![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
12 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Napthalene
|
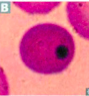
In mothballs.
Causes functional hyposplenia and the presence of Howell-Jolly bodies seen in RBC smear. |
|
|
Heparin Overdose
|
Protamine sulfate - positively charged molecule that binds negatively-charged heparin.
Heparin toxicities include bleeding, thrombocytopenia (HIT), osteoporosis, and drug-drug interactions. HIT - development of IgG antibodies against heparin bound to platelet factor 4. Ab-heparin-PF4 complex activates platelets --> thrombosis and thrombocytopenia. |
|
|
Warfarin OD:
|
Vitamin K.
For rapid reversal of severe warfarin OD, use fresh frozen plasma. Warfarin interferes with normal synthesis and gamma carboxylation of Vitamin K-dep clotting factors (2,7,9,10 + ptns C and S), thus is an antiocoagulant. |
|
|
Reversal agent for thrombolytics (streptokinase, tPA, rPA, TNK-tPA)?
|
Aminocaproic acid - inhibits fibrinolysis.
|
|
|
Iron poisoning: Symptoms (acute and chronic), MOA, and likely cause of exposure.
|
Sx:
Acute: gastric bleeding, hematemesis, and hypovolemic shock (and possibly death) Chronic: Metabolic acidosis (6-72 hours), Scarring leading to GI obstruction (2-8 weeks). MOA: Cell death due to peroxidation of membrane lipids. Cause: one of the leading causes of fatality from toxilogic agents in children - when they ingest Mom's prenatal vitamins or Fe replacements by accident. |
|
|
Zinc deficiency: (sorry, not a toxin but still relevant).
|
Delayed wound healing (needed for zinc fingers in ptn transcription).
Decreased immune function hypogonadism Rash: ANUS MOUTH NOSE EYES Dysgeusia Anosmia Anorexia Decreased adult hair (pubic, armpit, etc) Decreased mental functioning Infertility Growth retardation (esp in children) decreased night vision. |
|
|
Calcium overdose:
|
similar to hyperparathyroidism:
stones (kidney), groans (constipation), bones ( ? ), and psychiatric overtones (?) |
|
|
Calcium deficiency (sorry, not a toxin but still relevant):
|
tetany
neuromuscular junction irritability (spasticity) Trousseaus' sign: BP cuff causes carpopedal spasm Chvostek's sign: facial nerve tapping causes facial muscle contraction |
|
|
Lead poisoning:
|
LEAD:
Lead Lines on gingivae (Burton's lines) and epiphyses of long bones on X ray. Encephalopathy and Erythrocyte basophilic stippling Abdominal colic and sideroblastic Anemia Drops - wrist and foot. Other sx: decreased IQ, hearing problems, growth impairment, impaired peripheral nerve functioning, decreased hgb synthesis --> colic and abd pain, anemia, nephropathy, encephalopathy, and death. MOA: inhibits ferrochetalase and ALA dehydratase --> decreased heme synthesis. Also inhibits rRNA degradation, causing RBCs to retain aggregates of rRBA(basophilic stippling). High risk in kids who live in homes with chipped paint built before 1978. Rx: Kids:: Succimer, EDTA, and Dimercaprol (if severe) Adults: Succimer and EDTA |
|
|
Mercury poisoning
|
Accumulates in KIDNEY AND BRAIN
nephropathy neuropsych sx (tremor, excitability, and insomnia) Acrodynia (peeling of fingertips - like Kawasaki's) Abdominal pain Sources: Fish at the top of the food chain (shark, swordfish, tilefish, king mackarel) - C/I in pregnancy -organic form easier to assimilate Old thermometers, batteries -inorganic form easily sublimates (don't vacuum it up) |
|
|
Arsenic poisoning:
|
Poison of kings:
toxic to GI, CV SYSTEM, AND CNS SYSTEM Acute OD: - multi-system organ failure, ATP production is disrupted Long-term low grade exposure: - high risk of cancer in every tissue - especially LUNGS AND SKIN - basal cell carcinoma - squamous cell carcinoma |
|
|
Cadmium poisoning:
|
Toxic to LUNG, KIDNEY, AND BONE
Obstructive lung disease d/t destruction of alveolar macrophages. increased risk of lung cancer osteoporosis /osteomalacia 5% of US pop has low levels of cadmium contributing to subtle kidney injury. |

