![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
30 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
π radians = |
π radians = 180⁰ |
|
|
45⁰ = |
45⁰ = π/4 |
|
|
30⁰ = |
30⁰ = π/6 |
|
|
60⁰ = |
60⁰ = π/3 |
|
|
90⁰ = |
90⁰ = π/2 |
|
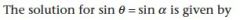
|
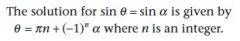
|
|
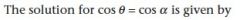
|
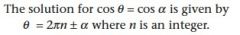
|
|
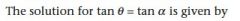
|
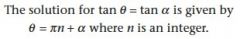
|
|
|
Length of arc is given by |
Length of arc is given by, l = rθ |
|
|
Area of a sector |
Area of a sector, A = ½r²θ |
|
|
Area of a minor segment |
Area of a minor segment, A = ½r²(θ - sinθ) |
|
|
Area of major segment |
Area of major segment = Area of circle - area minor segment |
|
|
For small x (radians) sin x ≈ |
For small x (radians) sin x ≈ x |
|
|
For small x (radians) tan x ≈ |
For small x (radians) tan x ≈ x |
|
|
For small x (radians) cos x ≈ |
For small x (radians) cos x ≈ 1 |
|
|
For small x (radians) order of tan x, x and sin x |
For small x (radians) sin x < x < tan x |
|
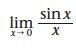
|
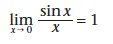
|
|
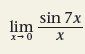
|
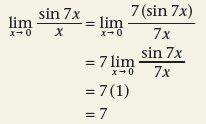
|
|
|
y = a sin bx has amplitude ? and period ? |
y = a sin bx has amplitude a and period 2π/b |
|
|
y = a cos bx has amplitude ? and period ? |
y = a cos bx has amplitude a and period 2π/b |
|
|
y = a tan bx has amplitude ? and period ? |
y = a tan bx has amplitude a and period π/b |
|
|
Solve graphically sin x = x + 1 |
Solve graphically sin x = x + 1
Graph y = sin x, y = x + 1, x co-ordinates of point(s) of intersection is the solution |
|
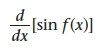
|
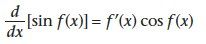
|
|
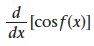
|
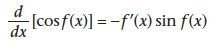
|
|
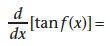
|

|
|
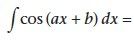
|
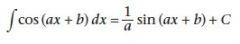
|
|
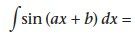
|
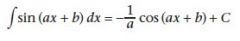
|
|
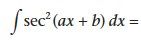
|
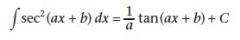
|
|
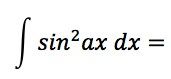
|

|
|

|
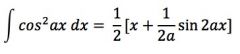
|

