![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
91 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Scientific notation |
Metric system used by scientist and scientific notation for very large or very small numbers |
|
|
Solar system |
Sun is center, all major planets plus their moons, asteroids, comets and dwarf planets bound to sun by its gravity. |
|
|
Astronomical unit |
Average distance from Earth to sun. Equal to 1.5 x 10^8 |
|
|
Star |
Self luminous ball of hot gas, ex. The sun |
|
|
Planet |
Spherical, non luminous bodies that orbit a star and shine by reflected light. Extra solar planets are small, faint and difficult to see because they r too close to parent stars |
|
|
Light year |
Distance light can travel in one year. Ex. Nearest star is 4.2 ly from the sun. |
|
|
Milky way |
Hazy band of light/stars That encircles the sky. Milky way galaxy is our home galaxy. |
|
|
Galaxies |
Cloud of stars, gas and dust held together by combined gravity of all its matter ex. Milky way galaxy- about 80,000 light year is diameter and contains more than 1 billion stars |
|
|
Galaxy spiral arms |
Arms winding outward from galaxy, including ours. Places where stars are formed. |
|
|
Big bang |
How universe began 14 billion years ago. Filled universe with hot gas. Stars cooled and first galaxies were formed |
|
|
Scientific method |
Method used by scientists to test hypotheses against evidence from experiments and observations |
|
|
International astronomical union |
Astronomers divided sky into 88 constellations. |
|
|
Magnitude scale |
System used to describe brightness of a star. First magnitude brighter than second and so forth. The larger the magnitude number the fainter the star. |
|
|
Apparent visual magnitude |
Describe how stars look to human eyes from Earth. |
|
|
Flux |
Measure of light energy striking one one square meter per second. Magnitude related directly to Flux of light received on earth by that star |
|
|
Celestial sphere |
Scientific model of the sky. Earth Rotates eastward while celestial sphere rotates westward on its axis |
|
|
North/south celestial poles. |
Pivots defining four cardinal directions around horizon (north, South, east, West points). Put Point directly overhead is zenith and below is nadir. |
|
|
Celestial equator |
Imaginary line around sky and above earth's equator. Divides sky into northern and southern hemisphere. |
|
|
Angular distance |
Angle between two lines extending from your eye to the two objects. Measured in degrees, arc minutes and arc seconds. Angular diameter is angular distance from one edge to another. |
|
|
Earth rotation |
Turning of body on its axis. Earth's rotation produces cycle of day and night |
|
|
Revolution |
Motion of body around a point outside the body. Earth revolving around sun produces annual cycle of seasons. |
|
|
Ecliptic |
Path of sun around the sky. Also called projection (shadow) of earth's orbit on the sky. Planets move eastward along ecliptic. |
|
|
Earth's seasons |
Dates sun crosses these points. Vernal equinox- March 20- spring begins. Summer solstice- June 22- summer begins. Autumnal equinox- September 22- autumn begins. Winter solstice- December 21- winter begins. |
|
|
Milankovitch hypothesis |
Changes in shape of earth's orbit, angle of axis tilt and axis orientation can alter planets heat balance and cause cycle of ice advances/retreats during ice age. |
|
|
Moon orbital motion |
Moon path is always close to ecliptic. It revolves counterclockwise around earth (from direction of North celestial pole) |
|
|
Waxing phaser of moon |

Moon "waxes" (illuminated portion increases) from new moon to first quarter. |
|
|
Waning phase of moon |

Moon wanes from full moon to third quarter back to new moon (illuminated part becomes smaller) |
|
|
Synodic period |
Complete cycle of lunar phase. Takes 29.5 days |
|
|
Waxing phase of moon |

