![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
16 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is static electricity
|
Charges that are not free to move. They build up in one place and often end with spark or shock
|
|
|
What are electrical conductors?
|
Conductors are materials that condict charge easilly like metals copper and silver
|
|
|
What are electrical insulators?
|
Stuff that doesn't condict charge very well like plastic and rubber
|
|
|
What are the tiny particles that make up materials called
|
atoms
|
|
|
What's in the nucleus of an atom?
|
+ charged protons and neutrons
|
|
|
What orbits the nucleus?
|
electrons
|
|
|
Why are some materials good conductors
|
Their atoms are held loosely to atom and can move around freely. These materials let electrons flow through them easily. e.g. metals
|
|
|
Whya re some materials poor conductors
|
Their atoms are held firmly to the atom and cannot move around freely. They are good insulators. Rubber, glass, air, plastics.
|
|
|
How is static built up?
|
By friction
|
|
|
Describe how static electricity is created
|
1. Two insulating materials rubbed together
2. electrons scraped off and dumped on another 3. one has positive charge other negative (depends on materials) |
|
|
What happens with polythene rod and duster?
|
electrons move from duster to rod. rod negative, duster positive. Equal charge.
|
|
|
What happens with acetate rod?
|
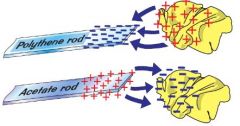
electrons from rod to duster. duster negative, rod positive. equal charge.
|
|
|
Do positive charges move?
|
NOOO!! Only electrons move. +ve and -ve are caused by movement of electrons. For a positive static charge the electrons have moved off to another surface!
|
|
|
How can a charged conductor be discharged safely?
|
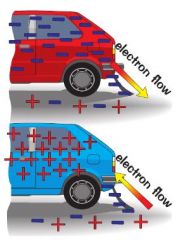
connecting it to earth with a metal strap. if negative then electrons flow down strap to ground, if positive then up strap.
|
|
|
What is the rate of flow of electrical charge called?
|
Current!!
|
|
|
What happens when a charge builds up in an isolated object?
|
So does the voltage. If voltage gets big enough then spark jumps across the gap
|

