recurrent pneumonia calls for what study? |
Chest CT --> Especially in smokers
--------------------------------------------------------------------- Peripheral Lesion --> CT guided needle Bx
Central Lesion --> Bronchoscopy |
|
|
Quad screen results expected for Down Syndrome?
B-HCG, MSAFP, Estriol, Inhibin A
(pg 263 SU2U) |
B-HCG: increased
MSAFP: decreased
Estriol: decreased
Inhibin A: increased
----------------------------------------------------------------- New Test in 1st Trimester = Full Integrated Test - Shows Decreased PAPP-A, High BCHG, Increased Nuchal translucency |
|
|
Nuchal translucency findings for:
Trisomy 21:
Trisomy 18:
Trisomy 13: |
Trisomy 21: ↑
Trisomy 18: ↑
Trisomy 13: ↓ |
|
|
Times you should take Sildenafil and 𝞪-blockers? |
Take them at least 4 hours apart |
|
|
Periodic epigastric pain that is relieved by meals |
Duodenal Ulcer |
|
|
Patient has abdominal pain for 2 months that is worse at night while lying down.
Food intake does not improve pain and he has experienced a 10lb weight loss from anorexia. |
Pancreatic Cancer
-------------------------------------------------------------- -Smoking History - Jaundice --> common bile duct obstruction -Migratory thrombophlebitis --> Trousseau Sign |
|
|
Gold standard test to confirm Duchenne MD? |
Genetic Testing
-------------------------------------------------------------------- Muscle Biopsy is not gold standard for confirmation. -may show fatty infiltration and fibrosis of the calf muscle. Immunostaining shows ABSENT DYSTROPHIN
Serum CPK and Aldolase levels are elevated in serum screening studies |
|
|
Most common cause of osteomyelitis in both infants and children? |
Staph aureus
------------------------------------------------------------ Other common causes: GBBS + E. coli in infants Strep pyogenes in children |
|
|
Most common cause of thyroid nodules? |
Colloid nodule
--------------------------------------------------------------- 2nd most common: Follicular Adenoma |
|
|
Acute cholecystitis in an elderly, diabetic male
US shows no gallstones, but a gallbladder with air fluid-levels |
Emphysematous Cholecystitis
----------------------------------------------------------------- - Clostridium, E. Coli, Staph, Strep Pseudomonas, Klebsiella all form gases and can cause this presentation.
-May have crepitus on palpation above the gallbladder |
|
|
Tea and toast diet produces a deficiency of _______ |
Folic Acid
--------------------------------------------------------------------
- Folic acid is heat-sensitive, so cooked foods decrease folic acid
- Stores can come depleted in 4-5 months
-Causes macrocytic anemia |
|
|
Succinylcholine is contraindicated in patients presenting with what metabolic problem? |
Hyperkalemia
-------------------------------------------------
-Succinylcholine can cause signifcant K+ release and life threatening arrythmias
-Crush patients, patients with demyelinating syndromes (Guillan-Barre) and patients with tumor-lysis syndrome should be given vecuronium or rocuronium instead |
|
|
Scoring system used to determine if patients with new-onset A-fib should be on Anti-coagulants? |
CHADS2 Scoring System |
|
|
New drug used for anticoagulation in patients with A-fib? |
DABIGATRAN (Pradaxa) |
|
|
A patient is presenting with symptoms highly suggestive of bacterial meningitis.
LP confirms this. You decide to start empiric therapy while waiting on the culture.
Along with Empiric antibiotics, what else should you give while waiting for the culture? |
Dexamethasone (Corticosteroid)
-------------------------------------------------------------------
Discontinue if cultures r/o Strep. pneumoniae |
|
|
Bug that likes to infect burn victims? |
Pseudomonas
------------------------------------------------------------------ Gram (-) , aerobic coccobacillus.
It is citrate, catalase, and oxidase positive
[Burn victims can also be infected with Staph a.] |
|
|
A patient on warfarin is experiencing an intracranial bleed confirmed on CT.
Her INR is 4. What is the next best step? |
Fresh Frozen Plasma
------------------------------------------------------------------ -FFP offers the fastest reversal of warfarin anticoagulation.
-Works almost immediately and lasts a few hours |
|
|
What do you give for a heparin overdose? |
protamine sulfate |
|
|
What do you give for a warfarin overdose with no acute bleeding? |
Vitamin K
------------------------------------------------------------- If patient is bleeding, give fresh frozen plasma it counteracts warfarin much quicker. |
|
|
Baby is born with hypoplasia of fingers and toes. Also has Microcephaly, hirsutism, and a cleft palate |
Fetal Hydantoin Syndrome (Anticonvulsants, typically Phenytoin)
----------------------------------------------------------------- Phenytoin and Carbamazapine are causes.
Carbamazapine (and Valproate) cause neural tube defects! |
|
|
Acid-base disorder most likely seen in CHF exacerbation? |
Respiratory Alkalosis
-CHF exacerbation can cause tachypnea as LV dyfunction allows fluids to pool in the lungs. This leads to pleural effusion and hypoxia.
-Tachypnea causes hypocapnia --> Resp. Alkalosis |
|
|
Best treatment for a premature infant with respiratory distress syndrome? |
Continuous Positive Pressure Ventilation |
|
|
Mother brings a 4-month old infant in who has been spitting up more frequently after breastfeeding. Yesterday, he also had a bloody stool.
Vital signs and physical exam are normal. Stool is positive for blood.
What is the best treatment? |
Elimination of Dairy and Soy from Maternal Diet
-------------------------------------------------
Milk or Soy-protein induced proctocolitis: - baby has allergy to either soy or milk proteins
- Non-IgE mediated inflammatory resoponse to either maternal milk or formula
- (+) rectal and colonic inflammation
- Severe Vomiting/ Painless bloody stools
- Eczema may be present
-Breastfeeding encouraged if mom cuts out soy/dairy (Should clear up in 3 days). Some infants may need a hydrolyzed formula
- Self resolving after 1 year of age and child will probably not be allergic after then
|
|
|
What is the urine calcium creatinine clearance ratio in patients with Familial Hypocalciuric Hypercalcemia? |
< 0.01 calcium creatinine clearance ratio
-------------------------------------------------------------------- - Autosomal Dominant disorder caused by abnormal calcium receptors on the parathyroid and renal tubules
- Patients develop asymptomatic hypercalcemia but have high-normal to borderline PTH levels.
- In contrast to patients with primary hyperparathyroidism, patients with FHH tend to very low levels of urinary calcium. The defective receptors cause excess Ca++ resorption.
- Hypercalcemia is benign and does not need treated
- Calcium Creatinine clearance in Primary Parahyperthyroidism is normally >.02 |
|
|
Eye symptom that can present in patients with Sarcoidosis? |
Uveitis (Most commonly, ANTERIOR UVEITIS) |
|
|
Treatment for an amebic liver abscess? |
Metronidazole
---------------------------------------------------------------- Try drugs first! DO NOT ASPIRATE!
DDX: Echinoccocal Hydatid Cyst -Solitary liver lesion - Sheep farmers/dogs
DO NOT ASPIRATE --> Anaphylaxis or seeding
|
|
|
A 24 year old G1P0 at 35 weeks presents with lower abdominal pain. She states she is having contractions. They are short and irregular.
Exam shows a posterior and closed cervix. U/S shows a fetus with gestational age of 35 weeks in the vertex position. Fetal heart tones are heard
Her symptoms improve after mild sedation.
Whats going on? |
False Labor ---> reassure and send her home
----------------------------------------------------------------- Short, irregular contractions without cervical changes. Contractions DO NOT increase in intensity
Common in the last 4-8 weeks of pregnancy |
|
|
Man complains of 3 months voluminous, greasy, foul-smelling stools that float on the top and are hard to flush. He has been having post-prandial epigastric pain after meals that radiates to the back.
He is thin and frail and faintly smells of alcohol.
