![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
38 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
drug?
ae: used after transplants, can cause irreversible renal tubule damage, dec the kidney's ability to excrete uric acid |
Cyclosporine
-damage leads to inc serum levels of urate which can precipitate as monsoduium urate crystals in joints causing gout |
|
|
what is the following disease and type of genetic mutation is assoc with it?
->muscle weakness and/or cardiac disease beginning in midadolescence, does not usually have intellectual impairment |
Becker's muscular dystrophy
in-frame deletion ->maintain reading frame during translation process in dystrophin gene result in abn dystrophin protien that retains some level of fxn |
|
|
what is this diseaee and assoc type of genetic mutation?
->weakness in pelvic girdle and progresses superiorly, onset before 5 years old |
Duchenne's Muscular dystrophy
X-linked type of genetic mutation: out of frame deletion ->deletion of dystrophin gene result in severly truncated or absent dystrophin protien, resulting in much more severe phenotype |
|
|
What is maternal imprinting and what disease is assoc with it?
|
maternal imprinting:
-inactivation (methylation) of imprinted allele disease: Angelman's syndrome |
|
|
what is paternal imprinting and what disease is assoc with it?
|
paternal imprinting:
-inactivation (methylation)of imprinted allele disease: Prader-Willi syndrome |
|
|
what is point mutations and what disease is an example of it?
|
point mutation:
-mutation of a single base pair and have myriad downstream effects, including altered protien fxn example: sickle cell anemia |
|
|
what is triple repeats and what disease are assoc wit this genetic mutation?
|
triple repeats
-inc in severity with each generation, see disease at younger age = anticipation examples: huntingoton's disease = CAG repeat Friedreich's ataxia= GAA fragile X syndrome = CGG X-linked diseases |
|
|
disease and txmt?
-when pt tx with general anesthetic to undergo sedation, pt has inc release of free Ca conc in pt skeletal muscle what is the genetic inheritance of this disease? |
Malignant hyperthermia
-autosomal dominant disorder affecting skeletal muscles ->presents as muscular rigidity and hyperthermia when pt exposed to general anesthesia such as Halothane txmt: Dantrolene ->prevents calcium release from sarcoplasmic reticulum and relaxes muscles |
|
|
what disease is assoc with:
inc Ca levels dec phosphorus levels mild inc in alk phos levels |
primary hyperparathyroid ism
|
|
|
what changes in Ca, Phosphours and Alk phos are assoc with osteoporosis?
|
none, they are all with in normal limits and no lab abn are expected
|
|
|
organism?
-bite by animal -see purulence and inflammation at site of bite -culture shows G(-) rod |
Pasturella multoceida
txmt: penicillin |
|
|
organism?
assoc with scratch of cat leading to chronic lymphadenitis mostly seen in young children |
Bartonella henselae
|
|
|
organism?
-bit by dog -cause fever, malaise, and hepatosplenomegaly in humans |
Brucella canis
|
|
|
what is the cellular rxn to a pt developing a rash 2 days after playing in the woods?
|
pt experiencing type IV or delayed-type hypersensitivity rxn
->requires prior exposure to trigger antigen and typically takes 24-48 hrs after new contact witha trigger Type 4 hypersensitivity -mediated by action of T lymphocytes which secrete cytokines and in turn recruit additional inflammatory cells to the contact ->T cell activation depends on interaction btwn cell surface T-lymphocyte receptor and antigen MHC comple on antigen presenting cell |
|
|
What disase assoc with following sx and what Ab is assoc?
>symmetric proximal weakness >purple rash over eye lid = heliotrope rash >elevated serum muscle enzyme >myopathic changes on electromyography >muscle biopsy abn in absence of histopathologic sign |
dermatomyositis
->Ab = Anti--Jo-1 heliotrope rash is highly specific for dermatomyositis |
|
|
disease assoc with anti-IgA autoantibodies
|
RA
|
|
|
diesease assoc with anti-microsomal auto antibodies
|
Hashimoto's thyroiditis
|
|
|
disease assoc with anti-mitochondrial auto antibodies
|
primary biliary cirrhosis
|
|
|
what structure is damaged if someone breaks the neck of the fibula?
|
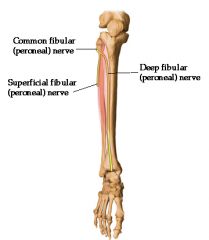
common peroneal nerve
|
|
|
what ae is described in the following sx and what drugs are assoc with it?
immune-complex-mediated hypersensitivity rxn ->involves mucutanious surface and is potentially fatial |
this is a description of Steven-Johnson syndrome
lamotrigine phenytoin ethosuximide carbamzepine CLEP |
|
|
what drug used to tx ptwith tonic-clonic or gland mal seizures, which is thought to act on voltage-sensitive sodium channels?
|
Lamotrigine
ae: stevens johnson's syndrome ->an immune-complex-mediated hypersensitivity rxn involving mucocutaneious surface and potentially fatal |
|
|
drug?
