![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
90 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Vertabrea are derived when and from?
|
At the same time as the spinal cord
Sclerotome portion of somites |
|
|
Sclerotomes form what?
|
Cartilaginous mesenchymal model of the vertabral column that during the 4 week migrates to surround the developping spinal cord and notochord. The mesenchymal model is later ossified to make bony vertabrae.
|
|
|
The neural tube induces the development of?
|
Vertebral arch (Spinous and transverse Process)
|
|
|
The notochord is induces the development of?
|
Vertebral body
|
|
|
Sclerotome origin of vertabrae
|
Sclerotome cells migrate to surround developing spinal cord (neural tube) and notochord.
They form a cartilaginous mesenchymal model of the vertebrae Happens at each segment to make series of vertebrae |
|
|
Endochondral Ossifacation??
|
Cartilaginous model that is latter ossified
|
|
|
Intervertebral Disc
|
Nucleus Pulposus+ Annulus Fibrosus
Pulposus--remnant of notochord Annulus Fibrosus--remnant of mesenchyme |
|
|
Ribs develop as?
|
Outgrowth of the costal processes of thoracic level vertebrae
|
|
|
Spina Bifida Occulta
|
Most common in low lumbar/upper sacral region. Common usually asymptomatic
|
|
|
Defective fusion of vertebral arches??
|
Spina Bifida occulta and spina bifida cyctica
|
|
|
Defective formation of vertebral body??
|
Hemivertebrae ((scoliosis))
Results from NOTOCHORD failur to induce formation of body |
|
|
Defective fusion of vertebral arches are the result of?
|
Failure of the neural tubes to induce formation of the arch
|
|
|
Spina bifida cystica
|
Meninges and/or spinal cord protrude
Much more serious condition that spina bifida occulta since it it produced neurlogical conditions |
|
|
Hemivertebra--
|
Failure of one half of the vertebrae to form
|
|
|
Cervical, lumbar or forked ribs
|
Lumbar ribs usually asymptomatic
Cervical ribs may produce neurovascual problems in upper limb by pressure on subclavian vessels |
|
|
Lumbar cistern==
|
Expansion of subarchnoid space that goes from vertebra L2 to S2.
|
|
|
Cauda Equina
|
Collection of lumbar, sacral and coccygeal nerve roots within cistern as they travel to origion intervertebral foramen.
DO SPINAL TAP HERE |
|
|
Overview of Spinal cord
|
45 cm long in men 43 in women. Continous with medulla of the caudal brainstem at the foramen magnum. Terminates at tapered conus medullaris at L2.
2 spindle shaped swellings (cervical and lumbar enlargement) <C4-T1 and L2-L3> respectively SC is surrounded by menninges and CFS in the subarachnoid space. |
|
|
Overview of SC continues
|
WHite and gray matter in SC denote its many functions, blood supply comes from vertebral arteries plus segmental and radicular arterila branches.
Segmental spinal nerves, nerve roots and ganglia are present along the length of the cord. |
|
|
Cervical Enlargement
|
C4 to T1 comprises that portion of the cord from which the nerves of the brachial plexus arise
|
|
|
Lumbar Enlargement
|
L2-S3, corresponds to the origional nerves innervating the lower extremity
|
|
|
Conus Medullaris
|
Cone shaped caudal end of the spinal cord. Filum terminal, the thin non nervous extension of pia extends beyond the tip of conus medullaris
|
|
|
Spinal cord segments and do not correspond with surrounding vertabrae!!! SUPER IMPORTANT FACT
|
Know that the spinal nerves of 1-7 exit above cervical vertabrea while nerves C8 and below exit below the the thoracic, lumbar and sacral vertebrae
|
|
|
Spinal Nerve C8 lies on which Vertebral body Level and Which vertebral spinous process?
|
C6-7 and C6
|
|
|
Spinal Nerve T6 lies on which vertebral body and spinous process?