Diagnosis? |
Chronic Pacreatitis
-------------------------------------------------------------------
He is experiencing steatorrhea, which occurs after the pancrease has lost 90% of its function and no longer releases enzymes
-Commonly seen in alcoholics
- Confirm with pancreatic function tests and monitor for steatorrhea (Sudan Stain, 72-hr collection) |
|
|
How does raising the cut-off point of a screening exam affect sensitivity and specificity? |
Sensitvity DECREASES
Specificity INCREASES
------------------------------------------------------------------ Increasing the cutoff point for a person to be diagnosed with the disease will result in fewer people testing positive.
Consequently, false and true positives will decrease and false and true negatives will increase |
|
|
Most patients with Paget's Disease of the breast have an underlying ___________________ |
adenocarcinoma |
|
|
How often should women ages 50-75 get mammograms? |
Every 2 years |
|
|
A 68 year old male presents with painless blue mottling of the skin on both of his feet. He is also experiencing some nausea and vomiting
He had a coronary angiogram and coronary stent placement 5 days ago and was discharged the day after the procedure.
Labs show acute renal failure with a creatinine of 3.0. He has an increased eosinophil count as well as decreased complement levels. |
Cholesterol Embolization
---------------------------------------------------------- Or Atheroembolic disease, follows surgical or manipulation of arterial tree (ie. Angiography), due to showering of cholesterol from aorta or other major arteries. Its mc seen in elderly pt with evidence of diffused Atherosclerotic dis..
-Renal failure, Livedo reticularis, systemic eosinophilia, and low complement levels, should make you think of this. Physical exam shows painless, reddish blue mottling of the skin of the extremities (livedo reticularis)
Tx is conservative, antocoags should be stopped since it may prevent healing of the ruptured plaque. |
|
|
What is the most effective intervention for newly diagnosed Stage I Hypertension in obese patients? |
Weight loss
5-20 mmHg per 10-kg loss
---------------------------------------------------------------------- For patients with a normal BMI, DASH Diet is most effective |
|
|
A patient presents with dyspnea and cough, weight loss, easy fatigability, hypercalcemia and a right hilar lung mass on chest x-ray |
Small Cell Lung Cancer
------------------------------------------------------------------ -presents as a hilar mass
- Parathyroid Hormone-related peptide (PTHrP) causes hypercalcemia by binding to PTH receptors and causes increased bone resorption from the bones and increased resorption in the distal tubule of the kindeys. |
|
|
What is the lactic acid level like in patients with CO-poisoning from smoke inhalation? |
Lactic Acid is INCREASED
-Anion-Gap Metabolic Acidosis -------------------------------------------------------------------- -- Carbon Monoxide poisoning can present with metabolic acidosis d/t tissue hypoxia!! - on ABG…PaO2 is usually NORMAL because oxygen diffusion is not affected ----------------------------------------------------- - CO binds to Hb with 260x more affinity than O2
-CO displaces O2 from Hb and causes a left shift in the oxygen dissociation curve from sigmoid to asymptoic
- This shift in Oxygen dissociation blocks the unloading of O2 from Hb in distal tissues. The result is tissue hypoxemia and lactic acidosis
|
|
|
Most common metabolic condition associated with Thyroidectomy? |
Hypocalcemia from accidental Parathyroid removal
------------------------------------------------------------- Phosphorous will be ELEVATED!!! |
|
|
____________ is a condition tat classically affects new mothers that hold their infants with the thumb outstretched (ABducted/extended)
The ABductor pollicus longus and extensor pollicis brevis tendons are affected; passive stretch of these tendons ellicits pain. |
De Quervain Tenosynovitis
Patients have a (+) Finkelstein Test |
|
|
A 30 year old business executive presents for increased anxiety and palpitations when in crowded spaces. He travels frequently and has high stress levels at work.
He takes no medications and has a negative family history. He drinks alcohol ocassionally, but denies illicit drug or tobacco use.
The vital signs, heart and chest examinations are normal. The liver span is 8 cm and there is no hepatosplenomegaly. There is no cervical lymphadenopathy or skin rash.
Lab results show a platelet count of 80,000/uL
Peripheral smear confirms a reduced platelet count without clumping or malignant cells.
What is the next appropriate exam for this patient? |
Hepatitis C and HIV Screening
--------------------------------------------------------------
This patient's presentation of thrombocytopenia without anemia or leukopenia suggests Idopathic Thrombocytopenic Purpura (ITP)
Thrombocytopenia may be a presenting finding in 5-10% of people with HIV
Therefore, it is recommended that all patients with thrombocytopenia and otherwise normal cell counts are screened for HIV and Hep. C |
|
|
HY
A 45 year old male presents with period difficulty breathing and wheezing. He visited an ENT for nasal blockage and polyps recently. His past medical history is significant for unstable angina 5 months ago.
His current medicines are aspirin, diltiazem, and pravastatin. He does not use tobacco, alcohol or drugs. Vital signs are normal.
What is the most likely cause of this patient's complaints? |
Aspirin Sensitivity Syndrome
-------------------------------------------------------------- This is considered a "pseudo-allergic reaction" since blockage of the COX1/COX2 pathway causes arachodonic acid to be shunted into a 5-lipoxygenase pathway which results in ↑↑ Leukotrienes
The imbalance of prostaglandins and leukotrienes causes bronchoconstriction and nasal polyps in susceptible patients.
Tx: Avoid NSAIDs, Leukotriene inhibitors (-lukast's / zileutron)
|
|
|
Metabolic complication that may occur in patients with subarachinoid hemorrhage? |
HYPOnatremia
Cerebral Salt-wasting Syndrome: 1) Inappropriate release of vasopressin causes ↑H20 retention 2) ↑ atrial/brain natriuretic peptide causes cerebral salt wasting |
|
|
Serum BUN and Creatinine are normally _______ in pregnant patients |
Decreased
- ↑ in renal plasma flow and GFR |
|
|
A patient is hospitalized for an acute anterior wall MI and and was treated with thrombolytic therapy 4 days ago. Today, he is experiencing very similar chest pain and dyspnea.
Vitals are all holding stable and lungs are clear to auscultation. S1/S2 are heard with no clicks or rubs.
What test should you order to see if he is having another MI? |
CK-MB
-CK-MB levels normalize within 1-2 days
-Troponin T, the most sensitive marker for MI, takes longer to return to normal |
|
|
What virus can cause aplastic crisis in patients with hereditary spherocytosis? |
Parvo-B19 |
|
|
Gold standard test for HIV in a child less than 18 months old? |
PCR |
|
|
When do you do HIV testing for high-risk pregnant women?
(IV drug use/Multiple sexual partners) |
1st Trimester and 3rd Trimester
---------------------------------------------------------------------- Remember, there is a "window period" where HIV viral loads will be high, but anti-envelope antibodies will be low. IT TAKES 3 MONTHS FOR ANTIBODIES TO BE PRESENT |
|
|
Syndrome that carries an increased risk for male breast cancer? |
Klinefelter Syndrome (XXY) |
|
|
Rhomboid, positively birefringent crystals on joint aspiration |
Pseudogout (calcium pyophosphate dehydrate crystals)
--------------------------------------------------------------- - occurs from sites of chondrocalcinosis (calcification of articular cartilage) into joint space
-Often occurs in the setting of recent surgery or medical illness
Positive birefringent = crystals are blue when aligned parallel with the slow ray of the compensator (yellow when perpendicular) ------------------------------------------------------------- Gout: Uric acid Crystals -Needle shaped, negatively birefringent (yellow) |
|
|
MEN Syndromes:
Pituitary Parathyroid (hypercalcemia) Pancreas (Hypergastrinemia leads to recurrent peptic ulcers = ZES)
(pg 125 SUS2)
|
MEN I |
|
|
MEN Syndrome:
Hyperparathyroidism Thyroid medulary carcinoma Pheochromocytoma
(pg 125 SUS2) |
Men IIa
------------------------------------------------------------ Medullary Thyroid Cancer: ↑ calcitonin, RET-Pro oncogene
Pheochromocytoma: ↑ urinary metanepharines
Total Thyroidectomy is recommended |
|
|
MEN Syndrome:
-Thyroid medulary cancer -Pheochromocytoma -oral/intestinal mucosal neuromas -Marfanoid habitus
(pg 125 SUS2)
|
MEN IIb
------------------------------------------------------------ Medullary Thyroid Cancer: ↑ calcitonin, RET-Pro oncogene
Pheochromocytoma: ↑ urinary metanepharines
Mucosal Neuromas: Tongue, GI tract
|
|
|
Murmur heard in acute aortic dissection? |
Aortic regurgitation (decrescendo diastolic murmur best heard on R) |
|
|
Best method to dx Aortic Dissection in a patient with Kidney disease? |
TEE
---------------------------------------------------------------- -Normally a CT w/ contrast could be used but is not recommended in patients with kidney disease |
|
|
Screening test for patients with suspected C. diff ? |
Stool studies for C. diff toxin (Cytotoxin B/ Enterotoxin A) |
|
|
A 25 yr old patient presents with mono-nucleosis type symptoms for 2 weeks. He lacks pharyngitis or cervical adenopathy. He does have splenomegaly.