-benzodiazepine that acts as anxiolytic and naticonvulsant moa: inc frequency of GABA channel opeining ->used to tx absence and myoclonic seizures ae: ataxia, sedation, dizziness |
clonazepam
|
|
|
drug?
anticonvulsant that is used as part of combo drug to tx seizures and neuropathic pain ae: sedation dizziness, ataxia, fatigue |
Gabapentin
|
|
|
drug?
anticonvulsant that is used for seizuress and for migraine prophyalaxis ->act on Na channels in neurons ae: psychomotor slowing, sedation, renal stones |
Topiramate
|
|
|
drug used for a wide variedy of seizures
-thought to affect levels of GABA in brain severe ae: ->hepatotoxicity, pancretitis, and teratogenicity |
Valproic acid
|
|
|
why does an the following hernia occur in men?
-nonpainful, reducible buldge in right groind that worsens when lifting |
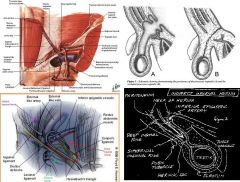
due patent processus vaginalis
|
|
|
what muscles allow a pt to say ah and what is the embryologic orgin of these muscles?
|
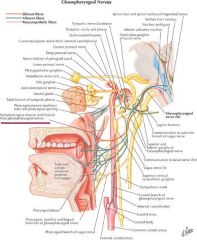
muscles that allow pt to say ah are muscles that elevate the palate which are
-> stylopharyngues - from brachial arch 3 - innervatedby CN9 (glossopharyngeal) -> levator veli palantini - from brachial arch 4 - innervatred by cn 10 (vagus nerve) |
|
|
if a pt has damage to lateral collateral ligament and post cruciate ligament, how did the injury occur?
|
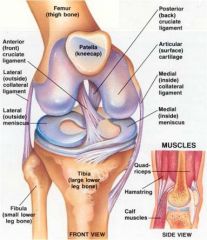
being kicked on medial aspec of knee
|
|
|
what changes in
alk phos Ca phosphate are seen in pt with Paget's disease? |
Phosphate - stays normal
Ca - normal or slightly elevated alk phos - does not exceed 10x upper limit of 4 mg/dL |
|
|
what is the following and what other disease(s) is it assoc with?
-several red, tender, subcutaneious nodules from ant lower leg histology: panniculitis (inflammation of subcutaneous fat) with widening of tissue septa from edema, inc neutrophils and fibrin exudation |
pt has erythemia nodosum
->inflammation of subcutaneious fat often accompanied by fever and malaise assoc with: -inflammatory bowel disease - Crohns's disease or UC -sarcoidosis -certain drugs - oral contraceptives and sulfonamides -certain neoplasms -certain infections |
|
|
diesase and other disease assoc with it?
nonpruritic inflammatory skin disorder |
psoriasis
-nonpruritic inflammatory skin disorder assoc with: arthritis enteropathy spondylitic disease certain HLA including: HLA-B27, HLA-13, HLA-17 |
|
|
disease and cause?
-pt present with pain in leg -fever -unable to stand on lef -organism found in blood culture |
osteomyolitis
->most common cause, Staph aureus-> G(+) cocci in cluster |
|
|
organism?
G(+) cocci in chains assoc with pharyngitis, impetigo, scarlet fever and cellulits |
Strep pyogenes
|
|
|
organism assoc with acute sinusitis and otitis media?
|
strep pneumo = G(+) cocci in pairs
|
|
|
cause of disease?
-involuntary mvmt of upper limbs joint swellings 1st - left knee few hrs later - left hip then couple hrs later right shoulder pmh - sore throat 3 weeks ago pe: fever and several nodules under sking of elbows |
pt has rheumatic fever
->autoimmune mulitsystem disease present several weeks after strep pyogenes (group A beta-hemolytic streptococci) -pt has: >migratory polyarthritis of large joints >subcut nodules under skin overlying bony prominences |
|
|
dx:
toddler with -multiple fractures -bruised swollen joints -multiple petichiae -> x-ray shows: metaphyseal thicking and fragmentation aaroudn epiphyseal plates labs: RBC count = 3.5 millin/mm3 WBC count = 2500 /mm3 MCV = 70 Hb conc = 33% |
pt has scurvy, defiency in vit c)(ascorbic acid)
Vit C has 3 roles: 1. hydroxylation of Lys and Pro residules in collagen 2. absorption of iron by reducing it in to a ferrous state 3. acting as antioxidant anemia -result of combo of poor iron uptake and blood loss from vessel leakage vessel leakage -result of malformed collagen, causes petechiae |
|
|
disease?
hereditary disorder caused by venule and cappilary malformation that tend to bleed in the skin and mucosa membrane |
Osler-Weber-Rendu syndrome
->hereditary hemorrhagic telangicetisia -> AD |
|
|
what organism causes the following sx and what causes its transmission and what is the source?
pt went camping PE: -> well demarcated skin lesion with a black base on arm -> small, itchy bump at site of lesion |
Francisella tulerensis -> G(-) coccobacilus
->ulceroglandular tularemia transmission: tick or deerfly bit source: deer or rabits can be transmitted through inhallation of aerosols and considered agent ofbioterrorism |