|
T4-5 and T4
|
|
|
Spinal Cord segement L1 lies on which vertebral process and body?
|
Body Is T11, T10
|
|
|
Meningeal Coverings??? 3 kinds
|
Dura mater, arachnoid, and pia. DAP
|
|
|
Dura mater
|
Strong, continous with foramen magnum of the skull with the inner or meningeal layer of cranial dura. Extends caudally to S2 vertabrea where it terminantes in filum terminale and attaches to periosteum of coccyx. Dural tube forms sleeves around spinal nerve roots within intervertebral formainait then becomes continous with epineurium of peripheral nerve.
|
|
|
Arachnoid mater
|
Arachnoid membrane and arachnoid trabeculae. MEMBRANE lies near dura and forms the intner wall of the subdural space. Inner surface of membrane creates numerous trabeculae that pass across underlying CSF filled subarachnoids space to become continous with the pia. Continous to S2 level like dura.
|
|
|
Pia mater
|
Innermost menineal layer directly connects to the SC, Blood vessels supplying cord are associated with pia.
|
|
|
Denticulate Ligaments-
|
Twenty one pair of bi lateral extensions of pia, attached to lateral surface of cord between dorsal and ventral roots then penetrate thru subarachnoid space to inner wall of dura. They are used to suspend the cord in subarachnoid space and provide lateral stability.
|
|
|
Filum terminale
|
continuation of pia beyond the caudal end of the cord, serves as the anchor for the caudal end of the spinal cord to be incorporated to coccygeal ligament.
|
|
|
Epidural Space
|
Between dura and the inner wall of the vertebral canal. FAT FILLED.
|
|
|
Subdural Space
|
Small potential space between dura and arachnoid that can enlarge if infection is present
|
|
|
Pachymeninx is another name for?
|
Dura mater
|
|
|
Spinal Ganglia are located where?
|
Intervertebral foramina
|
|
|
A stress fracture of the L5 vertabrae
|
Spondylolisthesis
|
|
|
For an injection into the subarachnoid space the most important land mark for determining where to insert the needle is the?
|
Iliac Crest
|
|
|
The Ligament flavum is located where?
|
Between the laminae of adjacent vertebrae?
|
|
|
What serves as the roof and floor of the intervertebral foramen?
|
The pedicles.
|
|
|
If there was a herniation of the L-4 and L-5 intervertebral disk which nerve would be compressed?
|
L-5
|
|
|
For a spinal block the drug is injected where?
|
The subarachnoid space
|
|
|
The cauda equina is located where?
|
Lumbar cistern
|
|
|
Denticulate Ligaments are made from what?
|
Pia mater
|
|
|
Conus Medullaris is what?
|
The caudal end of the spinal cord
|
|
|
Filum terminale is what?
|
The caudal extension of the pia mater onto the conus medularius
|
|
|
Subarachnoid Space
|
Filled with CSF, has lumbar cistern-enlargement of the dura-arachnoid tube and thus subarachnoid space. SAMPLE CSF HERE. SAS is immediately adjacent to the pia mater that covers the surface of the spinal cord
|
|
|
3 Things that create Longitudinal fissures and sulci of the spinal cord?
|
Posterior median sulcus, posterior median septum, anterior median fissure
|
|
|
Cauda equina
|
bundles of caudally directed spinal nerve roots
|
|
|
Posterolateral sulci
|
Location of dorsal roots entry into the spinal cord
|
|
|
Anterolateral sulci
|
location of ventral roots exit from the spinal cord
|
|
|
3 columns of longitudinally coursing nerve fibers?
|
Posterial funiculi, anterial funiculi, lateral funiculi
|
|
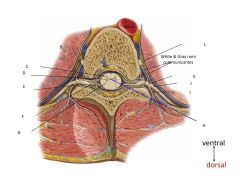
What are these structures?