Heterophile antibody test is negative. Smear shows a lymphocyte predominance but the lymphocytes have an atypical appearance |
CMV-Mononucleosis |
|
|
Acid Base Disorder that is commonly seen in patients infected with TB from an endemic area? |
Hyperkalemic, Normal Anion Gap Metabolic Acidosis
------------------------------------------------------------------- So, patients from endemic areas are more likely to have extra-pulmonary infections including of the adrenal gland. This creates an adrenal insufficiency (Addison Syndrome)
There is ↓ Cortisol, ↓ Adrenal Sex Hormones and ↓ Aldosterone
Aldosterone normally acts on the distal tubules to increase sodium reabsorption (saves sodium) and excrete K+ and H+ ions
If there is ↓ Aldosterone, sodium will be lost and K+ and H+ will be retained --> metabolic acidosis |
|
|
What can be given prophylactically to reduce the chance on pregnancy loss in a mother with antiphospholipid antibody syndrome? |
Low dose aspirin and Low-molecular weight Heparin
---------------------------------------------------------------- May see a false positve VDRL for syphilis |
|
|
A patient being treated for TB with isoniazid, rifampin, ethambutol and pyrazinamide presents with fatigue.
Blood tests show anemia with Elevated serum iron and a low TBIC.
You suspect the anemia is a side effect from isoniazid use and determine that the patient is deifcient in ___________________ |
Pyridoxine (B6)
------------------------------------------------------------------- -This is sideroblastic anemia
There is efective heme synthesis, most commonly due to pyridoxine-dependent impairment in early steps of protoporphrin synthesis.
Isoniazid is a well known pyridoxine antagonist |
|
|
25 year old patient, lower back pain worse at night and upon waking. Improves with movement throughout the day.
No rash, (-) straight leg test
(+) HLA-B27 |
Ankylosing Spondylitis
------------------------------------------------------------------- involves apophyseal joints (facet) joints
- may see anterior uveitis, enthesitis, hip or buttock pain
Other HLA-B27 (+) Arthritites: - psoriatic arthritis - reactice arthritis - arthritis with IBD |
|
|
Infective endocarditis following a dental procedure is most likely caused by what bug? |
Strep viridans Group - S. sanguinis - S. mitis - S. oralis - S. mutans - S. sobrinus - S. milleri |
|
|
Patients treated with high doses of Trimethoprim (eg, TMP-SMX for Pneumocystis jirovecci) have to be monitored for changes in __________________ |
Potassium --> HYPERkalemia |
|
|
DOC to treat Gestational DM? |
Insulin
-------------------------------------------------------------------- - Give insulin AFTER dietary changes have failed |
|
|
What causes a decreased O2 saturation in a patient with lung conolidation who is lying laterally on the side of the diseased lung? |
Physiologic Shunting
------------------------------------------------------------------- Lying with the affected lung down causes more ventilation/perfusion on that lung. Since there is consolidation in the left lung in this patient, deoxygenated blood is being shunted to the heart because gas exhange cannot occur in a consolidated area of lung |
|
|
Pneumocystis pneumonia occurs in AIDS patients with a CD4 count less than _________ |
CD4 < 200
------------------------------------------------------------------ Treat with TMP-SMX
Add a corticosteroid if PaO2 < 70mm Hg, or A-a gradiant > 35mm Hg |
|
|
Treatment for a patient with symptomatic bradycardia? |
Atropine
if that doesn't work
Transcutaneous Pacing |
|
|
Patients with PCOS have increased FSH or LH? |
LH |
|
|
What does respiratory alkalosis do to calcium levels? |
Decreased Calcium Levels
------------------------------------------------------------------- Increased extracellular pH causes an increased affinity of albumin binding to calcium |
|
|
Diaphragmatic irritation can cause the Kehr sign (Rupture/Bleeding spleen/blood in the abdomen).
What is the Kehr sign? |
Pain radiating to the Left Shoulder |
|
|
________ presents as a sudden loss of vision with floaters. Fundoscopic exam is obscurred and blurry. It occurs in patients with diabetic neuropathy. |
Vitreous Hemorrhage |
|
|
OCP use causes a reduction in risk of what cancers? |
Endometrial and ovarian cancer |
|
|
_______________is an uncommon benign liver tumor which is associated with the use of hormonal contraception with a high estrogen content |
Hepatocellular Adenoma
-------------------------------------------------------------------- - Frequently asymptomatic and untreated. May regress after stopping OCP or pregnancy.
DO NOT BIOPSY.. They will bleed a ton |
|
|
Microcytic anemia in a child with a RDW >20% |
Iron-deficiency Anemia --------------------------------------------------------------- - Associated with increased cow's milk intake
Thalassemias -Differentiate from 𝞫/𝞪 thalassemia using RDW. RDW in thalassemias is NORMAL
- Thalassemias will have normal/increased iron & ferritin
-Thalassemias has target cells
- Elevated Hb A2 on electrophoresis with 𝞫 thalassemia |
|
|
Treatment for thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP)? |
Plasmapheresis (Plasma Exchange) |
|
|
What is the gold-standard test for Strep. Throat? |
Throat Culture
----------------------------------------------------------------- -Rapid Strep Tests have a high specificity, but limited sensitivity. So (+) RSATs need to e followed by a throat culture |
|
|
A young boy is diagnosed with mumps. His parotid glands are swollen.
What other organ is the mumps virus most likely to affect? |
Testes (Orchitis)
-------------------------------------------------------------------- Since normally the infection isn't bilateral, infertility isnt a huge concern.
Treat parotids and testes with cold compresses. All other treatment is supportive |
|
|
A 23 year old mother at 39 weeks gestation presents with a painful vesicular "bump" on her vulva.
She is 2 cm dilated and the cervix is 50% effaced.
What is the next step in her treatment? |
Immediate C-section
----------------------------------------------------------------- - HSV in an infant can be fatal and neonates who are exposed through vaginal delivery are at greater risk. |
|
|
Which liver diseases are reversible with cessation of alcohol? |
1. Fatty Liver
2. Alcoholic Hepatitis 3. Early Fibrosis of the liver --------------------------------------------------------------------- Cirrhosis (with regnerative nodules) is irreversible |
|
|
What drug is given as prophylaxis against Mycobacterium avium complex in AIDS patients with a CD4 count < 50? |
Azithromycin
-------------------------------------------------------- In patients with MAC, treat with Clarithromycin + Ethambutol |
|
|
Treatment of choice for Dressler Syndrome? |
NSAIDs (Aspirin 1st, then Ibuprofen if ASA ineffective) --------------------------------------------------------------------
Dressler Syndrome: post-MI Pericarditis (immune-mediated)
-Peak occurence is 2-4 weeks after MI
- Non-specific/DIFFUSE ST elevation in most leads (classic in any pericarditis!!) with PR depression in certain leads.