Begins from new moon at waxing crescent to first quarter, then full moon at waxing gibbous. (Illuminated side gets smaller) |
|
|
Lunar phase |
Changing appearance of moon as it revolves around earth. We always see same side of the moon. Sunlight illuminates different amounts of this side, signaling the phases |
|
|
Sidereal period |
Moon orbits eastward around earth in 27.3 days. It is how long money takes to circle the sky once and return to same position relative to stars. |
|
|
Lunar eclipse |
Occurs only at full moon. If moon passes through earth's shadow, sunlight is blocked and moon darkens. |
|
|
Umbra |
Region of total shadow |
|
|
Penumbra |
Region of partial shadow. |
|
|
Total lunar eclipse |
Occurs once or twice a yr. When moon is completely within earth's umbra. |
|
|
Partial lunar eclipse |
When moon only grazes umbra |
|
|
Penumbral lunar eclipse |
Moon only passes through penumbra and doesn't reach umbra. Moon only partially dimmed |
|
|
Totality |
Eclipsed moon looks copper red. Sunlight refracts through earth's atmosphere and bounces off moon on night side of earth |
|
|
Small angle formula |
Used to calculate objects angular diameter. Uses linear diameter and distance of an object. Constant 2.06 x 10^5 is number of arc seconds in one radian |
|
|
Solar eclipse/total solar eclipse/partial solar eclipse |
When moon moves between earth and the sun. Total is when moon covers disk of sun completely. Partial is when moon covers only part of the sun |
|
|
Perigee |
When moon is at closest point to earth. Angular diameter 5.5 percent larger than average. |
|
|
Apogee |
When moon is at farthest point from Earth. Angular diameter 5.5 percent smaller than average |
|
|
Annular eclipse |
When moon crosses in front of sun when moons disk is smaller in angular diameter than suns. |
|
|
Saros cycle |
Pattern of eclipses. |
|
|
Archaeastronomy |
Study of astronomy of ancient peoples. Combo of archaeology and astronomy. structures like Stonehenge, newgrange, and other human made phenomena involve astronomical alignments |
|
|
Geocentric universe/heliocentric universe |
Geo is Belief that earth was center of universe. Helio is belief that sun is at center |
|
|
Uniform circular motion- Plato |
Plato argued most perfect geometrical form is sphere, so, heavens made up of spheres rotating at constant rates carrying objects around in circles. |
|
|
Retrograde motion |
Occasional westward, backward motion of the planets |
|
|
Hipparchus/ eccentrics |
Motion of sun moon, and planets follows circular path with earth near, but not at its center |
|
|
Aristotle/first principles |
Believed universe divided into two parts. Earth is imperfect and changeable while heavens is prefect and unchanging. Reasoned with first principles- something held to be obviously true and needs no further explanation |
|
|
Ptolemy |
Preserved principles of geocentrism and uniform circular motion. Added equant, epicycles and deferents. His model was not accurate and had to be revised numerous times |
|
|
Coepernican revolution |
Devised heliocentric universe. Preserved principle of uniform circular motion. Argued earth rotates on axis and revolves around sun once a yr. |
|
|
Scientific revolution/paradigm |
Shift from geocentric to heliocentric belief. Change that occurs in science. |
|
|
Tycho/kepler |
Tycho compiles detailed, precise observations of the positions of the sun, moon, and planets over period of 20 yrs. Observations later used by kepler |
|
|
Kepler laws of planetary motion (1st law) |
Orbits of planets are ellipses wroth the sun at one focus |
|
|
Kepler second law |
Line from planet to the sun sweeps over equal areas in equal intervals of time. |
|
|
Kepler third law |
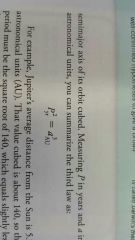
Planets orbital period squared is proportional to its average distance from the sun cubed |
|
|
Galileo |
Helped establish modern science. Used telescope to discover moon had features like earth (mountain and valleys). Phases of Venus and existence of 4 moons circling Jupiter (galilean moons). |
|
|
Acceleration of gravity |
Falling object falls at rate of 9.8m/s^2 every second |
|
|
Inertia |
Once begun, motion continues until something changes it. |
|
|
Newton's first law |
A body continues at rest or in uniform motion in a straight line unless acted on by an external force |
|
|
Newton's second law of motion |
Cause and effect. Acceleration of an object is dependent on the net force acting upon that object and the mass of the object. F=ma |
|
|
Newton's third law |
To every action there is an equal opposite reaction |
|
|
Momentum |
Continued motion of an object |
|
|
Acceleration |
Change in velocity |
|
|
Velocity |
Speed with a specific direction |
|
|
Inverse square law |

Rule that the strength of an effect (gravity) decreases in proportion as the distance squared decreases. Force of gravity inversely proportional to square of the distance between two masses. |
|
|
Universal mutual gravitation |
Earth's bigger size allows its gravitational force to accelerate the moon towards earth. |
|
|
Field |
Earth's mass produces gravitational field throughout space that is directed earth's center |
|
|
Geosynchronous satellite |
Orbits eastward with rotation of earth and remains above fixed spot on the equator |
|
|
Circular velocity |
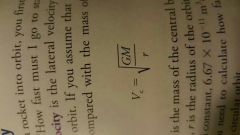
Sideways velocity an object must have to remain in circular orbit |
|
|
Escape velocity |

Velocity required to escape an astronomical body |
|
|
Newton's version of keplers law |

Balance force necessary to keep an object in circular motion with the gravitational force. Equivalent to keplers third law |
|
|
Postulates of relativity (Einstein) |
(Relative principle) observers can never detect their uniform motion except relative to other objects |
|
|
2nd postulate |
Speed of light is constant and will be same for all observers independent of their motion endive to light source |
|
|
3rd postulate (general theory) |
Observers cannot distinguish between inertial forces due to acceleration and uniform gravitational forces. |
|
|
Electromagnetic radiation |
Light made up of both electric and magnetic disturbance that transports energy at the speed of light. |
|
|
Wavelength |
Distance between peaks of wave, measured in nanometers or angstroms. Wavelength band of visual light is from 400 nm to 700 nm |
|
|
Frequency |

Correlates with wavelength. Number of waves that pass a stationary point in 1 sec. |
|
|
Photon |
Packet of light waves that can act as particle or wave. Energy proportional to frequency and inversely proportional to its wavelength. |
|
|
Spectrum |
Array of electromagnetic radiation displayed in order of wavelength. Contains gamma rays, x-rays, ultraviolet, radiation, visible light, infrared, microwaves, and radio waves |
|
|
Wavelength/frequency |
The shorter the wavelength, the higher the frequency. The longer the wavelength, the lower of frequency. |
|
|
Refracting telescopes |
Uses lens to gather and focus light (primary lens) |
|
|
Reflecting telescope |
Uses concave mirror to focus light on focal plane. Secondary mirror redirects light path towards back or side. |
|
|
Eyepiece |
Lens used to magnify image and make it convenient to view |
|
|
Chromatic aberration |
Different wavelengths are focused at different focal lengths (prism effect) |
|
|
Limits of telescope- light gathering power |
Ability of telescope to collect light. Depends on surface area of primary lens or mirror |
|
|
Limits of telescope- resolving power |
Ability to reveal fine detail |
|
|
Magnifying power |
Ability of telescope to make an object look bigger. Depends on ratio of length of primary mirror or lens and the eyepiece. |
|
|
Radio astronomy |
Radio waves can be observed from the ground. |
|
|
Types of telescopes |
Telescopes observing high frequency lights ex. Gamma rays, x-rays, ultraviolet must be located high in earth's atmosphere or in space. |