|
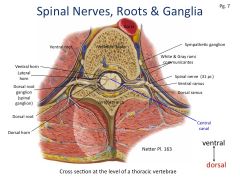
|
|
|
Gray and white Rami communicantes do??
|
Associated with sympathetic (autonomic) ganglia
|
|
|
Spinal Cord variations occur because and how?
|
The cord is smaller caudally and differs at each level there is less white matter at each level. due to nerve fibers decreasing caudally as descending tracts terminate and ascending tracts aren't yet complete.
cervical segments are larger and oval while lumbar and sacral segments are smaller and rounder. |
|
|
Spinal Enlargements that have more gray matter at these points?
|
Cervical C4-T1
Lumbosacral L2-S3 Lateral Horn T1-L2 |
|
|
Segmental Spinal nerves fuse where?
Branch? How many spinal nerves? |
Dorsal (sensory) and ventral (motor) roots fuse laterally outside the spinal cord.
The spinal nerves branch into the dorsal and ventral rami and then into peripheral nerves 31 pairs of spinal nerves 8 cervical 12 thoracic 5 lumbar and 5 sacral and 1 coccygeal |
|
|
Dorsal roots Do what?
|
They carry sensory (primary afferent) input to the cord from the somatic and visceral structures. NO SYNAPSIS FOR DORSAL ROOT GANGLIA. Cell bodies of all sensory neurons that send their axons via the dorsal roots are all located in the dorsal root ganglia and are made of PSEUDIOUNIPOLAR neurons that have only 2 processes.
|
|
|
Dorsal roots are made up of only??
The peripheral process of a primary afferent neuron extends? The central process of the PAN goes where? |
Pseudiounipolar neurons
Peripheral processes extend to receptors in the skin, joints, viscera Passes thru the dorsal root and then Branches multiple times before coming to rest in the CNS |
|
|
Ventral roots carry what?
Their cell bodies are located where |
Motor (efferent) output from the cord to the somatic and viscera structures.
The cell bodies are located in the anterior and lateral horns of the gray matter of the spinal cord |
|
|
Motor neurons in the ventral horn innervate ????
Motor neurons in lateral horn are ???? |
Skeletal Muscles
pre-ganglionic autonomic neurons |
|
|
Gray and white rami communicas??
|
Extend to and from the Spinal nerve
|
|
|
Pre ganglionic fibers are ?? and travel in ?? to ??
Post ganglionic ??? fibers travel in the ??? from the ???? |
Pre ganglionic fibers are mylenated fibers that travel in the white ramus to the automic ganglia
Post ganglionic (unmylenated) fibers travel in the GRAY RAMUS from the autonomic ganglia. There are synapses in the autonomic ganglia between pre and post ganglionic nerves |
|
|
The Central canal develops from??
|
The neural canal of the neural tube.
|
|
|
Central canal details
|
Very small canal opening that is continuous rostrally with the central canal and fourth ventricle of medulla (brain stem) it ends caudally within the conus medullaris. Very little CSF present in it even though there should be.
Primary circulation of CSF is associated with the subarachnoid space |
|
|
Gray Matter contains?
|
Nerve cell bodies and synapses
|
|
|
White matter consists of?
|
AXONS!! that form Tracts.
|
|
|
Posterior funiculus divided into??
|
2 Fasciculi
Fasciculi Gracilis and fasciculi cuneatus |
|
|
All sensory and motor activity associated with the body involves the spinal cord. What are the 4 functional components of the spinal cord
|
1 General Somatic Afferent (GSA)
2. General Visceral Afferent (GVA) 3. General Somatic Efferent (GSE) 4. General Visceral Efferent (GVE) |
|
|
Each Spinal nerve retains its relationship with its respective??? this allows what?
|
Respective somite during development, this allows for spinal cord segments to be related in a systematic fashion to the structures that they innervate such as skin or muscle.
|
|
|
Sensory Innervation involves 2 aspects what are they and what do they do?