Signs: pericardial & pleural friction rub, chest pain that’s worsened by leaning forward.
|
|
|
Which portion of the spine is RA most likely to affect? |
Cervical Spine→subluxation→cord compression |
|
|
How do anticholinergics and H1-Antihistamines (diphenhydramine) cause urine retention? |
Detrusor muscle inactivity |
|
|
Empiric ABX therapy for patients who are febrile and neutropenic? |
ceftazidime (3rd generation) or cefepime (4th generation)
--------------------------------------------------------------------
These cephalosporins cover G(+), G(-) and pseudomonas! |
|
|
What is mitral regurgitation's effect on the Left atrium? |
Increased Left Atrial Pressure |
|
|
A breastfeeding mother wants contraception for 1 year until she is ready to concieve again. What is the best option? |
Progestins
-combined OCPs have estrogen which can 1) decrease lactation 2) Cross into the breast milk and affect baby
-------------------------------------------------------------- -IUDs - Copper/Progestin are an option for someone looking for longer protection |
|
|
What is the most important goal of managing a patient with rib fractures in the hospital/ED? |
Pain management
------------------------------------------------------------------- -Allows for proper ventilation and reduces risk of atelectasis!! |
|
|
Newborn infant, billous vomiting, mom using cocaine at birth, no bowel movement, not feeding anymore
Abdominal X-ray shows a "tripple bubble" and a gasless colon |
Jejunal Atresia ---------------------------------------------------------------- Presents with bilious emesis in a newborn infant. Poor feeding, dehydration, absent bowel movements since birth, small for gestational age.
Atresia of the jejunum or ileum is thought to occur d/t a vascular accident in utero --> necrosis and resorption of the fetal intestine, seals off and leaves behind proximal ends of intestine so that the duodenum ends in a blind pouch.
Risk factors: Vasoconstrictive medications or cocaine or tobacco use. In contrast to duodenal atresia (Down Syndrome), it is NOT ASSOCIATED WITH A CHROMOSOMAL ABNORMALITY
Abdominal x-ray shows a “triple bubble sign” and gasless colon. There is airtrapping in the stomach, duodenum and jejunum.
Treatment is with rescusitation and surgical correction |
|
|
Most common cause of orbital cellulitis?
|
Bacterial Sinusitis ----------------------------------------------------------------------
Patient will present with painful eye movements, proptosis, ophthalmoplegia, and diploplia... |
|
|
Patients with hemochromatosis are more susceptible to infections caused by _________________. |
Listeria monocytogenes
----------------------------------------------------------------
Iron overload is also a risk factor for Yersinia enterolitica and Vibrio vulnificus --> iron loving bugs |
|
|
HY What do you monitor in patients with Guillan-Barre to make sure they aren't having respiratory failure? |
Vital Capacity |
|
|
Best study to find Squamous cell cancer source in a patient with a (+) SCC biopsy of cervical node? |
Panendoscopy
----------------------------------------------------------------- esophagoscopy +laryngoscopy + bronchoscopy |
|
|
Describe breastfeeding jaundice |
Caused by breastfeeding failure (caused by maternal/infant factors)
Presents as jaundice in the 1st week of life
Results in: Decreased bilirubin elimination, increased enterohepatic circulation, failure to gain weight, dehydration
Maternal factors = inadequate milk supply, cracked/clogged nipples, engorgement, infrequent feeding
Infant factors = poor latch, ineffective suck, falling asleep
Dehydration may show brick red urate crystals in diaper, too few wet diapers.
Treatment: Breastfeed 15 mins per side, every 2-3 hours
Supplementation to a cow’s milk formula if there are failed breastfeeding attempts |
|
|
Best imaging modality for sinus and periorbital edema? |
CT |
|
|
Treatment for NMS? |
Dantrolene > Bromocriptine > Amantadine |
|
|
Most common ear pathology scene in patients with AIDS? |
Serous Otitis Media (non-infectious effusion)
|
|
|
Best study to determine incidence? |
Cohort |
|
|
Best study to determine odds ratio? |
Case-control |
|
|
Best study to determine disease prevalance at a given time? |
cross-sectional |
|
|
Gram (+), branching filaments, oral/buccal mass that is painless, extends forming an absces, fistula and sinus tract oozing yellow "sulphur granules" |
Actinomyces Israeli
----------------------------------------- Tx: High-dose penicillin for 12 days |
|
|
DOC for Actinomyces israeli? |
High-dose penicillin for 12 days |
|
|
UTI with urine pH of 8.5 |
Proteus mirabilis
----------------------------------------------------------- Excretes urease which turns urea into ammonium and alkalizes the urine!
- Forms Staghorn Calculi (Struvite Stones) along with Klebsiella, Morganella and Pseudomonas
|
|
|
Brain MRI on elderly patient with dementia shows cortical and subcortical atrophy in the temporal and parietal lobes |
Alzheimers |
|
|
A patient gets chemicals in his eye. What should he do? |
No matter the chemical, he should continuously flush the eye for 15 min before seeking medical attention. |
|
|
What should a patient do if they have a cut/scratch/foreign body in their eye |
Seek medical attention. Do not flush it first. |
|
|
What are ACTH levels like in Addison's Disease (Primary Adrenal Insufficiency)? |
Increased ACTH
Cortisol and Aldosterone will be LOW due to autoimmune destruction of adrenal cortices
|
|
|
A patient presents with hypotension, increased skin pigmentation, HYPERkalemia, eosinophilia, ↓cortisol levels, and ↑↑↑ACTH levels |
Addison's Disease (Primary Adrenal Insufficiency)
----------------------------------------------------------------
***80% of pt have primary adrenal deficiency due to Autoimmune adrenalitis. These pts also present with autoimmune involvement of other glands as well, like thyroid, parathyroid, ovaries.
*** 70% of the Causes of Primary Adrenal Insufficiency autoimmune, mostly in developed countries. In underdeveloped countries TUBERCULOSIS, Fungal infection and CMV infection are the mcc, TB is the MCC in undeveloped countries.
Adrenal Calcification is a typical feature of TB PAI. Tx of TB does not result in normalization of adrenal gland.
PAI in HIV pt is common, mcc is CMV.
Sometimes Ketoconazole can cause it. PAI is very rare with adrenal tumor metastasis, even then calcification is not seen.
Pt presents with no rise in serum cortisol following injection of Cosyntropin (ACTH analog), CT shows calcification of adrenal glands.
|
|
|
Treatment for suspected Mycoplasma pneumoniae? |
Azithromycin or Levofloxacin or Moxifloxican |
|
|
Hydroceles that do not resolve spontaneously within 12 months put the patient at increased risk for _____________________ |
inguinal hernia |
|
|
A 47 year old female has just undergone a hysterectomy. In the post-op recovery room, she develops nausea, vomiting and acute abdominal pain. Her BP is 70/40.
Past medical history is significant for SLE, uterine fibroids, type 1 diabetes and chronic low back pain.
Meds are Insulin, prednisone, hydroxycholroquine and acetomeniphen.
Labs show: Na = 132 Potassium =5.1 Glucose = 50
What is causing this patient's condition? |
Acute Adrenal Insufficiency
Acute onset of nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain and hypoglycemia, hyponatremia, hyperkalemia andhypotension after a stressful event (surgery) in a pt who is steroid dependant is typical.
A clue is preoperative steroid use. Exogenous steroids depress pit-adrenal axis and a stressful situation can precipitate AAI.
Tx: Prevent with steroid dose before surgey "Stress dose" |
|
|
Aldosterone's effect on Potassium |
Aldosterone decreases potassium |
|
|
A previously unvaccinated nurse gets a needlestick when drawing blood from a patient with active Hepatitis B.
What measures should be taken? |
Hep. B Vaccination series as soon as possible And Hep. B immune Globulin immediately |
|
|
Active Hepatitis B infection:
HBsAg? HBeAg? Anti-Hbs? |
HBsAg (+) HBeAg (+) Anti-Hbs (-) |
|
|
Testicular Tumors:
In ____________, estrogen production is increased with inhibition of LH and FSH |
Leydig Cell Tumors ------------------------------------------------ Estrogen production is due to increased aromatase expression. Normally, Leydig cell tumors pump out lots of testosterone. |
|
|
_____________ is a chronic condition associated with pelvic pain worsened by bladder filling or sexual intercourse.
Accompanied by urinary frequency, urgency and nocturia.
