![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
21 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
response variable |
Variable that can be explained by the explanatory variable
|
|
|
Scatter diagram
|
Graph that shows the relationship between two quantitative variables.
|
|
|
Explanatory variable axis on Scatter diagram
|
Horizontal
|
|
|
Response variable axis on Scatter diagram
|
Vertical
|
|
|
Unusual cutoff %
|
Less than 5%
|
|
|
Independent multiplication
|
P(e and f) = p(E) * p(f)
|
|
|
Subjective probability
|
Outcome of probability based on personal judgement
|
|
|
Residual
|
Observed - predicted
|
|
|
Disjoint
|
Mutually exclusive
|
|
|
Conditional probability
|
"The probability of event F given event E"
|
|
|
Permutation or nPr |
Ordered arrangement in which r objects are chosen from n and repetition is not allowed. |
|
|
Combination or nCr |
A collection, without regard to order, in which r objects are chosen from n with r<=n and with repetition |
|
|
Random Variable |
Numerical measure of the outcome of a probability experiment. Value decided by chance.
Denoted by X |
|
|
Probability distribution |
Provides possible values of the random variable and corresponding probabilities (in table, graph or mathematical formula) |
|
|
Probability histogram |
Horizontal = value of the random variable Vertical = probability of each value |
|
|
Standard Deviation of a Discrete Random Variable |
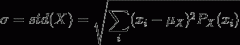
|
|
|
Binomial Criteria |
1. Experiment is performed a fixed number of times (each rep call a trial)
2. Trials are independent
3. Two possible outcomes (success or failure)
4. Probability of success is the same for each trial |
|
|
Mean of a binomial random variable |
μₓ = np |
|
|
Standard deviation of binomial random variable |
σₓ = sqrt( np (1-p) ) |
|
|
Discrete random variable
vs
Continuous random variable |
Finate number of values
vs
Infinate number of values |
|
|
Rules for a discrete probability |
1. ΣP(x) = 1
2. 0 ≤ P(x) ≤ 1 |