|
Sensory (or primary afferent) input arrives via spinal nerves to the dorsal roots (GSA and GVA) primary afferent or first order cell bodies are in the dorsal root ganglia
Dermatomes: spinal nerve associated primarily with one dermatome |
|
|
Motor Innervation invovles?
|
Motor output that leaves the spinal nerve via the ventral roots and spinal nerves to innervate skeltetal muscles GSE and to supply preganglionic neurons GVE that will terminate on postganglionic autonomic neurons. Skeletal muscles are innervated in a systematic fashion by spinal nerves.
|
|
|
Reflex Activity details
|
Ranges from simple or monosynaptic (knee jerk) to polysynaptic (flexor)
Maybe confined to spinal cord *one or more levels or involve brain stem connections. INFLUENCED BY DESCENDING TRACTS and local inputs ALTERED if either afferent or efferent neuron is damaged or there is a change in the influence of descending tracts. |
|
|
Gray Matter of the Dorsal Horn
|
SENSORY!!
Contains neurons (that send axons up the white matter of SC to form tracts that terminate in the brain) and interneurons which create synaptic connections with nearby neurons. Primary afferent of dorsal root GSA and GVA. Descending tracts that also travel in the white matter of spinal cord Nuclie-specialized for diff. functions t |
|
|
Nuclie
|
areas specialized for different functions, it is a collection of nerve cell bodies with similar functions and connections
|
|
|
Gray Matter of the lateral horn
|
Aka: Intermediolateral cell column. (Present in the rostral-caudal extent from T1 to L1/L2 cord segments)
PREGANGLIONIC SYPATHETIC NEURON CELL BODIES. |
|
|
Preganglionic Sypathetic cell bodies
|
Axons exit spinal cord via ventral roots, parasympathetic preganglionic cell bodies are also located in the lateral region o fthe spinal gray at S2-S4
|
|
|
Gray matter of ventral horn contains???/
|
MOTOR NEURONS: contains alpha neurons that innervate extra fusial skeletal fibers. Aka lower motor neurons or anterior horn cells.
Gama motor neurons that innervate the intrafusal muscle fibers of the muscle spindle receptors, interneurons that are similar to the dorsal horn |
|
|
Alpha motor neurons
|
Innervate the exrafusal muscle fibers that make up the bulk of the body
|
|
|
Gamma motor neurons
|
Innervate the small intrafusal muscle fbers of the muscle spindles which are found within the muscles
|
|
|
Muscle spindles??
|
Are sensory receptors that influence the contraction of the extrafusal muscle fibers
|
|
|
Phrenic nucleus
|
Medial position of the ventral horn at c3 to c5
reflects origin of the diaghrgm from cervical myotomes |
|
|
Accessory Nucleus
|
lateral position in ventral horn at c1 to c5/c6
Nerve rootlets exit spinal cord dorsal to the denticulate ligament and pass rostrally alon the cord to enter the skull thru foramen magnem. Gives ride to Cranial NERVE XI (ACCESSORY NERVE) |
|
|
Anterior Spinal Artery
Posterior Spinal Artery |
Supplies Ventral and lateral horns, base of dorsal horn central gray and anteraior and lateral funiculi
Dorsal horn, dorsal funiculi and possible dorsal part of lateral funiculus |
|
|
Fasciculus Gracillus
|
Portion of the lateral column that is most medial and brings input to the lower extremity
|
|
|
Fascicous Cuneatus
|
Portion of the lateral column that feeds the upper extremities is located laterally to the f. gracillus and stops at t6
|
|
|
Dorsal columns are responsible for??
|
Touch, vibration
|
|
|
Dorsal lateral fasciculi are responisble for?
|
Pain and temperature but they must travel ventally and pass thru the ventral white commissue
|
|
|
Ventral white commissue
|
Portion of SC that pain and temp. input must pass thrue
|
|
|
The lateral colums are responsible for?
|
Cortocspinal and Spinalthalmic tract
|