Urinalysis is sometimes negative. |
Interstitial Cystitis |
|
|
Treatment of primary dysmenorrhea? |
NSAIDs
-------------------------------------------------------------------- Pt present with hx of lower abdominal pain, that radiates to upper thighs and back. The pain is colicky and starts a few hours prior to menses, lasting 3-4 days. It usually appears 6-12 months after menarche.
Tx is NSAID (1st) and also OCPs.
The pathology here is that menstural fluid has higher levels of prostaglandins (NSAID’s lower prostaglandin levels, so that’s why they are 1st line for dysmenorrhea!)
|
|
|
A patient in labor is being given magnesium sulfate to prevent an eclamptic episode.
She develops a respiratory rate of 9 breaths/min and hypoactive DTRs.
What's going on? How do you treat? |
Magnesium Sulfate Toxicity
Tx: Stop Mg Sulfate, start Calcium Gluconate
--------------------------------------------------------------------- Magnesium causes toxicty by acting as a CNS depressant and blocking neuromuscular transmission |
|
|
Howell-Jolly Bodies are seen post- ____________ |
splenectomy
(Nuclear inclusions in RBCs on Wright Stain) |
|
|
Race with a higher risk of Prostate Cancer? |
African Americans
|
|
|
UC vs. Chron's:
- 30% of patients have granulomatous inflammation |
Chron's |
|
|
Seborrheic Dermatitis is found with increased frequency in patients with what 2 diseases? |
Parkinson's and HIV
----------------------------------------------------------------- Erythematous plaques, with fine, loose, yellow and greasy-looking scales.
Pityrosporum ovale may play a role in pathogenesis. Treated with topical antifungals |
|
|
______________ is characterized by rosy hue with telangiectasia over the cheeks, nose and chin.
Flushing may occur due to hot drinks, heat, emotion. |
Rosacea |
|
|
MMR is a live vaccine. Can it be given to HIV patients? |
Yes! Make sure the CD4 count >200 |
|
|
Vaccines contraindicated in patients with HIV? |
Live Vaccines ------------------------------------------------------------------ BCG, anthrax, oral typhoid, intranasal influnza, oral polio, yellow fever |
|
|
A patient involved in an MVA has multiple bruises on his chest. He is given 4L of fluids and stabilized. 6 hours later, he complains of dyspnea, tachypnea and chst pain.
Chest Xray shows patchy, irregular alveolar infiltrates |
Pulmonary Contusion
Adding the fluids causes pulmonary edema which causes hypoxemia |
|
|
Best test to order for a pregnant patient with renal colic? |
Ultrasound |
|
|
Anemia:
familial, pancytopenia, brown pigmentation, cafe au lait, short stature, upper limb abnormality, skeletal abnormality, it starts with thrombocytopenia then neutropenia and then anemia. |
Fanconi Anemia |
|
|
Anemia:
congenital RBC aplasia presents in the first three months of life w pallor and poor feeding. WBC and platelet counts are normal |
Diamond-Blackfan Anemia |
|
|
Virus that can cause aplastic anemia? |
Parvo-B19 |
|
|
Small intesine biopsy shows foamy, PAS-positive macrophages in the lamina propria containing non-acid fast bacilli |
Whipple's Disease ---------------------------------------- Tropheryma whippelli gram (+) baccilus
caused by bacterium Tropheryma whippelli, affects men 30-60yo.
Presents with joint pain + abdominal pain + chronic foul smelling diarrhea + weight loss (malabsorption sx = Loss of Vit ADEK…so blurry vision d/t Vit A loss, etc).
PAS+, foamy macrophages containing a glycoprotein in intestine is Dx.
Also skin Hyperpigmentation. Untreated dz is fatal and progressive.
Tx is TMP-SMX (for 12 months!), penicillin G, or ceftriaxone.
*Dx is by PAS staining, it can be confirmed with upper GI endoscopy with biopsy of the small intestine.
***D-xylose absorption is abnormal in both Whipple and bacterial overgrowth. However, the test becomes normal after antibiotic tx.
(D-xylose absorption is a laboratory test to determine how well the intestines absorb a simple sugar (D-xylose)…it is abnormal in any disease process which damages the intestine mucosa. It’s abnormal in Celiac disease (sprue), Crohn's disease, Giardia Lamblia infestation, Hookworm infestation, Lymphatic obstruction, Radiation enteropathy, Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth, Viral gastroenteritis, & Whipple's disease; The test is normal in pancreatic insufficiency since there is a problem with fat absorption & there is no damage to the mucosa wall) |
|
|
Test you order in any child less than 24 months old with their first UTI |
Renal U/S
-------------------------------------------------------------------- Recurrent UTIs in Children: voiding cystourethrogram |
|
|
Drug for a patient presenting with aortic dissection? |
Labetalol
------------------------------------------------------------------ Beta-blockade decreases high BP and prevents reflex tachycardia that can increase shearing pressures on the aortic lumen |
|
|
Difference in type A and type B Aortic dissection? |
Type A: Ascending aorta --> surgery
Type B: Descending aorta --> Labetalol |
|
|
Best treatment for non-smoking patients with chronic cough and post-nasal drip for several months? |
Antihistamines (Chlorpeniramine)
------------------------------------------------------------- Post-nasal drip can cause a cough for a long time. Smokers need a chest x-ray if they've had a cough for that long! |
|
|
Best test to confirm osteonecrosis in a patient who has taken prednisone long-term? |
MRI |
|
|
Acute symmetrical joint pain in a daycare worker following 5 days of flu-like symptoms. The joints are not swollen or red. Non-specific rash on trunk. |
Parvo-virus B19 |
|
|
Most common cause of aortic regurgitation in developed countries? |
Bicuspid Aortic Valve
-------------------------------------------------------------------- Most common in undeveloped countries: Rhuematic Fever
The murmur of aortic regurgitation is best heard along the left sternal border at the 3rd and 4th intercostals. It may be heard in some patients by having patient sit up, lean forward, and hold breath in full expiration.
|
|
|
Electrolyte abnormality seen in multiple myeloma.
Causes severe constipation, anorexia, weakness, polyuria and neurologic symptoms (confusion/lethargy) |
Hypercalcemia |
|
|
________________ is a condition that is characterized by painless blisters, hypertrichosis, and hyperpigmentation.
It is often associated with Hepatitis C infection, and can be triggered by ingestion of ethanol or estrogens. |
Porphyria Cutanea tarda
Deficiency of uroporphryinogen decarboxylase
Elevated urinary porphyria confirms Dx.
Phlebotomy or Hydroxychloroquine provides releif.
|
|
|
Inital treatment choice for myasthenia gravis? |
Oral Anti-ACh (Pyridostigmine)
For complete remission consider thymectomy or immunosuppressive agents. |
|
|
Painful retinal keratitis and uveitis in patients with HIV is most likely caused by __________ |
HSV or VZV |
|
|
A patient is diagnosed with a HER2 breast cancer. Before starting treatment with Trastuzumab, what should you order? |
Echocardiogram ---> cardiac toxicity |
|
|
What do you do whe you suspect a VSD in a child less than 2 years old? |
Get an echocardiogram
-If it is a small VSD, normally it will close by age of 2
- Large/symptomatic VSDs need surgical correction |
|
|
DOC for Nocardiosis? |
TMP-SMX |
|
|
Morning stiffness greater than 30 mins is suggestive of ______________ |
Inflammatory Arthritis |
|
|
Increased gastric residual volume, vomiting and abdominal distension in a premature neonate are highly suspicious for _________.
