![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
14 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Probability of an event E is given by |
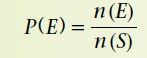
n(E) number of ways E can occur n(S) number of possible outcomes |
|
|
P(E) must be between |
0 ≤ P(E) ≤ 1 |
|
|
P(not E) = |
P(not E) = 1 - P(E) |
|
|
Fundamental Counting Principle If one event can happen in a different ways, a second event can happen |
Fundamental Counting Principle If one event can happen in a different ways, a second event can happen |
|
|
n! = |
n! = n(n - 1)(n - 2)(n - 3)......3×2×1 |
|
|
By convention 0! = |
By convention 0! = 1 |
|
|
The number of possible outcomes when |
The number of possible outcomes when |
|
|
For r selections from n objects (with repetitions), the number of possible outcomes is |
For r selections from n objects (with repetitions), the number of possible outcomes is n∧r |
|
|
A permutation describes |
A permutation describes an arrangement of r objects from a total of n objects in a certain order without replacement or repetition. |
|
|
Permutation nPr is the number of ways of making ordered selections of r objects from a total of n objects is given by |
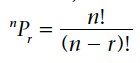
Permutation nPr is the number of ways of making ordered selections of r objects from a total of n objects is given by n(n - 1)(n - 2)(n - 3)......(n - r +1) or |
|
|
Number of arrangements for n objects in a circle - seated - on a ring |
Number of arrangements for n objects in a circle - seated (n - 1)! - on a ring (n - 1)!/2 |
|
|
The number of different ways of arranging n objects in which a of the objects are of one kind, b objects are of another kind, c of another kind and so on, is given by |
The number of different ways of arranging n objects in which a of the objects are of one kind, b objects are of another kind, c of another kind and so on, is given by n!/a!b!c!... |
|
|
A combination nCr is |
A combination nCr is the number of arrangements possible for an unordered |
|
|
nCr = |
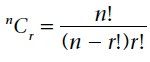
|