Abdominal x-ray may show pneumatosis intestinalis (intramural air) and portal venous air. |
Necrotizing Enterocolitis |
|
|
HY
Most common side effect of erythropoetin therapy in patients with normochromic, normocytic anemia and chronic kidney failure? |
HYPERTENSION (30%)
--------------------------------------------- Headaches (15%)
Flu-like Symptoms (5%)
Red-cell aplasia (rare) |
|
|
Treatment with acyclovir can cause crystalloid nephropathy if ____________ is not provided |
adequate hydration |
|
|
Most common cause of secondary Hypertension in Chidren? |
Fibromuscular Dysplasia --> renal a. stenosis |
|
|
HY
Treatment for a woman presenting with Occipital headache, hypertension (long-standing), and a right sided renal bruit? |
Angioplasty with Stent
--------------------------------------------------------------- Fibromuscular Dysplasia
Pt presents with Occipital HA, HT and renal bruit, suggestive of renovascular HT due to Renal Artery Stenosis. The usual cause in youner pt (30) is FMD.
In older pt its atheroslcerotic plaques. Goal of tx is decrease BP and restore perfusion to kidneys. Interventional therapy is better than medical mgmnt alone, so Angioplasty with stent replacemnt is best tx. If it fails then Surgery is indicated.
ACEI are reserved for Elderly pts who are not good candidate for surgery. Remember ACEI are CI in bilateral renal stenosis.
- ACEI are the tx of choice for unilateral renal stenosis!
- DX = Angiography is BEST test to confirm renal artery stenosis…NOT US!! Get electrolyte levels!! "String of beads" pattern on Angiography
------------------------------------------------------------- Is the mcc of secondary HT in children. It responsible for 20% of the cases of renal HT. Its also seen in premenopausal women
PE shows a hum or bruit (soft to-and-fro bruit) in the right costovertebral angle due to well developed collaterals. The right renal artery is more affected than the left.
Angiography shows 'string of beads ' pattern in the renal artery****
|
|
|
____________ is more common in African Americans. It is generally asymptomatic in the initial stages, followed by a gradual loss of peripheral vision over a period of years and eventually, tunnel vision... |
Open-Angle Glaucoma |
|
|
Pancreatic cancer marked by SEVRE watery diarrhea? |
VIPoma |
|
|
Best diagnostic study for diverticulosis/itis? |
CT scan |
|
|
Leading risk factor for cerebral palsy? |
Prematurity |
|
|
Test to monitor LMWH (Enoxaparin)? |
antifactor Xa levels |
|
|
A normal A-a gradient is between ___ to ____ mm Hg |
5-15 mm Hg |
|
|
Conditions that cause a false-normal A-a gradient? |
Hypoventilation
High Altitude |
|
|
Patient has a high-pitched voice, throat pain, difficulty opening the mouth, and uvula deviation |
Peritonsillar Abscess
---------------------------------------------------- Uvula deviates away from abscess |
|
|
Drug of choice for most cases of bacterial Sinusitis? |
Amoxicillin
(2 weeks for acute) (6-12 weeks for chronic) |
|
|
Type of necrosis in TB? |
caseous necrosis |
|
|
Higher risk of this bug causing pneumonia in patients with COPD or Sickle Cell |
H. influenzae |
|
|
(+) cold agglutin test |
Mycoplasma pneumoniae |
|
|
Chest X-ray finds a solitary pulmonary nodule..
next step? |
Compare to older x-ray |
|
|
Common complication of Cystic Fibrosis in men? |
INFERTILITY -------------------------------------------------------- >95% of men with CF are infertile due to bilateral absence of vas deferens
- Accumulaiton of inspissated mucus causes failure of vas deferens development
If testes have descended, sperm cannot be ejaculated --> obstructive azoospermia
About 20% of women are infertile due to either uterine/vaginal aplasia or viscous cervical mucus |
|
|
Mechanical cause of infertility in men with Cystic fibrosis? |
>95% of men with CF are infertile due to bilateral absence of vas deferens
- Accumulaiton of inspissated mucus causes failure of vas deferens development
If testes have descended, sperm cannot be ejaculated --> obstructive azoospermia |
|
|
Study used to diagnose chronic pancreatitis? |
CT
Shows calcification of pancreas (can also be seen on X-ray) |
|
|
What form of tetanus prophylaxis should be given to a patient with a severe dirty wound and an unclear or incomplete vaccination history? |
Tetanus Toxoid + Tetanus IG
-----------------------------------------------------------------
Only tetanus toxoid needed for patients with severe or dirty wounds who recieved a booster more than 5 years ago, and those with minor clean wounds who recieved a booster more than 10 years ago |
|
|
Autosomal dominant disease defined by diffuse telangectasias, recurrent epistaxis, and wide-spread AV malformations.
|
Hereditary Telangectasia (Osler-Weber-Rendu)
-------------------------------------------------------
AVMs tend to occur in mucous membranes, skin and GI tract. Can also be present in the brain, liver and lungs!
AVMs in the lungs can cause a right to left shunt causing chronic hypoxia and polycythemia --> massive hemoptysis |
|
|
Portion of brain affected by HSV encephalitis? |
Temporal Lobe ---> necrosis
------------------------------------------------------------------- May present acutely (<1 week duration), characteristic CSF findings are ↑lymphocytes, ↑RBCs, ↑Protein.
HSV polymerase chain reaction analysis of CSF is gold standard |
|
|
Gold standard for diagnosing herpes encephalitis? |
PCR of HSV DNA in CSF |
|
|
Pregnancy hormone that causes normal respiratory alkalosis of pregnancy? |
Progesterone stimulates the respiratory centers in the brain to cause increased tidal volume, increased minute ventilation, increased PaO2, and chronic compensated respiratory alkalosis |
|
|
Right ventricular infarction occurs with ______ wall MI. It presents with hypotension. |
inferior wall MI |
|
|
What drug is indicated in Sickle Cell patients with frequent, acute, painful crisises? |
Hydroxyurea
Increases Fetal Hemoglobin (HbF) levels by stimulating erythropoeisis in primitave RBC pre-cursors.
Sickled Hb, is then proportionaly decreased resulting in reduced polymerization of RBCs and less instances of occlusion
It's dose limiting side effect is myelosuppression, but it is relatively safe |
|
|
MCC of croup (laryngotracheobronchitis)? |
Parainfluenza Virus -Types 1 and 2 |
|
|
MCC of Epiglottitis? |
H. influenzae type B |
|
|
MCC of Bronchiolitis? |
RSV |
|
|
upward lens dislocation |
Marfans |
|
|
downward lens dislocation |
Homocystinuria |
|
|
MOST COMMON consequence of cardiac malformation in Down Syndrome? |
Complete Atrioventricular Septal Defect (40%) -Heart failure within 6 months of age -Loud S2 d/t pulmonary hypertension
VSD (30%)
ASD (15%) |
|
|
Before placing a trauma victim on positive pressure mechanical ventilation, what should always be done in order to decrease the chance of circulatory collapse induced by the increased intrathoracic pressure of positive pressure mechanical ventilation? |
Volume Rescusitation
PPMV inreases intrathoracic pressure, which decreased venous return to the heart and thereby decreases ventricular preload.
In patients in hypovolemic shock, this may cause cirulatory collapse |
|
|
Most common site of metastais in colon cancer? |
The liver |
|
|
Live vaccines safe to give to HIV patients if CD4 count >200? |
- MMR -Varicella Zoster |
|
|
Most common causes of secondary digital clubbing? |
Lung malignancies, Cystic fibrosis, and Right-Left cardiac shunts
-------------------------------------------------------------------- COPD DOES NOT CAUSE CLUBBING --> if clubbing occurs you should look for malignancy |
|
|
MCC of Myocarditis? |
Coxsackie B Virus |
|
|
Haptoglobin levels in hemolytic anemias? |
Haptoglobin will be decreased
---------------------------------------------------------- Haptoglobin binds free Hb that is released from RBCs when they are destroyed. As more cells are destroyed, there is more free Hb in the plasma and Haptoglobin binds it up. As a result there is less free Haptoglobin |
|
|
Most SPECIFIC lab test is = anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide (anti-CCP) |
RA |
|
|
DOC for treatment-resistant Schizophrenia and schizophrenia assosciated with peristent suicidality? |
Clozapine |
|
|
You suspect a patient has acute pancreatitis. First test you should order? |
Serum Amylase and Lipase
----------------------------------------------------------------- Serum amylase rises within 6-12 hours and may remain for 3-5days
Serum lipases rises within 4-8 hours and remains elevated longer (8-14days) so it is more sensitive than amylase |
|
|
MC non-melanoma skin cancer? |
Basal Cell Carcinoma
-Second most common is Squamous Cell! |
|
|
Hospitalized patient has normal TSH, Normal T4 and Low T3
What is this? |
Sick Euthyroid Syndrome ("Low T3 Syndrome") |
|
|
Involves C1 inhibitor deficiency, dysfunction or destruction |
Angioedema
------------------------------------------------------------ Low C1 inhibitor --> increased C2b and Bradykinin (which produce edema) |
|
|
Patients with Ankylosing Spondylitis for 20 years or more are at an increased risk for _____________ |
vertebral fractures |
|
|
Effect of administering Lidocaine to a patient with head trauma before intubation? |
Blunt ICP increases |
|
|
Elevating the head of the bed, incentive spirometry, coughing and frequent ambulation all increase ________, which can decrease the chance of post-operative atelectasis |
Functional Reserve Capacity (FRC) |
|
|
Fetal monitoring shows Variable Decelerations |
Cord compression/prolapse, oligohydramnios
------------------------------------------------------------------- VEAL-CHOP Variable Decels--Cord compression/prolapse Early decels ----Head compression Accelerations ----- OK (normal fetal oxygenation) Late Decels ----- Placental Insufficiency |
|
|
Fetal monitoring shows Early Decelerations |
Cord Compression
-------------------------------------------------------------------- VEAL-CHOP Variable Decels--Cord compression/prolapse Early decels ----Head compression Accelerations ----- OK (normal fetal oxygenation) Late Decels ----- Placental Insufficiency |
|
|
Fetal monitoring shows Late Decelerations |
Placental insufficiency/Hypoxia/Acidosis
----------------------------------------------------------------- VEAL-CHOP Variable Decels--Cord compression/prolapse Early decels ----Head compression Accelerations ----- OK (normal fetal oxygenation) Late Decels ----- Placental Insufficiency |
|
|
Heinz bodies are seen in _____________? |
G6PD deficiency |
|
|
Howell-Jolly Bodies are seen in ___________? |
Sickle Cell Anemia/Asplenia |
|
|
A baby is born to a mother with an active Hepatitis B infection. What is the next best step? |
Administration of Hep. B immune globulin followed by Hepatitis B Vaccination |
|
|
A nonhealing, painless, bleeding ulcer associated with a chronic scar suggests ______________ |
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
-------------------------------------------------------------------- Biopsy (punch/shave/excisional) is next step |
|
|
Parkinsonism causes an accumulation of _____ within the neurons of the substantia nigra pars compacta, which ultimately leads to the death of these neurons |
alpha synuclein |
|
|
Best test to order for pancreatic carcinoma? |
Abdominal CT
----------------------------------------------------------------- CA 19-9 is more useful when evaluating post-op removal of pancreatic cancer |
|
|
Dementia that features visual hallucinations and motor features of Parkinsonism |
Lewy Body Dementia |
|
|
What's the other name for fronto-temporal dementia? |
Pick's Disease |
|
|
What are the only two treatments for COPD that LOWER MORTALITY? |
Smoking cessation and Home O2 Use |
|
|
Consequence of drinking alcohol while taking metronidazole? |
Disulfiram-like reaction |
|
|
DOC for Lyme disease in a child less than 8 years old? |
Amoxicillin or Cefuroxime
----------------------------------------------------------------- Doxyclycline is a tetracycline that is contraindicated in children less than 8 (bone growth, teeth defects) |
|
|
Immunodeficiency:
-Absence of pus formation at sites of infxn
- Delayed Umbilical Cord Separation (>30days)
- Poor wound healing
- Recurrent skin + mucosal infxn
- Peridontitis |
Leukocyte Adhesion Deficiency
--------------------------------------------------------------------- Deficient CD18, an essential component of integrins present on leukocytes.
Inabolity of leukpcytes to migrate to areas pf infection or inflammation.
Results in leukocytosis with a neutrophil predominance and complete absence of PMNs in inflamed or infected tissue |
|
|
DOC for acute, cervical adentitis classically caused by Strep or Staph infection? |
Clindamycin (+) Incision and Drainage |
|
|
In a patient with IBD and signs of sepsis, you need to rule out ________________ |
Toxic Megacolon
-------------------------------------------------- Get an abdominal x-ray |
|
|
Most common complication seen in patients with sickle cell trait? |
Painless hematuria |
|
|
HY _____________ is the most common type of spinocerebellar ataxia. It features a combination of neurologic (ataxia,dysarthria), skeletal (scoliosis, "hammer toes"), and cardiac (HCM) manifestations.
The most common causes of death are cardiomyopathy and respiratory complications |
Friedrich Ataxia
--------------------------------------------------------------- Autosomal recessive, symptoms begin before 22 years of age
Degeneration of spinal tracts: -Spinocerebellar -Posterior Columns -Pyramidal Tract |
|
|
Vitamin D Deficiency (malabsorption/diarrhea):
Calcium levels? Phosphorus levels? PTH levels? |
Low Calcium Low Phosporus High PTH
-------------------------------------------------------------------- Vitamin D deficiency d/t kidney failure: Low Calcium High PTH High Phosporus (kidneys can't remove) |
|
|
Congenital absence of GnRH secretion associated with anosmia |
Kallaman Syndrome |
|
|
Treatment of CMV esophagitis in patients with HIV? |
GANCYCLOVIR ----------------------------------------- Acyclovir is not useful against CMV as the virus does not encode thymidine kinase which activates Acyclovir
CMV Esophagitis - Severe pain - LINEAR ulcers on endoscopy
Presence of intranuclear and intracytoplasmic inclusions on biopsy
HSV Esophagitis If ulcers are caused by HSV (tx is Acyclovir) they are multiple, well circumscribed and look like volcanos, may be vesicular
|
|
|
Emperic treatment for esophagitis in an HIV patient? |
Fluconazole --> Candida
-Candida is the most common cause of HIV dysphagia
-----------------------------------------------------------------
If symptoms persist after fluconazole, must do an endoscopy to check for CMV (ganciclovir) or HSV (Acyclovir) ulcerative esophagitis |
|
|
Why would you see normal glucose-6-phosphatase levels in a patient with G6PD deficiency following a hemolytic episode? |
The RBCs that were G6PD deficient were hemolysed. Reticulocytes have normal G6PD and are abnormally high after an episode of hemolysis |
|
|
Renal vein thrombosis presents with sudden onset abdominal pain, fever and hematuria.
It is most likely to occur in this nephrotic syndrome. |
Membranous Glomerulonephritis |
|
|
DOC for in-patient treatment of Community acquired pneumonia? |
Levofloxacin or moxifoloxacin (newer -quinolones have better coverage of Strep. pneumo and atypical pneumonias than older -quinolones such as ciprofloxacin) |
|
|
DOC for outpatient treatment of community acquired pneumonia? |
Azithromycin or Doxycycline |
|
|
________ is a monoclonal antibody aainst RSV that is used for prophylaxis in children < 2 years who are at exceptionaly high risk of complications of RSV infection (bronchopulmonary dysplasia, prematurity, severe congenital heart dz) |
Pavlivizumab |
|
|
DOC to treat hairy cell leukemia? |
Cladribine |
|
|
There are two types of post-infectious glomerulonephritis. Which one normally arises within 5 days of an upper respiratory tract infeciton? |
IgA Nephropathy
-----------------------------------------------------------------
The other is poststreptococcal GN, which presents 10-21 days after upper respiratory infection. |
|
|
HY
Anticonvulsant drug that impairs the absorption of folic acid |
Phenytoin
-----------------------------------------------------------------
-The most common cause of folic acid deficiency is nutritional due to poor diet/alchololism
-Drugs that antagonize folic acid effects *Methotrexate *Trimethoprim |
|
|
______________ is a multisystem inflammatory condition characterized by recurrent oral and genital ulcers and skin lesions. Seen most commonly in Turkish, Asian and Middle Eastern Population.
Diagnosis includes: Recurrent oral ulcers plus two of the following: 1. Recurrent genital ulcers2. Eye lesions - anterior and posterior uveitis 3. Retinal vascularization 4. Skin lesions - erythema nodosum, acneiform nodules, papulopustular lesions 5. Positive pathergy test |
Bechet Syndrome |
|
|
Male infant is virtually asymptomatic for 6-9 months of age, after which he begins to experience recurrent pyogenic (Strep. pneumoniae & H. influenzae) infections.
Labs show decreased IgA, IgG, IgM and IgE along with markedly decreased B cells on the smear. |
X-linked Brutons Agammaglobinemia |
|
|
During the development of diabetic retinopathy, what pathologic change presents as the first sign of vision loss? |
Macular Edema |
|
|
DOC for agitation in an elderly patient? |
Haloperidol
------------------------------------------------------------------ Atypical Antipsychotics like quetiapine and risperidone may also be used |
|
|
At birth, classic findings include macrosomia, macroglossia, hemihyperplasia and abdominal wall defects (omphalacele/umilical hernia)
Increased risk of Wilm's tumor and hepatoblastoma |
Beckwith-Wiedemann Syndrome
associated with duplication of CH 11p, this region has the gene for IGF-2, which may explain macrosomia and hypoglycemia
Increased incidence of WILM'S TUMOR and HEPATOBLASTOMA: -frequent monitoring of alpha-feto protein and abdominal ultrasounds |
|
|
Drug of choice for Scarlett Fever? |
Penicillin V |
|
|
Most common cause of pneumonia in a child with Cystic Fibrosis? |
Staph Aureus!!!
Pseudomonas is the mcc in adults! |
|
|
Most sensitive lab to show acute (fullminant) liver failure? |
INCREASED PT/INR -Bilirubin may also increase
Liver enzymes are often decreased due to a small amount of living liver tissue |
|
|
A patient who is IgA deficient has had an acute anaphylactic reaction to blood transfusion in the past.
He needs another blood transfusion, what special step can be taken to reduce the risk of anaphylactic reaction? |
Washed Red Cell Products and IgA Deficient Plasma |
|
|
Common complication that occurs in nearly all patients with CF? |
Recurrent Sinus Infections |
|
|
Inspissated meconium is responsible for life-threatening obstruction at the level of the ileum |
Meconium ileus seen in Cystic Fibrosis
--------------------------------------------------------------------- Hirschsprung's Disease will show normal meconium at the level of the Rectosigmoid jxn |
|
|
A patient with a history of rheumatoid arthritis presents with enlarged kidneys, hepatomegaly, 4+ proteinuria and and weight gain.
Renal biopsy reveals deposits that show apple-green birefringence under polarized light after a Congo-red stain. |
Amyloidosis
|
|
|
Most common site of ischemic colitis after in patients with atherosclerotic disease? |
Splenic Flexure
- supplied by endarteries of the superior mesenteric artery
Note: Rectosigmoid jxn is another common site Supplied by inferior mesenteric a. |
|
|
patients with nephrotic syndrome are at increased risk for developing ___________ complications |
Atherosclerotic Complications --------------------------------------------------------- Nephrotic syndrome alters lipid metabolism (increases LDL), and is associated with a hypercoaguable state.
Increased risk of MI or Stroke |
|
|
Most common primary lung cancer seen in smokers and nonsmokers. It is the most prominent type in nonsmokers |
Adenocarcinoma ------------------------------------ Located peripherally, may be seen as a solitary nodule |
|
|
Test used to identify ovarian/testicular torsion? |
Color Doppler Ultrasound |
|
|
When is the oral glucose tolerance test administered during a pregnancy? |
26-28 weeks
-------------------------------------------------------------------- 1) 50g glucose administered, if over 140 ↓ 2) 100g glucose administered, then, fasting glucose and glucose each hour for 3 hours: ↓ Patient has gestational DM if, Fasting glucose >95 1-hour > 180 2-hour > 155 3-hour > 140 |
|
|
Whenever IV access can't be obtained during a pediatric emergency, _________ access should be tried next |
interosseous |
|
|
A patient in an automobile crash sustains what is thought to be a spelnic laceration as he has LUQ pain and blood in the left retroperitoneal space as seen on US.
He has recieved 4L of IV fluids and is hemodynamically stable.
What is the next best step? |
CT Scan
--------------------------------------------------------------- CT scan will show the extent of the splenic injury and the decision to operate can be made
If the patient is hemodynamically unstable after FAST scan shows retroperitoneal blood --> emergent laparotomy |
|
|
How do these affect Warfarin? :
-Acetominophen/NSAIDs - Amiodarone - Antibiotics/Antifungals - Cranberry Juice, ginko biloba, Vitamin E - Omeprazole - Thyroid Hormone - SSRIs |
Increase the Warfarin effect --> ↑ bleeding |
|
|
How do these affect Warfarin? :
-Rifampin -Carbamazapine -Oral Contraceptives -Ginseng - St. John's Wort - Green Leafy Vegetables (spinach/kale) |
Decrease Warfarin effect
↓ effect = hypercoaguability |
|
|
___________ is common in travelers in tropical regions (including Southeast US) and is characterized by pruritic, elevated, serpiginous lesions on the skin.
Infection is often acquired through contact with sand where dogs or cats have defecated |
Cutaneous larva migrans
Ancyclostoma braziliense
Helminthic disease caused by the larva of the dog and cat hookworm |
|
|
HY
ALL patients with Hepatitis C should also be vaccinated for _______ and ________ if not already immune |
Hep. A & Hep. B - Even pregnant women
Also of note, the vertical transmission rate of Hepatitis C during pregnancy is 2-5% |
|
|
Vitamins deficient in patients with CF? |
A D E K --> fat soluble |
|
|
What is assosciated with the highest rate of Aortic Aneurysm expansion and rupture in patients with a dilated aortic aneurysm? |
Cigarette Smoking |
|
|
Patients with neutropenia due to chemotherapy are at a higher risk for mucositis of the GI tract due to __________________ |
Pseudomonas
----------------------------------------------------------------- Anti-pseudomonal empiric therapy: - cefepime - meropenum - pipercillin-tazobactam |
|
|
HY Treatment of acute renal transplant rejection? |
High-Dose IV Steroids |
|
|
Most common bacteria causing osteomyelitis following a puncture wound with a rusty nail? |
Pseudomonas
--------------------------------------------------- Treat with Surgical debridement and FQs |
|
|
HY
Dietary Recommendations for patients with recurrent nephrolithiasis? |
1. Decreased protein and oxalate diet
2. Decreased sodium intake 3. Increased Fluid Intake 4. Increased Dietary Calcium |
|
|
Prophylaxis Treatment of choice for a HIV patient with a PPD of more than 5 mm? |
Isoniazid and Pyridoxine (B6) for 9 months
-------------------------------------------------------------------- Monitor LFTs, as INH is hepatotoxic
Remember that INH causes B6 deficiency
ANY Patient with a (+) PPD should be on INH and Pyridoxine for 9 months |
|
|
Most common cause of increased Maternal-Alphafeto Protein levels during inital laboratory studies of a pregnant patient? |
Gestational Age Error
------------------------------------------------------------ Must do an ultrasound to check for neural tube or gastric defects and determine gestational age |
|
|
DOC for patients diagnosed with Syphillis that have a penicillin allergy? |
Doxycycline
------------------------------------------------------------- If the patient has tertiary syphillis --> ceftriaxone
if the patient is pregnant --> desensitize and use PN G (benzathine penicillin) |

